马铃薯(Solanum tuberosum L.)分布在世界158个国家和地区,盛有人类的“第二面包”美称,也是世界第四大粮食作物,在我国粮食安全战略部署和农业发展方式转变中具有重要作用[1-3]。目前,中国马铃薯种植面积约564.5万 hm2,是世界第一生产大国[4]。近年来,随着马铃薯栽培面积逐步加大,病害也愈发严重。其中。马铃薯疮痂病(Potato common scab)是由习居土壤内多种致病链霉菌(Streptomyces spp.)引起的重要土传病害之一,在全球马铃薯主产区均有发生,如亚洲、北美、欧洲等[5-7],对马铃薯的产量与品质造成极大的损失[8]。
马铃薯疮痂病通常在发病初期薯块表面产生浅褐色斑点,后期逐渐扩大,病薯组织粗糙呈木栓化,主要分为凸起型、凹陷型或扁平型病斑[9],其病斑类型与病原菌种类、品种感病程度和环境条件有关[10-11],而土壤有机质的含量与病薯严重程度密切相关[12]。该病害于1890 年Thaxter[13]首次从马铃薯疮痂病薯块茎上分离到具有灰色孢子链且能产生黑色素的病原菌Oospora scabies,随后将其病原菌命名为Streptomyces scabies [14],之后不同研究学者对引起马铃薯疮痂病菌的不同菌种相继报道。目前,经研究表明,有600 多种链霉菌属,其用途较为广泛,其中60%以上均生产为工业和制药业抗生素[15-16],目前,国际上已报道引起马铃薯疮痂病菌种类有20 余种[17],主要致病种类为 S. scabies[14]、 S. acidiscabies[18]和 S. turgidiscabies[5]。国内学者报道马铃薯疮痂病菌种类仅有10多种,研究表明疮痂病菌有明显的地域差异性及多样性,此外新致病种S. anulatus、S. enissocaesilis、S. galilaeus 和 S. bobili等不断出现[17,19-21]。山东高密地区地理独特,气候温暖,适宜马铃薯常年种植,近几年调研发现疮痂病发病较为严峻,随着土壤内病菌常年累积,逐年呈现恶化趋势,目前,报道的病原菌为S. scabies和S. acidiscabies[22],因此全面系统的研究高密地区马铃薯疮痂病的种类组成对于病害防治至关重要,以便更好地了解病菌在植物致病性中的作用[23]。本研究首次对山东高密地区马铃薯主产区疮痂病病样进行病原菌分离、纯化和鉴定,为进一步明确山东高密疮痂病致病菌的种类,开展病害防治技术研究提供病原学依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料
2018-2019年采集自山东省高密市李家营镇、孟家庄、张家庄、城律村和祝家庄马铃薯主产区带有典型疮痂病斑的病薯块茎。
供试培养基:见表1。
试剂及仪器:甘油、溶菌酶、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)、胰蛋白胨大豆肉汤培养基(TSB)、氯仿、异戊醇、蛋白酶K、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA-Na2)、琼脂糖、TE缓冲液、酒精(70%,100%)等。
表1 供试培养基及配方
Tab.1 Test media and formula
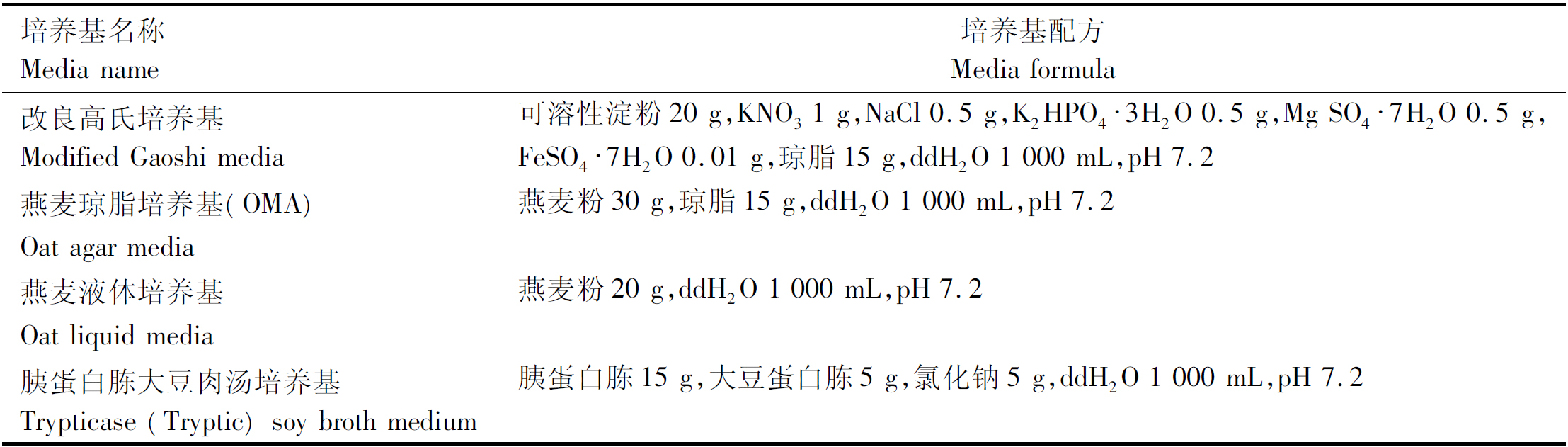
