磷是作物生长发育所必需的大量营养元素,是作物主要的营养限制因子。作物吸收的磷基本来自土壤中的有效磷,而土壤中的磷素来源主要是肥料中带入的磷素,因此,施磷肥是增加土壤磷含量,提高作物产量和磷素有效性的主要方法[1-2]。由于磷肥在土壤中的移动性差,长期施入磷肥导致磷素在土壤中积累,磷肥利用率低,磷素当季利用率只有10%~25%[3-5],且潮土是石灰性土壤,富含碳酸钙,对磷有强烈的固定作用,极大地降低了土壤中磷的有效性,过量的磷固定在土壤中还可能造成土壤磷素的淋失,加剧环境风险[6-9],所以在农田施肥中,应根据土壤磷素状况科学施肥[10]。
而磷肥的有效性和作物产量与磷肥自身组成、形态以及施入土壤的特性及数量有关[11-14],所以探究磷肥类型及磷肥施用量对作物产量及土壤磷含量的影响,对合理施用磷肥提高土壤磷有效性,既能保证我国粮食安全生产,又不破坏土壤及水环境具有重要意义。
大量研究表明,长期合理施用磷肥可显著提高土壤全磷含量,提高有效磷库、土壤无机态磷含量[15-20]。而不同外源磷形态及施肥方式对土壤磷素有效性及磷素在土壤中的累积和转化存在差异[15,21]。郭斗斗等[22]分析化肥、有机肥、秸秆作为主要外源磷素形态对潮土磷素有效性的影响,结果表明,化学磷素与有机肥磷素协同使用可促使无效态磷向有效态磷及缓效态磷转化,提升土壤磷素有效性;金亮等[23]研究结果表明,磷酸一铵施入石灰性土壤后,肥料磷具有较高的移动性和有效性,明显提高了土壤磷的有效利用;张皓禹等[12]研究不同种类的磷肥施用后土壤磷有效性的动态变化和分布特点,结果表明,水溶性聚磷酸铵在土壤中移动性较好,使土壤深层有效磷含量增加,利于根系生长和养分的吸收,提高产量;马丹等[24]田间试验结果表明,磷酸一铵和磷酸脲提高壤土土壤有效磷含量,作物产量及磷肥利用率的效果优于重过磷酸钙。已有研究表明,不同磷肥种类对土壤磷有效性的影响不同,但针对磷肥种类影响潮土土壤磷有效性的机理及磷肥种类对潮土磷形态的影响鲜有报道。
磷肥的有效性及作物产量与磷肥自身组成、形态及施用量有关,潮土作为黄淮海平原最主要的农业土壤,探究不同磷肥对潮土土壤作物产量及磷有效性影响的差异,为提高潮土磷有效性及作物产量提供理论依据,显得尤为重要。为此,于2016-2019年采用田间微区试验,分析磷酸一铵和过磷酸钙在不同施用量条件下,对作物产量和潮土土壤磷素有效性影响的差异,并通过对比不同磷肥对土壤有效磷、各形态无机磷含量的影响,进一步分析土壤磷素有效性差异的原因,以期为磷肥的合理施用提供理论参考。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验区概况及试验设计
试验设置在国家潮土土壤肥力和肥料效益长期监测基地,其属于温带季风气候,年均降雨量约660 mm,主要集中于7-9月。选择试验基地内原始磷水平(Olsen-P含量)为22.5 mg/kg的试验区,分割成1.20 m×0.60 m=0.72 m2的微区,每个微区用60 cm×40 cm×3 cm的石板隔开。选用过磷酸钙(标记为SSP)和磷酸一铵(标记为MAP)2个磷肥品种,分别设置3个磷肥水平(P1、P2、P3),P2O5用量分别是,小麦季:55.1,82.5,110.0 kg/hm2,玉米季:62.6,93.8,125.0 kg/hm2;各处理N、K肥用量相同(小麦季N:165.0 kg/hm2,K2O:82.5 kg/hm2;玉米季N:187.5 kg/hm2,K2O:90.0 kg/hm2),每个水平重复3次,对比施用过磷酸钙和磷酸一铵作为磷肥来源的效果。氮肥使用尿素,钾肥使用KCl试剂。
试验从2016年10月开始,小麦玉米轮作,连续种植。各年度依据土壤和天气状况播种,小麦播种时间为10月中旬,玉米为6月上旬。施肥时间为播种前一天,施肥后,各小区深翻一次。各年度依据土壤状况适当灌溉,保证作物正常生长。
1.2 样品采集及测定方法
