疫病(Phytophthora capsici Leon.)是影响辣椒生产的最具破坏性的病害之一,该病原菌可在任何阶段侵染植株,引起腐烂、叶片萎蔫甚至死亡[1],经常导致产量的大幅度下降[2-4]。目前,国内外学者均把选育抗疫病的辣椒品种作为辣椒育种的首要任务。
辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)抗疫病的鉴定方法主要以田间鉴定和接种鉴定方法为主,但这2种方法易受环境影响、费时费力,且存在人为的误差。随着分子生物学的不断发展,人们开始通过辣椒QTL定位和遗传图谱构建的研究,已开发出了与辣椒疫病基因紧密连锁的一系列分子标记,并应用于分子辅助育种中。该方法直接从DNA水平鉴定抗病基因,受外在影响因素较小。Wang等[5]利用分子标记将该疫病基因定位到5号染色体上3.3 cM的间隔上并确定了2个候选基因。Liu等[6]通过BSA基因分离法,将抗疫病基因进行了QTL定位,获得一个可靠的SNP标记Phyto5NBS1。刁卫平等[7]获得了19个辣椒NAC转录因子,该转录因子在抗、感基因池中均能被诱导表达。王博等[8]在辣椒中克隆得到500 bp的疫病同源序列,命名为RGA1。Muhammad等[9]研究发现,CaChiVI2基因通过减少活性氧的积累和调节防御相关基因的表达来抵抗辣椒疫病。这些抗病基因的报道为抗疫病分子标记辅助育种奠定了基础。
本试验通过分子标记辅助育种的方法对性状优良的甜辣椒材料进行抗疫病基因的筛选,有效加快了抗疫病辣椒品种选育的进程,为进一步开展辣椒选育双抗或三抗新品种奠定基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料
试验材料共40份,为河北省农林科学院经济作物研究所茄果类研究室提供。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 辣椒总DNA的提取取 每个材料的幼嫩叶片,利用CTAB法提取总DNA,用TE溶解,1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测基因组DNA条带完整性,-20 ℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.2 引物筛选 根据王博等[10]、巩振辉等[11]、Qririn等[12]和王得元等[13]等公布的与辣椒疫病紧密连锁的分子标记合成引物,引物由华大基因科技服务有限公司合成(表1)。
表1 与疫病紧密连锁的STS标记引物序列
Tab.1 The STS primers of closely linked to the Phythophtora blight
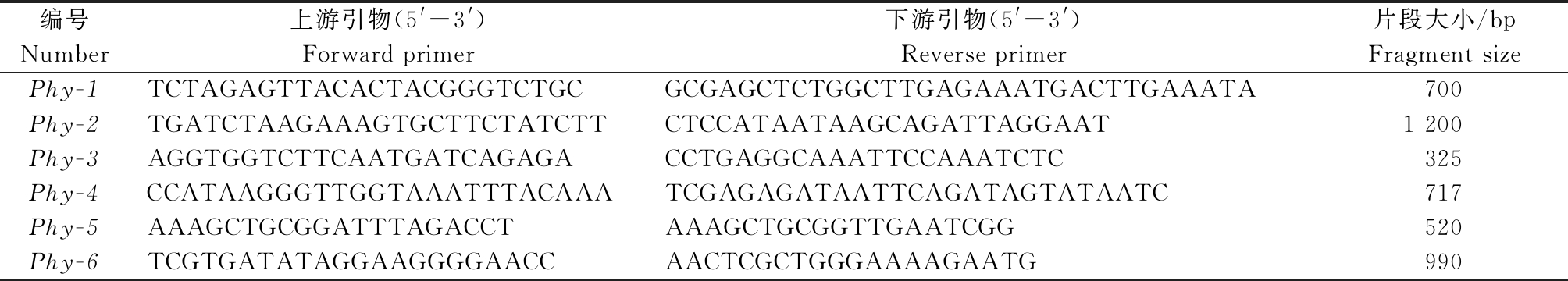