培养基名称Media name培养基配方Media formula改良高氏培养基Modified Gaoshi media可溶性淀粉20 g,KNO3 1 g,NaCl 0.5 g,K2HPO4·3H2O 0.5 g,Mg SO4·7H2O 0.5 g,FeSO4·7H2O 0.01 g,琼脂15 g,ddH2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.2燕麦琼脂培养基(OMA)燕麦粉30 g,琼脂15 g,ddH2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.2Oat agar media燕麦液体培养基燕麦粉20 g,ddH2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.2Oat liquid media胰蛋白胨大豆肉汤培养基Trypticase (Tryptic) soy broth medi-um胰蛋白胨15 g,大豆蛋白胨5 g,氯化钠5 g,ddH2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.2
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 病菌的分离和纯化 首先对病薯进行清洗、消毒,取病健交界处薯块放置于 1% NaClO溶液中浸泡约 30 s,用无菌刀切成 1 mm 厚小块,放 1.8%的琼脂培养基上于 28 ℃ 培养 5~7 d;随后挑取单菌落于燕麦培养基上“Z”形划线进行纯化,纯化 3 次后的链霉菌备用[6]。
1.2.2 致病性测定 利用薯片法、萝卜幼苗法和盆栽接种法对纯化的链霉菌株进行致病性测定[19,21,24]。
1.2.3 病原菌分子生物学鉴定 马铃薯疮痂病菌的DNA采用SDS法[25]提取,最后室温挥发至近干,溶于50 μL ddH2O。
分别采用链霉菌特异性引物和通用引物对其菌株DNA进行分子生物学扩增,引物序列见表2。 PCR扩增体系:2×Taq PCR Master Mix 10 μL,上下游引物各0.5 μL,cDNA模板1 μL,ddH2O补足至20 μL。扩增条件:预变性94 ℃→ 4 min;变性94 ℃→30 s,退火53 ℃→30 s,延伸72 ℃→45 s,34个循环;72 ℃→10 min。扩增结束后取5 μL PCR产物于1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测并拍照成像。PCR产物送至博迈德生物科技(北京)有限公司进行测序,通过NCBI网站Blast工具(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)进行序列对比,根据核酸序列同源性确定马铃薯疮痂病致病链霉菌种类。
表2 马铃薯疮痂病分子检测的引物信息
Tab.2 Primers used for detecting Streptomyces of the potato common scab

病原Pathogen引物名称Primer name引物序列(5'-3')SequencePCR产物/bpFragment size参考文献Reference 链霉菌属27FAGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG1 500[26]Streptomyces spp.1492RGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTTPAFGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG1 