冬小麦6月上旬收获,收获方法为贴地面收割各小区地上部全部小麦,整捆装网袋,测产。夏玉米9月下旬收获,收获方法为各小区地上部玉米全部收割,放入网袋风干后测产。小麦、玉米收获后采集土壤样品,使用取土钻在各小区内随机取两点混合为一个土样,取土深度为0~20 cm,土样带回实验室风干,拣去杂物后研磨,过2 mm筛测定土壤有效磷含量,过0.149 mm筛测定土壤无机磷形态。试验开始连续4季试验取耕层土样后,从第4季开始,每周年取一次耕层土样。基础供试土壤有效钾含量为62.6 mg/kg、有效磷22.5 mg/kg、碱解氮79.9 mg/kg、有机质13.6 g/kg、全磷0.64 g/kg、全氮0.75 g/kg。
土壤有效磷含量使用0.5 mol/L NaHCO3浸提-钼锑抗比色法测定[25],土壤无机磷形态分级使用顾益初等[26]的无机磷分级法测定。
1.3 数据计算及处理
磷肥偏生产力(kg/kg)=施磷处理产量/施肥量,无机磷相对含量(%)=(某一形态无机磷含量(mg/kg))/(无机磷总量(mg/kg))×100%。
试验数据采用Microsoft Excel和Origin 2018进行分析和制图。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同磷肥对小麦、玉米产量的影响
在各施磷水平下,小麦、玉米产量除2018年外,均表现为磷酸一铵处理高于过磷酸钙处理(表1)。与过磷酸钙处理相比,磷酸一铵处理在3种施磷水平(P1、P2、P3)下,小麦平均产量分别增加24.9%,19.7%,22.0%,玉米平均产量分别增加29.6%,28.7%,32.2%。磷酸一铵对玉米平均产量的提高效果整体大于小麦。受年际间产量变化的影响,2018年和2019年小麦、玉米产量较2017年均有所降低,但在产量降低的情况下,磷酸一铵处理小麦、玉米产量仍高于过磷酸钙处理。
表1 不同磷肥对小麦、玉米产量的影响
Tab.1 Effects of different phosphate fertilizer on wheat and maize yield kg/hm2
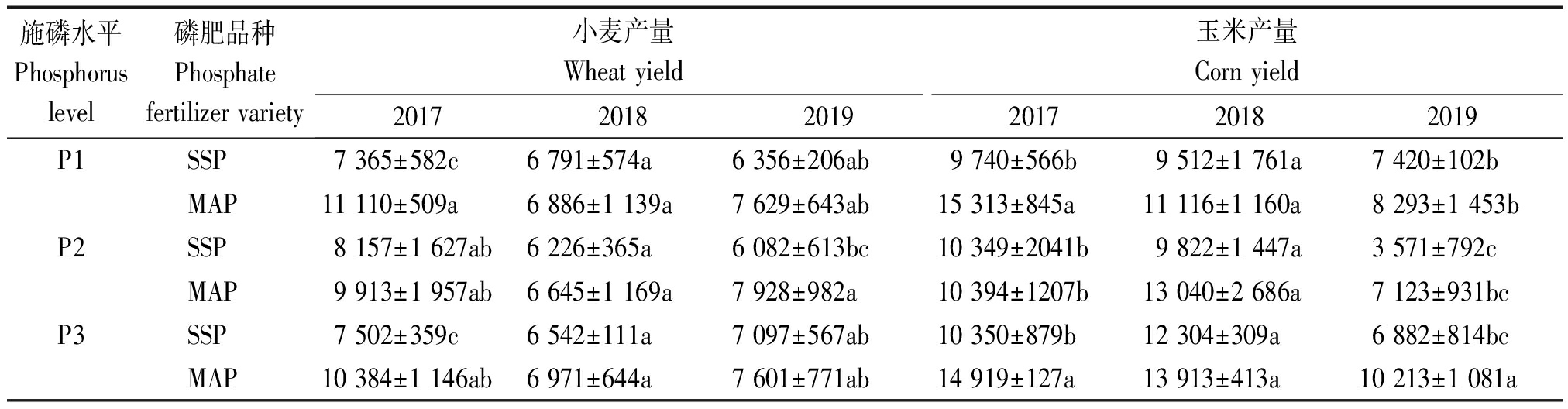
施磷水平Phosphorus level磷肥品种Phosphate fertilizer variety小麦产量Wheat yield玉米产量Corn yield201720182019201720182019P1SSP7 365±582c6 791±574a6 356±206ab9 740±566b9 512±1 761a7 420±102bMAP11 110±509a6 886±1 139a7 629±643ab15 313±845a11 116±1 160a8 293±1 453bP2SSP8 157±1 627ab6 226±365a6 082±613bc10 349±2041b9 822±1 447a3 571±792cMAP9 913±1 957ab6 645±1 169a7 928±982a10 394±1207b13 040±2 686a7 123±931bcP3SSP7 502±359c6 542±111a7 097±567ab10 350±879b12 304±309a6 882±814bcMAP10 384±1 146ab6 971±644a7 601±771ab14 919±127a13 913±413a10 213±1 081a
注:同列不同小写字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05)。表2-3同。
Note:Different lowercase letters in the same column indicate significant difference at 0.05 level among treatments.The same as Tab.2-3.