450[27]PARAAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCAPuCATTCACGGAGAGTTTGATCC1 500[28]PdAGAAAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCgyrBF2TCTGCACGGYGTSGGYGTCTC400[29]gyrBR2TTGCGGGAGTTGAGGTACPrimer-F AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG1 500[30]Primer-R AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCAPATTTGATCCTGGCTCAG1 535[31]PHAAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCAITS-L GTCAAGTCATCATGCCCCTT650[32]ITS-RAAACTTGGCCACAGATGCTC酸疮痂链霉菌Aci-FTCACTCCTGCCTGCATGGGCG1 278[23]S.acidiscabiesAci-RCGACAGCTCCCTCCCACAAG肿痂链霉菌Tur-FCCCTCGCATGGGGGTGGGTTC1 273S.turgidiscabiesTur-RCGACAGCTCCCTCCCCGTGAGS.stelliscabiesstelFGAAAGCATCAGAGATGGTGCC476stelRCGACAGCTCCCTCCCCGTAAG金霉素链霉菌aurFTCCGCATGGGGGTTGGTG943[33]S.aureofaciensaurRTGTGAGTCCCCGACATTACT毒素基因Txt AB1CCACCAGGACCTGCTCTTC385[34]Toxin geneTxt AB2TCGAGTGGACCTCACAGATGNf ATGAGCGCGAACGGAAGCCCCG-GA700[35]NrGCAGGTCGTCACGAAGGATCG
1.2.4 毒素基因检测 分别采用 Txt 和Nec 2种毒素基因对已鉴定为链霉菌株进行测定,引物序列:Txt AB[1/2][34]:5′-CCACCAGGACCTGCTCTTC-3′,5′-TCGAGTGGACCTCACAGATG-3′;Nec[Nf/Nr][35] :5′-ATGAGCGCGAACGGAAGCCCCGGA-3′,5′-GCAGGTCGTCACGAAGGATCG-3′。PCR反应程序同方法1.2.3。使用1.5% 琼脂糖凝胶对扩增产物进行检测,根据凝胶成像仪显示的结果进行整理。
1.2.5 链霉菌16S rDNA 序列聚类分析 对分离的链霉菌16S rDNA 序列校对后,将测序结果进行Blast比对及序列下载,利用软件MEGA 6.0邻接法(Neighbor-Joining,NJ)和FigTree软件构建系统发育树进行聚类分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 疮痂病菌的分离和致病性测定
2.1.1 病菌分离结果 针对所有待测疮痂病薯,每个病薯选取1个典型病斑进行分离,分离后保留1个菌株进行纯化,共分离纯化链霉菌菌株178个。按照采集病薯的时间进行分类编号,如2019年3月8日分离出第一份疮痂病菌,命名为MLS19030801,菌株具体信息见表3。
2.1.2 致病性测定 采用薯片法、萝卜幼苗法和盆栽接种法对分离到的178株分离物进行致病性测定,结果表明:将菌株菌饼接种到薯片中央,4 d后可观察到薯片表面变褐,菌饼周围长出白色浓密菌丝,发病率高达100%(图1-A)。采用萝卜幼苗接种法,结果表明:致病菌株均能显著的抑制萝卜苗的生长,个别处理甚至使幼苗腐烂致死,而非致病菌株对幼苗的生长几乎不产生影响(图1-B);将178株链霉菌进行温室盆栽致病性测定,结果显示:178个菌株均能引起薯块发病,发病症状为叶片逐渐变黄、枯萎,但不同菌株造成的发病严重度和症状表现存在明显差异(图1-C),发病果实产生凹陷或凸起的疮痂状硬斑块,表皮细胞木栓化导致表面粗糙,而对照表现正常(图1-D)。因此,所分离的菌株均具有致病性,而对照无发病症状。
表3 马铃薯疮痂病菌信息
Tab.3 Information of potato common scab
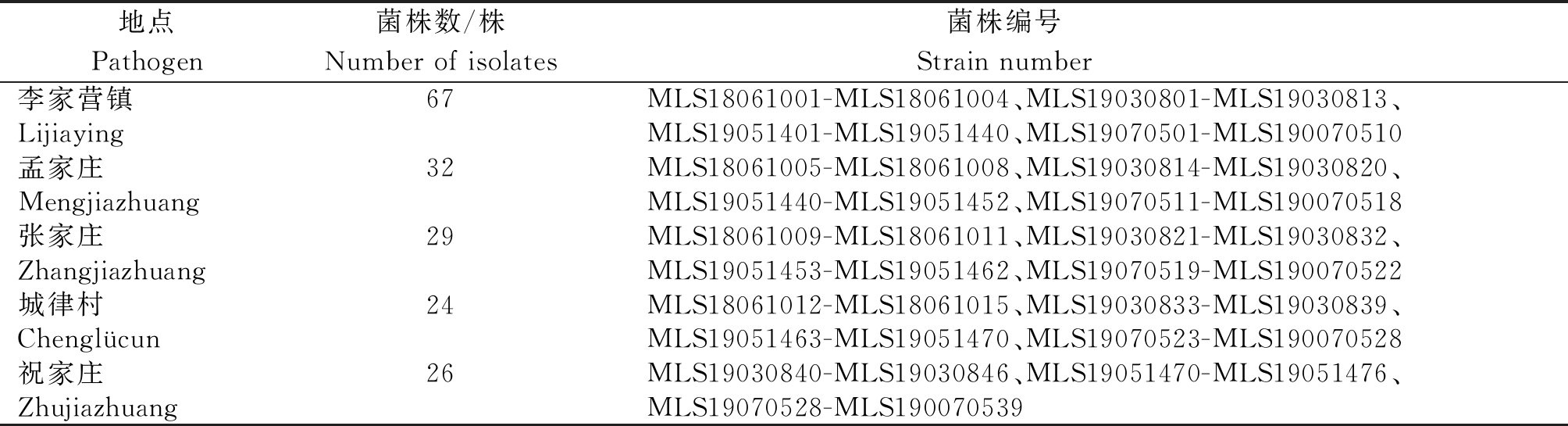
地点Pathogen菌株数/株Number of isolates菌株编号 Strain number 李家营镇 67MLS18061001-MLS18061004、MLS19030801-MLS19030813、LijiayingMLS19051401-MLS19051440、MLS19070501-MLS190070510孟家庄 32MLS18061005-MLS18061008、MLS19030814-MLS19030820、MengjiazhuangMLS19051440-MLS19051452、MLS19070511-MLS190070518张家庄 29MLS18061009-MLS18061011、MLS19030821-MLS19030832、ZhangjiazhuangMLS19051453-MLS19051462、MLS19070519-MLS190070522城律村24MLS18061012-MLS18061015、MLS19030833-MLS19030839、ChenglücunMLS19051463-MLS19051470、MLS19070523-MLS190070528祝家庄 26MLS19030840-MLS19030846、MLS19051470-MLS19051476、ZhujiazhuangMLS19070528-MLS190070539
2.2 病原菌鉴定
2.2.1 形态学鉴定 通过对病薯进行培养鉴定,发现菌株MLS19030805的菌落为圆形,孢子为白色,孢子链呈直-柔曲状,未产生黑色素,由此鉴定为 Streptomyces acidiscabies;其中孢子灰色、光滑,孢子链螺旋弯曲,产生黑色素,其主要特征与S. scabies 相符;另外部分菌株产生橙色或淡绿色色素,单个菌落为圆形。表明不同链霉菌株其菌落颜色、气生菌丝和基内菌丝形态存在明显的差异(图2)。
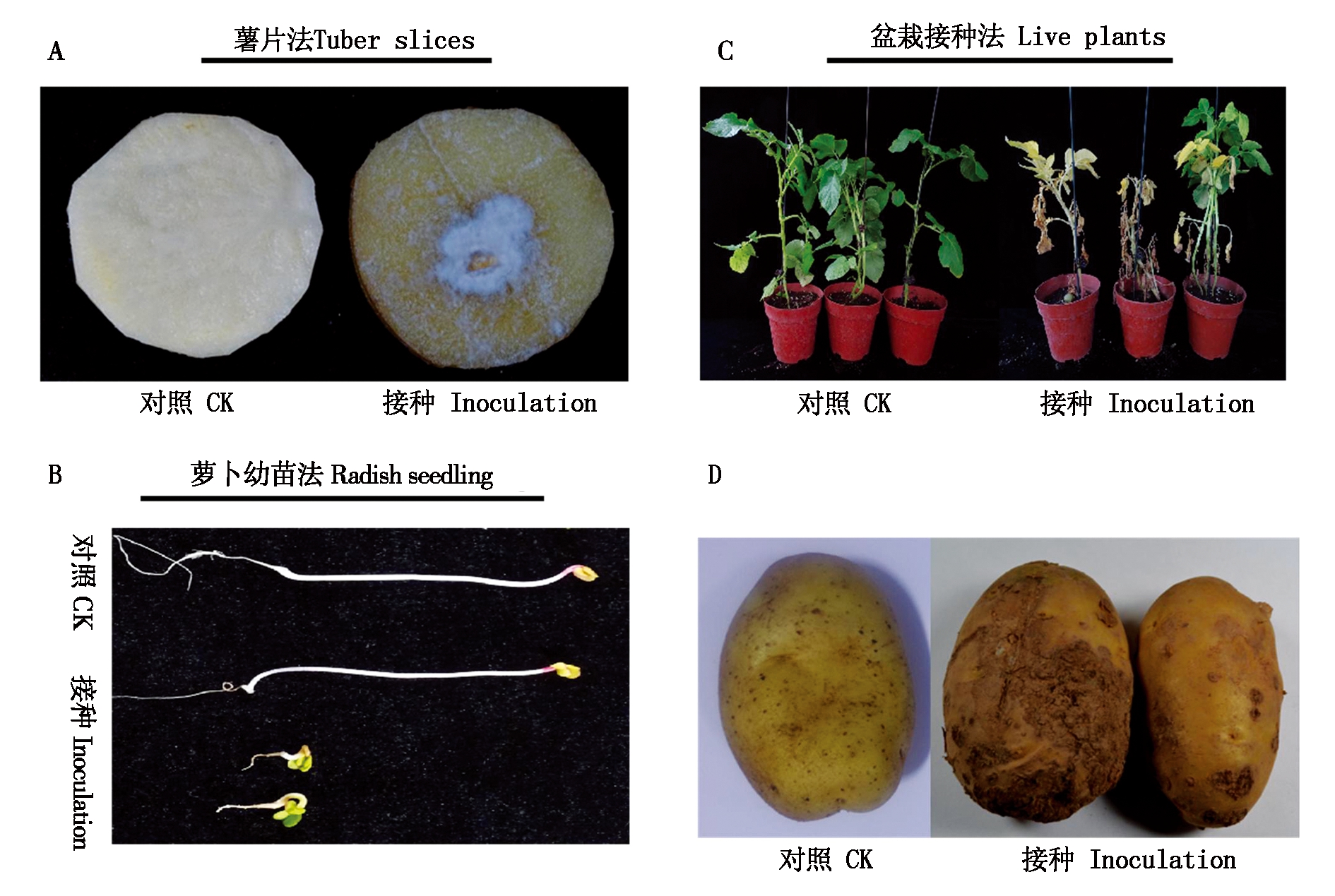
图1 致病性测定照片
Fig.1 Pathogenicity determination of isolate of potato scab pathogen
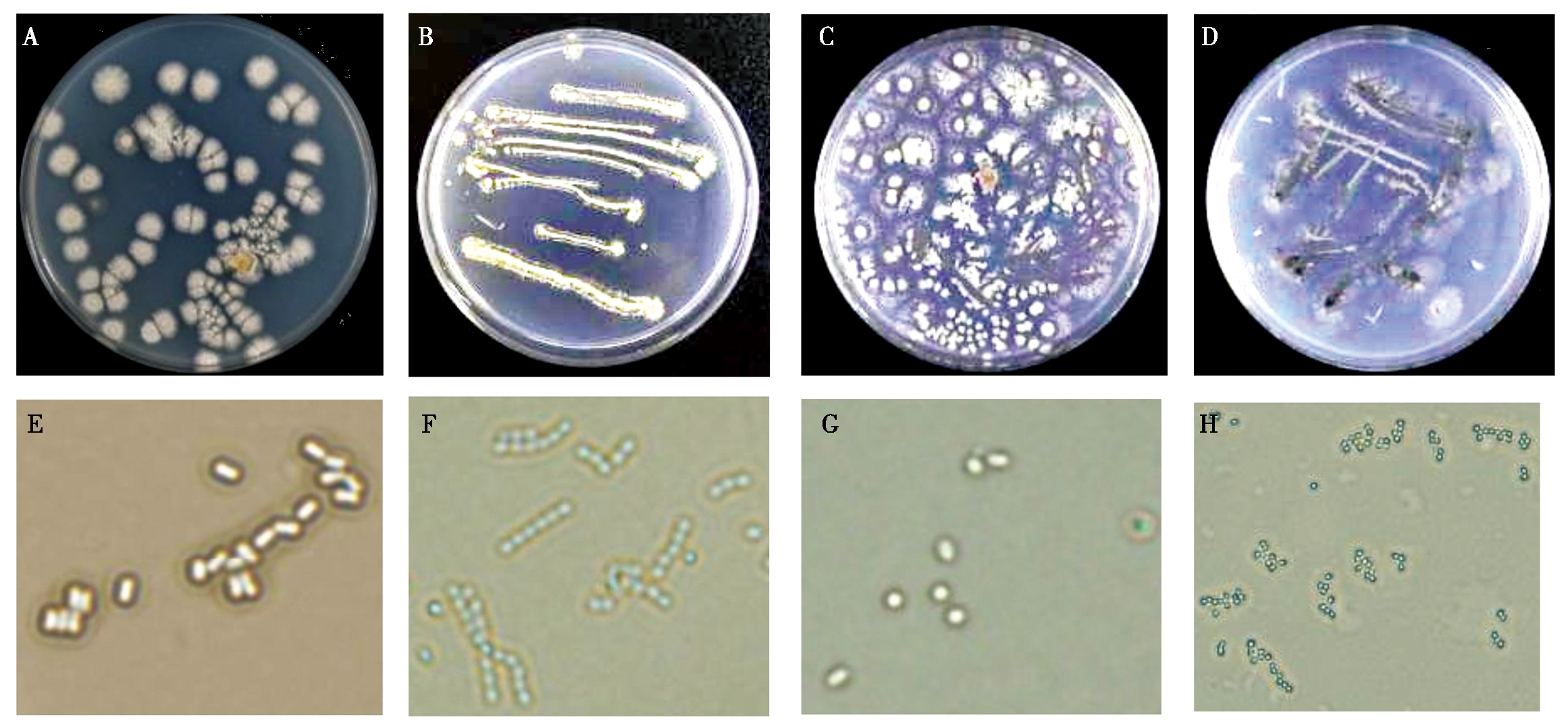
A、E. 酸疮痂链霉菌;B、F. 疥链霉菌;C、G. 灰橙链霉菌;D、H. S. luridiscabiei。
A, E. S. acidiscabies;B, F. S. scabies;C, G.S. griseoaurantiacus;D, H. S. luridiscabiei.