对小麦玉米年均总产量分析,过磷酸钙处理在3种施磷水平(P1、P2、P3)下,小麦玉米年均总产量分别为15 728,14 736,16 872 kg/hm2,磷酸一铵处理分别为20 063,18 348,21 334 kg/hm2。与P1水平相比,P3水平下过磷酸钙和磷酸一铵处理的小麦玉米年均总产量分别提高7.3%,6.3%,与P2水平相比分别提高14.5%,16.3%。
2.2 不同磷肥对潮土磷肥偏生产力的影响
由表2可知,不同施磷水平下,过磷酸钙和磷酸一铵处理小麦、玉米磷肥偏生产力存在差异。对小麦、玉米年均磷肥偏生产力分析,其随施磷水平的增加呈降低趋势。过磷酸钙处理在3种施磷水平(P1、P2、P3)下,小麦季磷肥年平均偏生产力分别为124.2,82.7,62.0 kg/kg,玉米季分别为142.1,84.4,78.8 kg/kg;磷酸一铵处理小麦季磷肥年平均偏生产力分别为155.2,98.9,75.7 kg/kg,玉米季分别为184.2,108.6,104.2 kg/kg。与过磷酸钙处理相比,在P1、P2、P3水平下磷酸一铵处理小麦季磷肥年平均偏生产力分别提高31.0,16.2,13.6 kg/kg,玉米季磷肥年平均偏生产力分别提高42.1,24.2,25.4 kg/kg。不同施磷量下小麦、玉米的磷肥偏生产力表现为磷酸一铵处理高于过磷酸钙处理,磷酸一铵对玉米磷肥偏生产力的提高效果优于小麦。
表2 不同磷肥对小麦、玉米磷肥偏生产力的影响
Tab.2 Effects of different phosphate fertilizer on the partial productivity of phosphate fertilizer in wheat and maize kg/kg
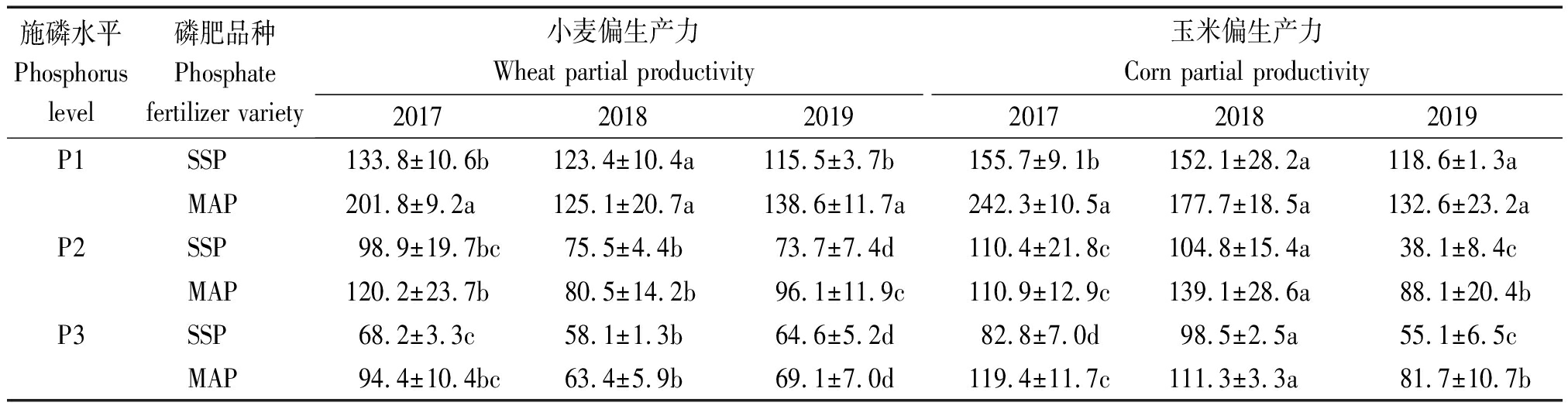
施磷水平Phosphorus level磷肥品种Phosphate fertilizer variety小麦偏生产力Wheat partial productivity玉米偏生产力Corn partial productivity201720182019201720182019P1SSP133.8±10.6b123.4±10.4a115.5±3.7b155.7±9.1b152.1±28.2a118.6±1.3aMAP201.8±9.2a125.1±20.7a138.6±11.7a242.3±10.5a177.7±18.5a132.6±23.2aP2SSP98.9±19.7bc75.5±4.4b73.7±7.4d110.4±21.8c104.8±15.4a38.1±8.4cMAP120.2±23.7b80.5±14.2b96.1±11.9c110.9±12.9c139.1±28.6a88.1±20.4bP3SSP68.2±3.3c58.1±1.3b64.6±5.2d82.8±7.0d98.5±2.5a55.1±6.5cMAP94.4±10.4bc63.4±5.9b69.1±7.0d119.4±11.7c111.3±3.3a81.7±10.7b
2.3 不同磷肥对潮土土壤有效磷的影响
由表3可知,在不同施磷水平下,土壤有效磷含量总体随施磷量的增加呈增加趋势。对连续3 a施用不同磷肥的土壤有效磷平均含量进行分析,P3水平下过磷酸钙和磷酸一铵处理的土壤有效磷平均含量分别比P1水平提高34.1%,29.0%,分别比P2水平提高9.9%,20.0%。与施用过磷酸钙处理相比,磷酸一铵处理在施磷水平P1、P3下,土壤有效磷平均含量分别提高9.6%,5.4%;在施磷水平P2下土壤有效磷平均含量降低3.4%,磷酸一铵对土壤有效磷含量的提高效果总体优于过磷酸钙。
表3 不同磷肥对土壤有效磷的影响
Tab.3 Effect of different phosphate fertilizer on soil available phosphorus mg/kg
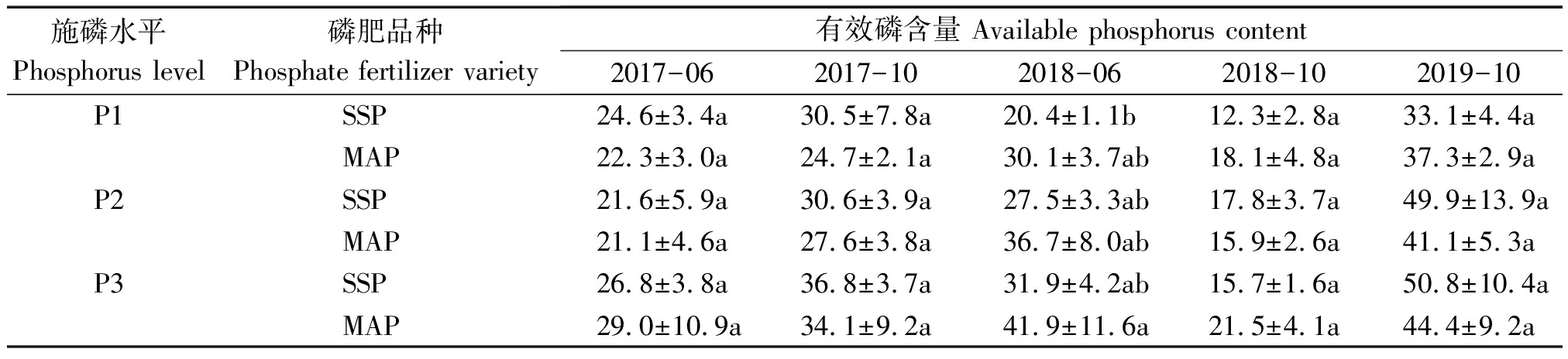