图2 马铃薯疮痂病菌株形态特征
Fig.2 Morphology of isolate of potato scab pathogen
2.2.2 病原菌PCR分子鉴定结果 采用链霉菌Streptomyces spp.通用引物对分离纯化的待测链霉菌株DNA进行PCR扩增,结果显示:PCR产物均在相应处扩增出条带,纯度较好,初步判定为链霉菌属(图3)。之后利用S. acidiscabies、S. turgidiscabies、S. stelliscabies、S. aureofaciens特异性引物,对获得的所有链霉菌株DNA进行PCR扩增反应及测序Blast比对,结果表明:S. acidiscabies引物在约1 278 bp处扩增出亮带(图4),其他菌株测序获得序列与NCBI网站Blast比对后同源性高达100%,分别为S. acidiscabies、S. scabies、S.griseoaurantiacus和S.luridiscabiei;此外,不同地区所分离的菌株所占比例不同,其中李家营镇共分离出71株菌株,占总数比例为37.37%,在所有地区中比例最大,其次为孟家庄、张家庄、城律村和祝家庄,其中S. acidiscabies在各地区均为优势菌株(表3)。
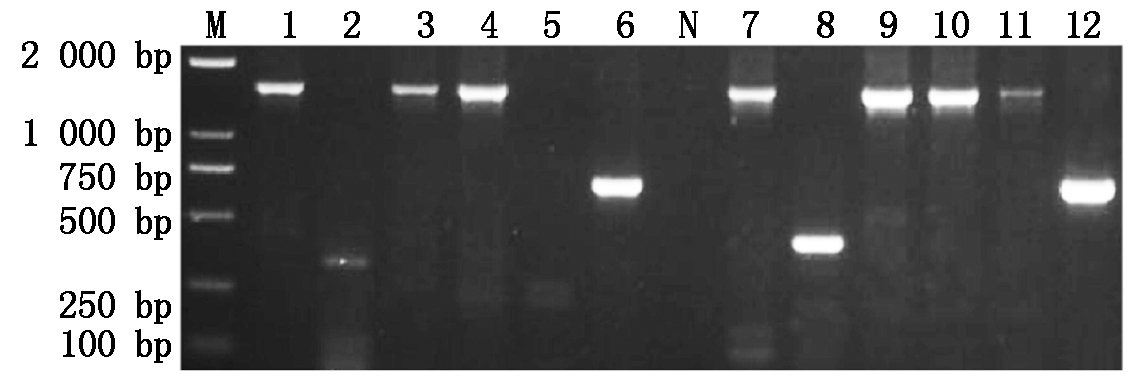
M. BM5000 DNA Marker;1,7. Pu/Pd;2,8. gyrBF2/gyrBF2;3,9. Primer-F/Primer-R;4,10. PAF/PAR;5,11. PA/PB.6,12. ITS-L/ITS-R; N. ddH2O。
图3 链霉菌Streptomyces spp.检测
Fig.3 The specificity of the selected primes to Streptomyces

M. BM5000 DNA Marker;1.27F/1492R;2.Aci-F/R;3.Tur-F/R;4.aurF/R;5.stelF/R;6.NF/R;7.Txt AB1/2.
图4 链霉菌属引物特异性检测
Fig.4 The specificity of the selected primes to Streptomyces
2.2.3 病原菌致病基因检测 利用Txt和Nec基因特异性引物Txt AB1/2和NF/R对178株致病菌DNA进行PCR扩增,预期目的条带大小分别为 385,700 bp。PCR 扩增产物用琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后,所得目的条带分别在250~500,500~750 bp(图3),因此,该 178 株链霉菌均具有致病基因(Txt和Nec 呈阳性反应)。此外,所有致病性菌株共分为2种致病基因型:Txt和Nec。其中Txt基因的菌株占总数68.42%,在5个主产区均占据主导地位(表4)。
2.3 16S rDNA序列聚类分析结果
通过扩增、测序和序列比对后,下载NCBI 数据库中Blast 对比结果,选取同源性较高的登记菌株进行系统发育树构建(图5)。聚类分析结果表明:178 株链霉菌共为 4 种,82株与S. acidiscabies(KM283419.1)菌株亲缘关系最近,序列相似度为100%时,结合形态学特征,将其鉴定为酸疮痂链霉菌;50株与S. scabies(AM293591.1)菌株聚为一类;20株与S. griseoaurantiacus(KY412831.1)菌株聚为一类;26株与S.luridiscabiei(MG827308.1)菌株聚为一类。
表4 马铃薯疮痂病菌种类统计
Tab.4 Statistics on the species of potato common scab
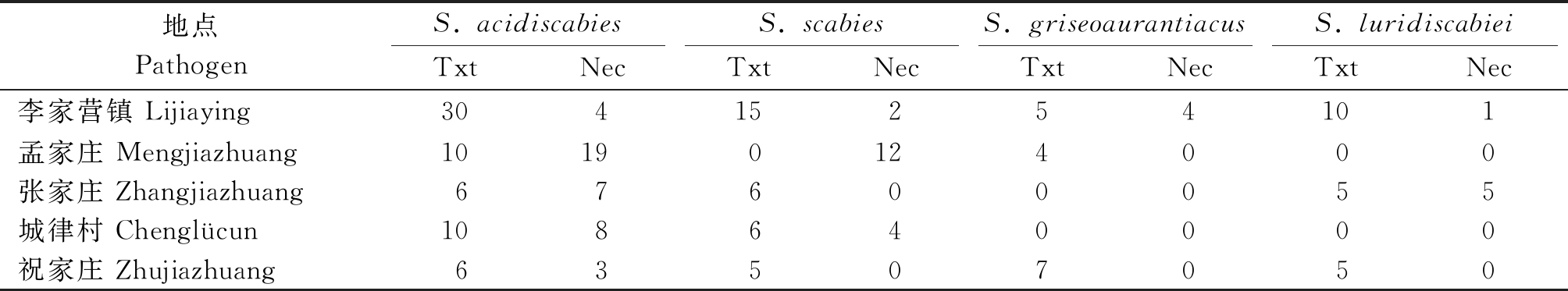
地点PathogenS. acidiscabiesS. scabiesS. griseoaurantiacusS. luridiscabieiTxtNecTxtNecTxtNecTxtNec李家营镇 Lijiaying30415254101孟家庄 Mengjiazhuang 10190124000张家庄 Zhangjiazhuang67600055城律村 Chenglücun108640000祝家庄 Zhujiazhuang63507050
3 结论与讨论
目前,国际上对马铃薯疮痂病病原研究报道很多,其中国外学者研究发现马铃薯疮痂病病原菌种类有20余种[17],均为链霉菌属,如 S. turgidiscabies、S. europaeiscabiei 和 S. scabies 等在美国相继报道[5,34,36],S. scabies、S. europaeiscabiei、S. stelliscabiei和 S. reticuliscabiei等在法国也纷纷报道[37],另外日本、芬兰、加拿大等国也报道了多种疮痂致病链霉菌[5,38-40]。国内已报道的有10余种,已有科研团队对我国马铃薯主栽区不同省份及自治区等地的疮痂病菌进行分析,发现我国疮痂链霉菌多样性丰富,其中S. scabies和S. galilaeus分布较为较广[17,21,32]。例如李驰等[41]通过形态学特征、生理生化特性及16S rDNA 序列分析明确了内蒙古马铃薯疮痂病病原菌为Streptomyces galilaeus。2016年杜魏甫[42]对云南省病薯分离得到143株链霉菌,利用形态学和16S rDNA分子方法鉴定出7种链霉菌。2017年王甄等[43]通过病薯分离和PCR分子鉴定发现湖北地区马铃薯疮痂病菌的菌源为S. scabies、S. acidiscabies、S. turgidiscabies。而殷修鲁[44]对我国9个省份马铃薯主栽区进行广泛采集,鉴定结果为S. bobili、S. galilaeus、S. scabies、S. acidiscabies 和 S. bottropensis。王丹等[45]对山西地区马铃薯疮痂病病原菌进行调查研究,发现导致山西地区马铃薯疮痂病的病原菌是 S. scabies。河北研究小组根据该菌株的形态学、生理生化特征和 16S rRNA 序列,初步将其鉴定为S. bottropensis[46]。本研究主要采用形态学辨别、致病性测定和16S rDNA 序列分析相结合的方法,对山东省高密市马铃薯种植区分离到的178 株链霉菌进行鉴定,结果表明,引起山东高密地区马铃薯疮痂病的病原为4 种链霉菌,分别为 S. acidiscabies、S. scabies、S.luridiscabiei和S.griseoaurantiacus。而陈君[22]从山东地区采集536株放线菌,分离获得2种链霉菌,分别为 S. acidiscabies、S. scabies。这可能与山东高密不同土壤条件复杂多样相关,因此该研究结果也证实了链霉菌的种类受当地周围环境、气候和区域性影响较大,同一市区不同种植区域间病原菌种类差异显著[20]。

图5 基于致病相关链霉菌株16S rDNA序列构建近邻系统发育树
Fig.5 Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rDNA sequences of pathogenic Streptomyces spp. and the related Streptomyces strains