施磷水平Phosphorus level磷肥品种Phosphate fertilizer variety有效磷含量 Available phosphorus content2017-062017-102018-062018-102019-10P1SSP24.6±3.4a30.5±7.8a20.4±1.1b12.3±2.8a33.1±4.4aMAP22.3±3.0a24.7±2.1a30.1±3.7ab18.1±4.8a37.3±2.9aP2SSP21.6±5.9a30.6±3.9a27.5±3.3ab17.8±3.7a49.9±13.9aMAP21.1±4.6a27.6±3.8a36.7±8.0ab15.9±2.6a41.1±5.3aP3SSP26.8±3.8a36.8±3.7a31.9±4.2ab15.7±1.6a50.8±10.4aMAP29.0±10.9a34.1±9.2a41.9±11.6a21.5±4.1a44.4±9.2a
注:按照试验设计,连续4季试验取土样后,从第4季开始,每周年取一次耕层土样。
Note:According to the experimental design,after 4 consecutive seasons of testing soil samples,starting from the 4th season,soil samples of the cultivated layer are taken once a year.
在本试验条件下,通过对施用不同磷肥土壤pH值与有效磷含量相关关系进行分析,土壤有效磷含量与pH值呈负相关,相关方程为:YSSP=-6.225 1X+70.08,YMAP=-21.214X+198.17,土壤pH值每降低1个单位,过磷酸钙处理土壤有效磷约增加6.23 mg/kg,磷酸一铵处理土壤有效磷约增加21.21 mg/kg,也证明了磷酸一铵提高土壤磷素有效性的能力强于过磷酸钙。
2.4 不同磷肥对潮土无机磷组分的影响
由表4可知,施用不同磷肥土壤无机磷组分转化不同。施用过磷酸钙和磷酸一铵均能增加土壤无机磷总量,与2017年相比,2019年过磷酸钙处理在3种施磷水平(P1、P2、P3)下土壤无机磷总量分别增加70.5,42.2,134.5 mg/kg,以Al-P、Fe-P增加为主,其中土壤Al-P含量分别增加19.1%,23.7%,23.1%,Fe-P含量分别增加24.9%,23.3%,32.6%;磷酸一铵处理土壤无机磷总量分别增加22.2,26.0,37.2 mg/kg,以Ca2-P、Ca8-P增加为主,其中土壤Ca2-P含量分别增加13.4%,18.5%,26.1%,Ca8-P含量分别增加17.2%,21.3%,15.8%。磷酸一铵处理土壤Ca10-P、O-P平均含量分别减少2.8%,14.5%,过磷酸钙处理土壤Ca10-P、O-P平均含量分别增加2.1%,10.9%。磷酸一铵对土壤Ca2-P、Ca8-P的提高程度高于过磷酸钙处理,且降低了无效态的Ca10-P、O-P的含量,故磷酸一铵提高土壤磷素有效性的能力高于过磷酸钙。
表4 2019年不同磷肥处理土壤各形态无机磷的含量
Tab.4 The content of inorganic phosphorus under different phosphorus fertilizer treatments in 2019 mg/kg
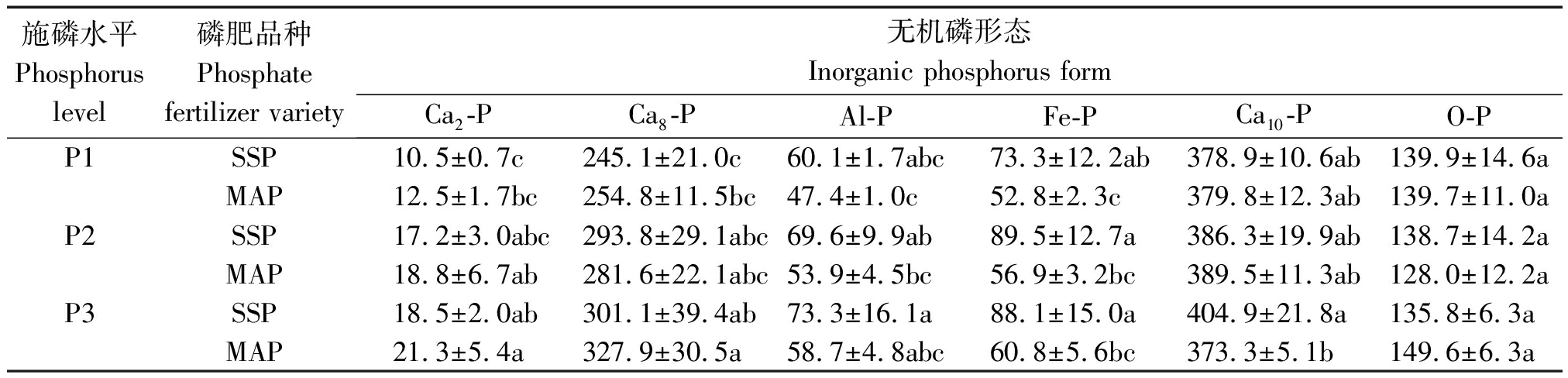