近年来,不断有新的疮痂致病种被报道,2018年国内学者在甘肃省定西市对马铃薯疮痂病病原进行了分离,最终鉴定为S. galilaeus,为甘肃省新报道病原菌[47]。云南省的疮痂病菌优势链霉菌为S. enissocaesilis和S. anulatus,而S. anulatus在我国属于首次报道[20]。本次研究发现S.griseoaurantiacus在国内属于首次报道,对于马铃薯疮痂病菌组成具有多样性原因,可能由于马铃薯产业规模大、耐运输、耐贮藏,外贸市场流通交易频繁,导致不同地区疮痂病薯相互交叉感染,再加上外来入侵菌株在适应新环境过程中发生某种结构、性状上的改变所致。目前,对于同种病害为何由如此多样的链霉菌种组成成为困扰科研学者的热门话题。因此,需要从不同的疮痂病菌的致病机理着手分析,为探明病原菌组成的多样性成因提供理论依据。
[1] Hadi M R,Balali G R. The effect of salicylic acid on the reduction of Rhizoctonia solani damage in the tubers of marfona potato cultivar[J]. American-Eurasian Journal of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences,2010,7(4):492-496.
[2] 农业部. 农业部关于推进马铃薯产业开发的指导意见[J]. 中华人民共和国农业部公报,2016(3):4-7.
Ministry of Agriculture. Guiding opinions of the ministry of agriculture on promoting the development of the potato industry[J].Bulletin of The People′s republic of China,2016(3):4-7.
[3] 韩鹏,付羚. 内蒙古马铃薯种植业发展现状、问题及对策研究[J]. 内蒙古财经大学学报,2017,15(6):8-11. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-5871.2017.06.003.
Han P,Fu L. Research on the present situation,problems and countermeasures of potato planting in Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University of Finance and Economics,2017,15(6):8-11.
[4] 秦军红,李文娟,卢肖平,谢开云. 世界马铃薯产业发展概况[C]//屈冬玉,陈伊里. 马铃薯产业与中国式主食. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨地图出版社,2016:7-14.
Qin J H,Li W J,Lu X P,Xie K Y. Overview of the development of the world potato industry[C]//Qu D Y,Chen Y L. Potato Industry and Chinese Style Food. Harbin:Harbin Map Publishing House,2016:7-14.
[5] Miyajima K, Tanaka F, Takeuchi T, Kuninaga S.Streptomyces turgidiscabies sp. nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,1998,48(2):495-502. doi:10.1099/00207713-48-2-495.
[6] Liu D Q,Anderson N A,Kinkel L L. Biological control of potato scab in the field with antagonistic Streptomyces scabies[J]. Phytopathology,1995,85(7):827-831. doi:10.1094/Phyto-85-827.
[7] Kreuze J F,Suomalainen S,Paulin L,Valkonen J P T. Phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA genes and PCR analysis of the nec1 gene from Streptomyces spp. causing common scab,pitted scab,and netted scab in Finland[J]. Phytopathology,1999,89(6):462-469. doi:10.1094/PHYTO.1999.89.6.462.
[8] 张良,程林润,卞晓波,谢关林. 中国马铃薯疮痂病的研究与防控[J]. 浙江农业科学,2019,60(10):1778-1781.doi:10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20191024.
Zhang L,Cheng L R,Bian X B,Xie G L. Research and prevention of potato scab in China[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2019,60(10):1778-1781.
[9] Locci R. Actinomycetes as plant pathogens[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology,1994,100 (3-4):179-200. doi:10.1007/BF01876235.
[10] Scholte K,Labruyere R E. Netted scab:a new name for an old disease in Europe[J]. Potato Research,1985,28(4):443-448. doi:10.1007/BF02357520.
[11] Bouchek-Mechiche K,Pasco C,Andrivon D,Jouan B. Differences in host range,pathogenicity to potato cultivars and response to soil temperature among Streptomyces species causing common and netted scab in France[J]. Plant Pathology,2000,49 (1):3-10. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3059.2000.00419.x.