施磷水平Phosphorus level磷肥品种Phosphate fertilizer variety无机磷形态Inorganic phosphorus formCa2-PCa8-PAl-PFe-PCa10-PO-PP1SSP10.5±0.7c245.1±21.0c60.1±1.7abc73.3±12.2ab378.9±10.6ab139.9±14.6aMAP12.5±1.7bc254.8±11.5bc47.4±1.0c52.8±2.3c379.8±12.3ab139.7±11.0aP2SSP17.2±3.0abc293.8±29.1abc69.6±9.9ab89.5±12.7a386.3±19.9ab138.7±14.2aMAP18.8±6.7ab281.6±22.1abc53.9±4.5bc56.9±3.2bc389.5±11.3ab128.0±12.2aP3SSP18.5±2.0ab301.1±39.4ab73.3±16.1a88.1±15.0a404.9±21.8a135.8±6.3aMAP21.3±5.4a327.9±30.5a58.7±4.8abc60.8±5.6bc373.3±5.1b149.6±6.3a
过磷酸钙和磷酸一铵处理土壤Ca2-P、Ca8-P、Al-P、Fe-P含量均随施磷量的增加而增加。与过磷酸钙处理相比,2019年磷酸一铵处理在不同施磷水平(P1、P2、P3)下,土壤Ca2-P含量分别提高18.5%,9.4%,14.9%,土壤Ca8-P含量在P1、P3水平下分别提高4.0%,8.9%,在P2水平下降低4.1%;与磷酸一铵处理相比,过磷酸钙处理在不同施磷水平(P1、P2、P3)下,土壤Al-P含量分别提高21.1%,22.6%,19.9%,土壤Fe-P含量分别提高27.9%,36.4%,31.0%。磷酸一铵处理土壤无机磷增加以Ca2-P、Ca8-P为主,过磷酸钙处理以Al-P、Fe-P为主,且过磷酸钙对土壤Al-P、Fe-P的增加幅度高于磷酸一铵对Ca2-P、Ca8-P的增加幅度,所以与过磷酸钙相比,磷酸一铵更能提高土壤中有效性较高的无机磷含量。
2.5 不同磷肥对潮土无机磷组分分布的影响
对施用不同磷肥土壤各形态无机磷的相对含量变化进行分析(图1),在3种施磷水平(过磷酸钙处理标记为SSP-1、SSP-2、SSP-3,磷酸一铵处理标记为MAP-1、MAP-2、MAP-3)下,2019年磷酸一铵处理土壤Ca2-P相对含量分别为1.4%,2.0%,2.1%,比过磷酸钙处理提高0.25,0.30,0.33百分点,土壤Ca8-P相对含量分别为28.7%,30.3%,33.1%,比过磷酸钙处理提高1.73,0.80,3.60百分点;而过磷酸钙处理土壤Al-P相对含量分别为6.6%,7.0%,7.2%,比磷酸一铵处理提高1.27,1.19,1.26百分点,土壤Fe-P相对含量分别为8.1%,9.0%,8.6%,比磷酸一铵处理提高2.12,2.87,2.49百分点。磷酸一铵处理增加Ca2-P、Ca8-P相对含量的效果优于过磷酸钙处理,而过磷酸钙处理增加土壤Al-P、Fe-P相对含量的效果强于磷酸一铵处理。与2017年相比,过磷酸钙处理土壤Ca10-P相对含量平均减少2.87百分点,O-P相对含量平均提高0.19百分点;磷酸一铵处理土壤Ca10-P、O-P相对含量分别平均减少2.47,2.07百分点,磷酸一铵处理降低O-P相对含量的效果优于过磷酸钙处理。过磷酸钙主要提高土壤中Al-P、Fe-P相对含量,而磷酸一铵可以提高有效性强的Ca2-P、Ca8-P相对含量,减少Ca10-P、O-P相对含量,从而减少磷在潮土中的固定和沉淀,所以磷酸一铵提高土壤磷有效性的能力强于过磷酸钙。
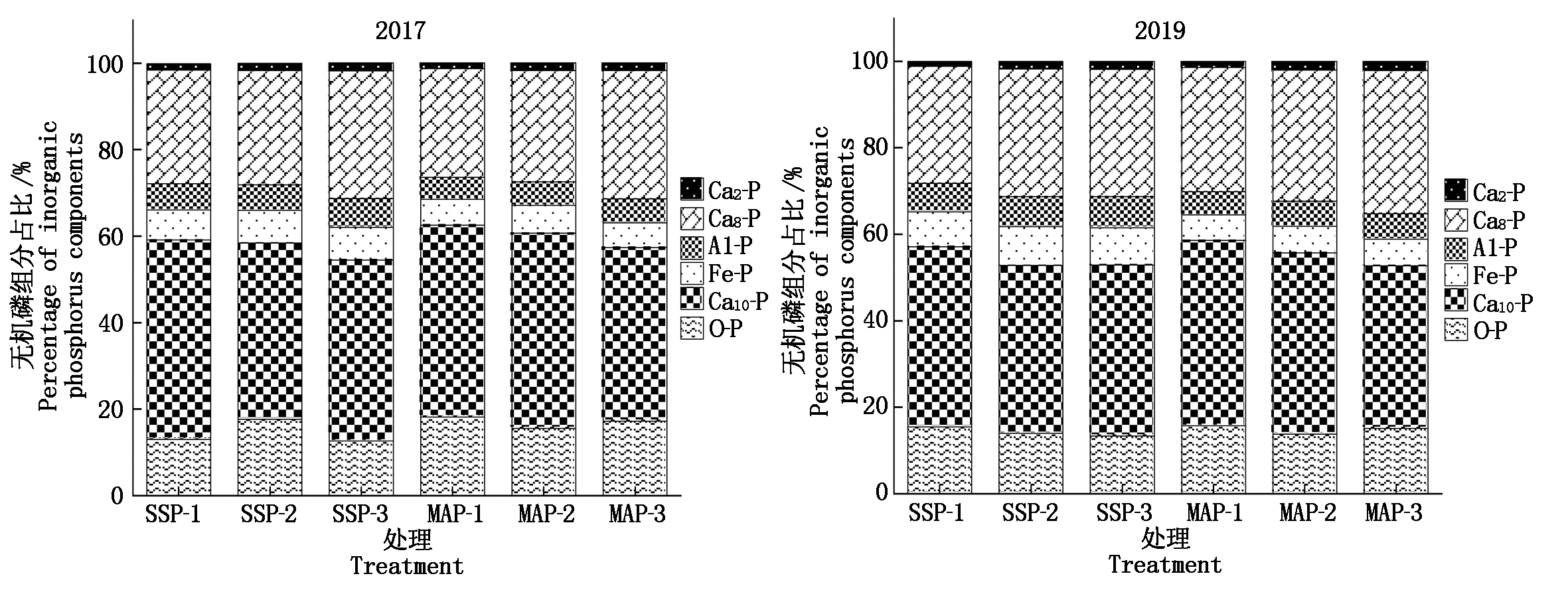
图1 不同磷肥种类对土壤无机磷组分分布的影响
Fig.1 Effects of different phosphate fertilizer varieties on the distribution
of inorganic phosphorus components in fluvo-aquic soil
3 结论与讨论
与过磷酸钙处理相比,磷酸一铵能够提高潮土土壤作物产量及磷肥偏生产力。施用磷酸一铵与过磷酸钙均能提高土壤有效磷、无机磷含量,且施磷水平越高提高程度越大。磷酸一铵对土壤有效磷、Ca2-P、Ca8-P的提高程度均高于过磷酸钙处理,过磷酸钙对土壤Al-P、Fe-P的增加幅度高于磷酸一铵处理,磷酸一铵提高潮土磷素有效性的能力高于过磷酸钙。