[12] Sagova-Mareckova M,Omelka M,Kopecky J. Sequential analysis of soil factors related to common scab of potatoes[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology,2016,93(1):201. doi:10.1093/femsec/fiw201.
[13] Thaxter R. Potato scab[R]. Connectict Agricultural Experiment Station Report,1892:153-160.
[14] Goyer C,Beaulieu C. Host range of streptomycete strains causing common scab[J]. Plant Disease,1997,81(8):901-904. doi:10.1094/pdis.1997.81.8.901.
[15] Wanner L A,Kirk W W. Streptomyces-from basic microbiology to role as a plant pathogen[J]. American Journal of Potato Research,2015,92(2):236-242. doi:10.1007/s12230-015-9449-5.
[16] 杨亚东,胡韵菲,栗欣如,马力阳,王道龙,罗其友. 中国马铃薯种植空间格局演变及其驱动因素分析[J].农业技术经济,2017(8):39-47. doi:10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2017.08.004.
Yang Y D,Hu Y F,Li X R,Ma L Y,Wang D,Luo Q L. Analysis of the evolution of potato planting spatial pattern in China and its driving factors[J].Agricultural Technology and Economy,2017 (8):39-47.
[17] 邢莹莹,吕典秋,魏琪,万书明,董学志,邱彩玲,金光辉. 黑龙江省部分地区马铃薯疮痂病菌种类及致病性鉴定[J]. 植物保护,2016,42 (1):26-32,50. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2016.01.005.
Xing Y Y,Lü D Q,Wei Q,Wan S M,Dong X Z,Qiu C L,Jin G H. Species and pathogenicity identification of Streptomyces species causing potato coommon scab in part of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Plant Protection,2016,42 (1):26-32,50.
[18] Lambert D H,Loria R. Streptomyces acidiscabies sp.nov[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,1989,39 (4):393-396. doi:10.1099/00207713-39-4-393.
[19] 赵伟全,杨文香,李亚宁,刘大群,孟庆芳,张汀. 中国马铃薯疮痂病菌的鉴定[J]. 中国农业科学,2006,39(2):313-318. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0578-1752.2006.02.014.
Zhao W Q,Yang W X,Li Y N,Liu D Q,Meng Q F,Zhang T. Characterization and identification on the pathogen of potato scab in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica.2006,39(2):313-318.
[20] 杨梦平,王瑞仙,杜魏甫,巩晨,于德才,赵伟全,宋双伟,张红骥. 云南省马铃薯疮痂病致病链霉菌种类组成研究[J]. 植物病理学报,2018,48(4):445-454. doi:10.13926/j.cnki.apps.000134.
Yang M P,Wang R X,Du W F,Gong C,Yu D C,Zhao W Q,Song S W,Zhang H Y. The pathogenic Streptomyces species causing potato scab in Yunnan Province[J].Acta Phytopathologica Sinic,2018,48(4):445-454.
[21] 张萌,赵伟全,于秀梅,杨文香,张汀,刘大群. 中国马铃薯疮痂病病原菌16S rDNA的遗传多样性分析[J]. 中国农业科学,2009,42(2):499-504. doi:10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2009.02.015.
Zhang M,Zhao W Q,Yu X M,Yang W X,Zhang T,Liu D Q. Genetic diversity of potato scab pathogens in China based on 16S rDNA sequences[J].Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2009,42(2):499-504.
[22] 陈君. 山东地区马铃薯疮痂病病原菌的多样性及主要致病类型研究[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学,2017.
Chen J. Study on the diversity and main pathogenic types of potato scab in Shandong area[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University,2017.
[23] Hiltunen L H,Weckman A,Ylhäinen A,Rita H,Richter E,Valkonen J P T. Responses of potato cultivars to the common scab pathogens, Streptomyces scabies and S. turgidiscabies[J]. Annals of Applied Biology,2005,146(3):395-403. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7348.2005.040083.x.
[24] Faucher E,Savard T,Beaulieu C. Characterization of actinomycetes isolated from common scab lesions on potato tubers[J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Pathology,1992,14(3):197-202. doi:10.1080/07060669209500874.
[25] 刘炳辉,曹远银,闫建芳,齐小辉,程浩,刘秋. 6种链霉菌基因组DNA提取方法比较[J].河南农业科学,2008,37(10):86-89. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-3268.2008.10.024.
Liu B H,Cao Y Y,Yan J F,Qi X H,Cheng H,Liu Q. Comparison among six methods of genome DNA extraction from Streptomyces[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Science,2008,37(10):86-89.
[26] Osborne C A,Galic M,Sangwan P,Janssen P H. PCR-generated artefact from 16S rRNA gene-specific primers[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters,2005,248(2):183-187. doi:10.1016/j.femsle.2005.05.043.
[27] Edwards U,Rogall T,Blöcker H,Emde M,Böttger E C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,1989,17(19):7843-7853. doi:10.1093/nar/17.19.7843.
[28] 杨德洁,关欢欢,于秀梅,李寿如,赵伟全,刘大群. 2013-2017 年我国北方马铃薯产区疮痂病病原菌组成分析[J]. 河南农业科学,2018,47(8):72-77. doi:10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2018.08.012.
Yang D J,Guan H H,Yu X M,Li S R,Zhao W Q,Liu D Q. Analysis of potato scab pathogens in Northern China from 2013 to 2017[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Science,2018,47(8):72-77.
[29] 魏琪,闵凡祥,王晓丹,高云飞,杨帅,董学志,王文重,张抒,吕典秋,宿飞飞,张静华,李辉. 一种马铃薯疮痂病病原菌种类鉴定通用引物及检测方法:黑龙江,CN106957923A[P]. 2017-07-18.
Wei Q,Min F X,Wang X D,Gao Y F,Yang S,Dong X Z,Wang W Z,Zhang S,Lü D Q,Su F F,Zhang J H,Li H. Universal primer for detecting species of potato scab pathogen and its detection method:Heilongjiang,CN106957923A[P].2017-07-18.