在磷肥施用量相同的前提下,不同的磷肥种类对作物产量和磷肥有效性的影响存在差异,应从土壤类型、肥料的酸碱度和水溶性等因素综合考虑[27-29]。本试验结果表明,磷酸一铵在潮土的施用效果优于过磷酸钙,其原因可能包括:由于磷在土壤中的不易移动性和易固定性,肥料在土壤中的溶解度对其是否易被吸收显得尤为重要,磷酸一铵的溶解度高于过磷酸钙,故磷酸一铵施入土壤后,能够较快地溶解并被作物吸收,被土壤固定下来的量减少,其有效性高于过磷酸钙,最终磷酸一铵的磷肥利用率显著高于过磷酸钙;也有可能与土壤的酸碱度有关,苏同庆等[30]结果表明,土壤Olsen-P含量与pH值呈明显的负相关,此结果与本试验结论一致。
在潮土各形态无机磷组分中,以Ca2-P最容易被作物吸收利用,有效性最高,其次是Ca8-P;Al-P、Fe-P的有效性低于Ca2-P和Ca8-P,Ca10-P和O-P有效性最低。对本试验条件下,不同磷肥种类对土壤各形态无机磷的影响分析可知,与过磷酸钙处理相比,磷酸一铵处理能提高土壤Ca2-P、Ca8-P含量及相对含量,降低Ca10-P、O-P含量及相对含量,在作物带走土壤磷基础上,通过提高土壤有效性较高的无机磷含量,保持土壤中有效磷含量高于过磷酸钙处理,增加作物产量,此结果与金亮等[23]提出的MAP施用后,土壤各种形态无机磷以有效性较高的Ca2-P、Ca8-P的增幅较大的结论基本一致。
[1] 俄胜哲,杨志奇,曾希柏,王亚男,罗照霞,袁金华,车宗贤.长期施肥黄绵土有效磷含量演变及其与磷素平衡和作物产量的关系[J].应用生态学报,2017,28(11):3589-3598.doi:10.13287/j.1001-9332.201711.037.
E S Z,Yang Z Q,Zeng X B,Wang Y N,Luo Z X,Yuan J H,Che Z X.Soil Olsen-P content changing trend and its relationship with phosphorus surplus and crop yield under long-term fertilization in loessial soil region on the Loess Plateau,China[J].Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2017,28(11):3589-3598.
[2] Ahmad M,Ahmad M,El-Naggar A H Usman A R A, Abduljabbar A, Vithanage M, Elfaki J, Al-Faraj A,Al-Wabel M I.Aging effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on phosphorus fractionation in a calcareous sandy loam soil[J]. Pedosphere,2018,28(6):873-883.doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60363-1.
[3] Pavinato P S,Merlin A,Rosolem C A.Phosphorus fractions in Brazilian Cerrado soils as affected by tillage[J].Soil and Tillage Research,2009,105(1):149-155.doi:10.1016/j.still.2009.07.001.
[4] 黄绍敏,宝德俊,皇甫湘荣,张夫道,徐明岗,介晓磊.长期施肥对潮土土壤磷素利用与积累的影响[J].中国农业科学,2006,39(1):102-108.doi:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2006.01.015.
Huang S M,Bao D J,Huangfu X R,Zhang F D,Xu M G,Jie X L.Effect of long-term fertilization on utilization and accumulation of phosphate nutrient in fluvo-aquic soil[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2006,39(1):102-108.
[5] 闫湘,金继运,梁鸣早.我国主要粮食作物化肥增产效应与肥料利用效率[J].土壤,2017,49(6):1067-1077.doi:10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2017.06.001.
Yan X,Jin J Y,Liang M Z.Fertilizer use efficiencies and yield-increasing rates of grain crops in China[J].Soils,2017,49(6):1067-1077.
[6] Yang Y J,Zhang H P,Qian X Q,Duan J N,Wang G L.Excessive application of pig manure increases the risk of P loss in calcic cinnamon soil in China[J].The Science of the Total Environment,2017,609:102-108.doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.149.
[7] Bai Z H,Li H G,Yang X Y,Zhou B K,Shi X J,Wang B R,Li D C,Shen J B,Chen Q,Qin W,Oenema O,Zhang F S.The critical soil P levels for crop yield,soil fertility and environmental safety in different soil types[J].Plant and Soil,2013,372(1/2):27-37.doi:10.1007/s11104-013-1696-y.
[8] Xi B,Zhai L M,Liu J,Liu S,Wang H Y,Luo C Y,Ren T Z,Liu H B.Long-term phosphorus accumulation and agronomic and environmental critical phosphorus levels in Haplic Luvisol soil,Northern China[J].Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2016,15(1):200-208.doi:10.1016/S2095-3119(14)60947-3.
[9] Pizzeghello D,Berti A,Nardi S,Morari F.Phosphorus-related properties in the profiles of three Italian soils after long-term mineral and manure applications[J].Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment,2014,189:216-228.doi:10.1016/j.agee.2014.03.047.
[10] 张阳阳,张淑利,谢迎新,康国章,陈波,马冬云,王晨阳,郭天财.沿黄淮稻麦轮作区农田土壤磷库现状及减量施磷农学效应初探[J].河南农业科学,2021,50(3):67-73.doi:10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2021.03.009.
Zhang Y Y,Zhang S L,Xie Y X,Kang G Z,Chen B,Ma D Y,Wang C Y,Guo T C.Phosphorus pool and agronomic effects of phosphorus fertilizer reduction in rice-wheat rotation field along the Yellow River and Huai River of China[J].Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2021,50(3):67-73.
[11] 李青军,张炎,哈丽哈什·依巴提,冯固.膜下滴灌棉花对3种水溶性磷肥的利用效率和产量响应[J].棉花学报,2018,30(2):172-179.doi:10.11963/1002-7807.lqjfg.20180305.
Li Q J,Zhang Y,Harlhax Y,Feng G.Phosphorus utilization efficiency and yield responses of drip irrigated cotton under plastic film mulching to three types of water soluble phosphorus fertilizers[J].Cotton Science,2018,30(2):172-179.
[12] 张皓禹,张君,张凤麟,刘地,危常州.滴灌条件下不同磷肥品种对土壤磷有效性及玉米产量的影响[J].水土保持学报,2019,33(2):189-195.doi:10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2019.02.030.
Zhang H Y,Zhang J,Zhang F L,Liu D,Wei C Z.Effects of different phosphorus fertilizerson soil phosphorus availability and maize yield under drip irrigation[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2019,33(2):189-195.
[13] 韩梅,李东坡,武志杰,油伦成,崔磊,杨立杰.持续六年施用不同磷肥对稻田土壤磷库的影响[J].土壤通报,2018,49(4):929-935.doi:10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2018.04.24.
Han M,Li D P,Wu Z J,You L C,Cui L,Yang L J.Response of soil phosphorus pool after 6 years application of different phosphorus fertilizers in a paddy field[J].Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2018,49(4):929-935.
[14] 陆梅,孙敏,高志强,任爱霞,雷妙妙,薛玲珠.不同施磷水平对旱地小麦产量及其构成要素的影响[J].灌溉排水学报,2018,37(7):13-19.doi:10.13522/j.cnki.ggps.2017.0645.
Lu M,Sun M,Gao Z Q,Ren A X,Lei M M,Xue L Z.Impact of different phosphorus application levels on yield and grain traits of winter wheat in drylands[J].Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2018,37(7):13-19.
[15] 金欣,姚珊,Batbayar Javkhlan,贾丽洁,张树兰,杨学云.冬小麦-夏休闲体系作物产量和土壤磷形态对长期施肥的响应[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(6):1660-1671.doi:10.11674/zwyf.18260.
Jin X,Yao S,Javkhlan B,Jia L J,Zhang S L,Yang X Y.Response of wheat yield and soil phosphorus fractions to long-term fertilization under rainfed winter wheat-summer fallow cropping system[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2018,24(6):1660-1671.
[16] 陈磊,郝明德,戚龙海.长期施肥对黄土旱塬区土壤-植物系统中氮、磷养分的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2007,13(6):1006-1012.doi:10.3321/j.issn:1008-505x.2007.06.004.
Chen L,Hao M D,Qi L H.Effects of long-term fertilization on nutrient variety of soil and plant systems in dry-land of Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2007,13(6):1006-1012.
[17] 慕韩锋,王俊,刘康,刘文兆,党廷辉,王兵.黄土旱塬长期施磷对土壤磷素空间分布及有效性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2008,14(3):424-430.doi:10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2008.03.003.