[30] 王甄,沈艳芬,肖春芳,高剑华,陈巧玲. 马铃薯疮痂病病原菌的分离纯化方法及分子鉴定方法:湖北,CN107586749A[P].2018-01-16.
Wang Z,Shen Y F,Xiao C F,Gao J H,Chen Q L. Isolation and purification method and molecular identification method of potato scab pathogen:Hubei,CN107586749A[P]. 2018-01-16.
[31] 杜娟,任娟,赵思峰,任毓忠. 新疆马铃薯疮痂病病原的鉴定[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2010,28 (4):414-417. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-7383.2010.04.004.
Du J,Ren J,Zhao S F,Ren Y Z. Identification of pathogen on potato scab in Xinjang[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural science),2010,28(4):414-417.
[32] Song J,Lee S C,Kang J W,Baek H J,Suh J W,Affiliations V. Phylogenetic analysis of Streptomyces spp. isolated from potato scab lesions in Korea on the basis of 16S rRNA gene and 16S 23S rDNA internally transcribed spacer sequences[J].International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,2004,54 (1):203-209. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.02624-0.
[33] Lehtonen M J,Rantala H,Kreuze J F,Bång H,Kuisma L,Koski P,Virtanen E,Vihlman K,Valkonen J P T. Occurrence and survival of potato scab pathogens (Streptomyces species) on tuber lesions:quick diagnosis based on a PCR-based assay[J]. Plant Pathology,2004,53(3):280-287. doi:10.1111/j.0032-0862.2004.01009.x.
[34] Wanner L A. A survey of genetic variation in Streptomyces isolates causing potato common scab in the United States[J]. Phytopathology,2006,96(12):1363-1371. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-96-1363.
[35] Bukhalid R A,Chung S Y,Loria R. nec1,a gene conferring a necrogenic phenotype,is conserved in plant-pathogenic Streptomyces spp. and linked to a transposase pseudogene[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,1998,11(10):960-967. doi:10.1094/MPMI.1998.11.10.960.
[36] Loria R,Bukhalid R A,Fry B A,King R. Plant pathogenicity in the genus Streptomyces[J]. Plant Disease,1997,81 (8):836-846. doi:10.1094/PDIS.1997.81.8.836.
[37] Bouchek-Mechiche K,Gardan L,Normand P,Jouan B. DNA relatedness among strains of Streptomyces pathogenic to potato in France:description of three new species,S. europaeiscabiei sp. nov. and S. stelliscabiei sp. nov. associated with common scab,and S. reticuliscabiei sp. nov. associated with netted scab[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology,2000,50(1):91-99. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-1-91.
[38] Natsume M,Komiya M,Koyanagi F,Tashiro N,Kawaide H,Abe H. Phytotoxin produced by Streptomyces sp. causing potato russet scab in Japan[J]. Journal of General Plant Pathology,2005,71(5):364-369. doi:10.1007/s10327-005-0211-6.
[39] Park D H,Yu Y M,Kim J S,Cho J M,Hur J H,Lim C K. Characterization of Streptomycetes causing potato common scab in Korea[J]. Plant Disease,2003,87(11):1290-1296. doi:10.1094/pdis.2003.87.11.1290.
[40] St-Onge R,Goyer C,Coffin R,Filion M. Genetic diversity of Streptomyces spp. causing common scab of potato in eastern Canada[J]. Systematic and Applied Microbiology,2008,31(6-8):474-484. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2008.09.002.
[41] 李驰,刘艳,梁燕,邢星,张建平,李得宙,张笑宇. 马铃薯疮痂病病原菌鉴定及其生物学特性[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2019,27(5):897-907. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7968.2019.05.013.
Li C,Liu Y,Liang Y,Xing X,Zhang J P,Li D Z,Zhang X Y. Identification and biological characteristics of pathogen in potato common scab[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,2019,27 (5):897-907.
[42] 杜魏甫.云南省马铃薯疮痂病菌鉴定及品种资源抗性评价[D]. 昆明:云南农业大学,2016.
Du W F. The identification of potato scab pathogen and evaluation of variety resource resistance in Yunnan Province[D]. Kunming:Yunna Agricultural University,2016.
[43] 王甄,沈艳芬,肖春芳,高剑华,张远学,叶兴枝,李大春. 湖北恩施马铃薯疮痂病的致病菌鉴定[C]//中国植物病理学会.中国植物病理学会2017年学术年会论文集,2017.
Wang Z,Shen Y F,Xiao C F,Gao J H,Zhang Y X,Ye X Z,Li D C. Pathogen identification of potato scab in Enshi,Hubei[C]//Chinese Society of Plant Pathology. Proceedings of the 2017 Annual Conference of Chinese Society of Plant Pathology,2017.
[44] 殷修鲁. 我国马铃薯疮痂病病原菌多样性及主要致病类型分析[D].泰安:山东农业大学,2018.
Yin X L. Diversity and main pathogenic types of pathogen isolates from potato scab in China[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University,2018.
[45] 王丹,姚晓东,李新凤,王美琴,郝晓娟,王建明. 山西晋城马铃薯疮痂病病原菌鉴定[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2015,35(5):495-498. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-8151.2015.05.009.
Wang D,Yao X D,Li X F,Wang M Q,Hao X J,Wang J M. Identification of the pathogen of potato scab in Jincheng,Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University(Natural Science Edition),2015,35 (5):495-498.
[46] Zhou B,Zhang M S,Ma X K. First report of Streptomyces bottropensis causing potato common scab in Hebei Province,China[J]. Plant Disease,2017,101(3):1-2.doi:10.1094/PDIS-05-16v0671-PDN.
[47] 崔凌霄,杨成德,魏立娟,薛莉,张俊莲.甘肃省定西市马铃薯疮痂病新病原Streptomyces galilaeus的分离、鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 植物保护,2018,44(5):206-211. doi:10.16688/j.zwbh.2018109.
Cui L X,Yang C D,Wei L J,Xue L,Zhang J L. Isolation,identification and biological characteristics of Streptomyces galilaeus,a new pathogen of potato scab in Dingxi City,Gansu Province[J].Plant Protection,2018,44 (5):206-211.