Mu H F,Wang J,Liu K,Liu W Z,Dang T H,Wang B.Effect of long-term fertilization on spatial distribution and availability of soil phosphorus in Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2008,14(3):424-430.
[18] 黄晶,张杨珠,徐明岗,高菊生.长期施肥下红壤性水稻土有效磷的演变特征及对磷平衡的响应[J].中国农业科学,2016,49(6):1132-1141.doi:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2016.06.009.
Huang J,Zhang Y Z,Xu M G,Gao J S.Evolution characteristics of soil available phosphorus and its response to soil phosphorus balance in paddy soil derived from red earth under long-term fertilization[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2016,49(6):1132-1141.
[19] 裴瑞娜,杨生茂,徐明岗,樊廷录,张会民.长期施肥条件下黑垆土有效磷对磷盈亏的响应[J].中国农业科学,2010,43(19):4008-4015.doi:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2010.19.013.
Pei R N,Yang S M,Xu M G,Fan T L,Zhang H M.Response of Olsen-P to P balance in black loessial soil under long-term fertilization[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2010,43(19):4008-4015.
[20] 王柏寒,黄绍敏,郭斗斗,张水清,宋晓,岳克,张珂珂.长期定位施肥下潮土磷素盈亏及对无机磷的影响[J].中国农业科学,2019,52(21):3842-3851.doi:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2019.21.013.
Wang B H,Huang S M,Guo D D,Zhang S Q,Song X,Yue K,Zhang K K.Phosphorus profit and loss and its effect on inorganic phosphorus in fluvo-aquic soil under long-term located fertilization[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2019,52(21):3842-3851.
[21] Blake L,Johnston A E,Poulton P R,Goulding K W T.Changes in soil phosphorus fractions following positive and negative phosphorus balances for long periods[J].Plant and Soil,2003,254(2):245-261.doi:10.1023/A:1025544817872.
[22] 郭斗斗,黄绍敏,张珂珂,张水清,宋晓,王柏寒,岳克.有机无机外源磷素长期协同使用对潮土磷素有效性的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(6):1651-1659.doi:10.11674/zwyf.18226.
Guo D D,Huang S M,Zhang K K,Zhang S Q,Song X,Wang B H,Yue K.Effects of long-term synergistic use of organic and inorganic exogenous P on phosphorus availability in fluvo-aquic soil[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2018,24(6):1651-1659.
[23] 金亮,周健民,王火焰,陈小琴,杜昌文.石灰性土壤肥际磷酸一铵的转化及其机制探讨[J].中国土壤与肥料,2008(6):5-10.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-6257.2008.06.002.
Jin L,Zhou J M,Wang H Y,Chen X Q,Du C W.Transformation and translocation of fertilizer-P with monoammonium phosphate application in fertisphere in calcareous soil[J].Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China,2008(6):5-10.
[24] 马丹,赵库,沙木和别克·阿咱别克,袁芳,努尔居马·卡德尔别克,盛建东,张凯.磷肥种类和施用方式对新疆棉田磷素利用及棉花产量的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2020,38(2):86-92.doi:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2020.02.12.
Ma D,Zhao K,Azanbieke S,Yuan F,Kadeerbieke N,Sheng J D,Zhang K.Effects of phosphate fertilizer types and application methods on phosphorus utilization and cotton yield in Xinjiang cotton field[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2020,38(2):86-92.
[25] 鲁如坤.土壤农业化学分析方法[M].北京: 中国农业科技出版社,2000.
Lu R K.Soil agrochemical analysis method[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Science and Technology Press,2000.
[26] 顾益初,蒋柏藩.石灰性土壤无机磷分级的测定方法[J].土壤,1990,22(2):101-102.doi:10.13758/j.cnki.tr.990.02.013.
Gu Y C,Jiang B F.Method for determining the classification of inorganic phosphorus in calcareous soil[J]. Soil,1990,22(2):101-102.
[27] Nest T V,Ruysschaert G,Vandecasteele B,Houot S,Baken S,Smolders E,Cougnon M,Reheul D,Merckx R.The long-term use of farmyard manure and compost:Effects on P availability,orthophosphate sorption strength and P leaching[J].Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,2016,216:23-33.doi:10.1016/j.agee.2015.09.009.
[28] 朱宏斌,王晓波,蒋光月,房运喜,郭志彬,何传龙.不同品种磷肥运筹对砂姜黑土玉米生长及产量的影响[J].中国农学通报,2014,30(30):209-212.
Zhu H B,Wang X B,Jiang G Y,Fang Y X,Guo Z B,He C L.Influences of different varieties of phosphate management on corn growth and yield in Shajiang black soil[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2014,30(30):209-212.
[29] 王晓红,柳小琪,吴璐璐,吕家珑.3种磷肥在北方6种土壤中的吸持固定特点[J].河南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(4):75-81.doi:10.15926/j.cnki.issn1672-6871.2020.04.012.
Wang X H,Liu X Q,Wu L L,Lü J L.Adsorption and fixation characteristics of three kinds of phosphate fertilizers in six soils in northern China[J].Journal of Henan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science),2020,41(4):75-81.
[30] 苏同庆,邢璐,王火焰,周健民.氮磷配施和施肥方式对潮土Olsen-P和小麦磷吸收的影响[J].华北农学报,2021,36(1):152-158.doi:10.7668/hbnxb.20191575.
Su T Q,Xing L,Wang H Y,Zhou J M.The impacts of nitrogen combined with phosphorus and application methods on Olsen-P and phosphorus uptake of wheat in fluvo-aquic soil[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2021,36(1):152-158.