编号Number上游引物(5'-3')Forward primer下游引物(5'-3')Reverse primer片段大小/bpFragment sizePhy-1TCTAGAGTTACACTACGGGTCTGCGCGAGCTCTGGCTTGAGAAATGACTTGAAATA700Phy-2TGATCTAAGAAAGTGCTTCTATCTTCTCCATAATAAGCAGATTAGGAAT1 200Phy-3AGGTGGTCTTCAATGATCAGAGACCTGAGGCAAATTCCAAATCTC325Phy-4CCATAAGGGTTGGTAAATTTACAAATCGAGAGATAATTCAGATAGTATAATC717Phy-5AAAGCTGCGGATTTAGACCTAAAGCTGCGGTTGAATCGG520Phy-6TCGTGATATAGGAAGGGGAACCAACTCGCTGGGAAAAGAATG990
1.2.3 STS-PCR扩增和产物检测 PCR反应体系为:20 μL,10×Buffer(Mg2+)2 μL,0.2 mol/L dNTP 1.5 μL,Taq酶0.2 μL,上下游引物各1.0 μL,模板DNA 2.0 μL。反应程序为:94 ℃预变性5 min;94 ℃变性30 s,55~58 ℃退火45 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,共30~40个循环;72 ℃延伸5 min,4 ℃保存。扩增产物于1.0%的琼脂糖凝胶上检测,Gold-view染色,120 V电泳45~60 min,利用紫外凝胶成像仪记录并统计结果,重复3次。
2 结果与分析
2.1 STS分子标记检测结果
2.1.1 引物Phy-1抗疫病材料检测结果 疫病抗性基因特异性引物Phy-1的部分检测结果如图1所示,40份辣椒材料中有14份材料在700 bp处有特异性条带,为抗疫病的辣椒材料,其余26个辣椒材料均无特异性条带(部分结果如图1)。
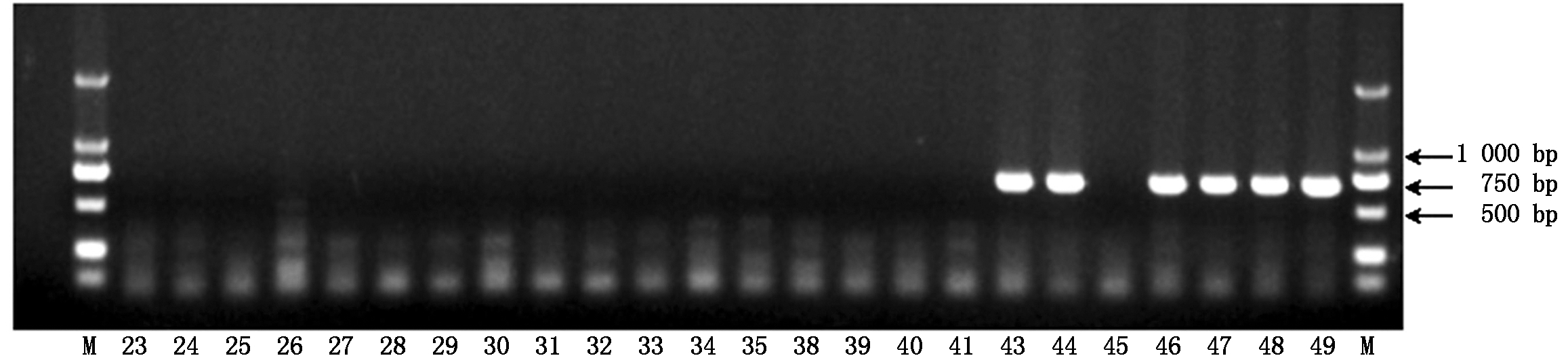
图1 疫病抗性基因特异性引物Phy-1的检测结果
Fig.1 Detection results of Phytophthora blight resistance gene using specific primer Phy-1
2.1.2 引物Phy-4抗疫病材料检测结果 疫病抗性基因特异性引物Phy-4的部分检测结果如图2所示,40份辣椒材料中有7份材料在717 bp处有特异性条带,为抗疫病的辣椒材料,其余33个辣椒材料均无特异性条带(图2)。
2.1.3 引物Phy-6感疫病材料检测结果疫病抗性基因特异性引物Phy-6的部分检测结果如图3所示,40份辣椒材料中有2份材料在990 bp处有特异性条带,为感疫病的辣椒材料,其余38份辣椒材料均无特异性条带(图3)。
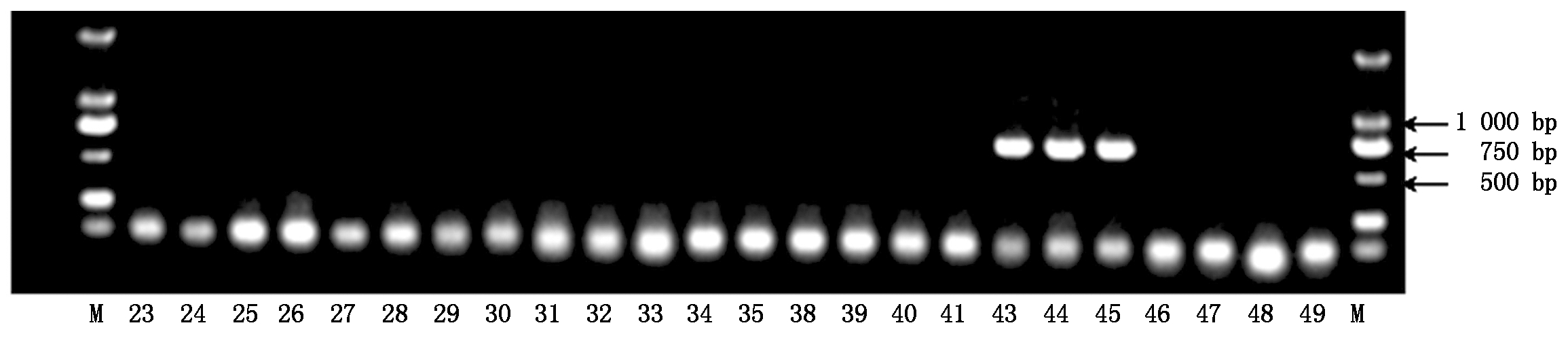
图2 疫病抗性基因特异性引物Phy-4的检测结果
Fig.2 Detection results of Phytophthora blight resistance gene using specific primer Phy-4
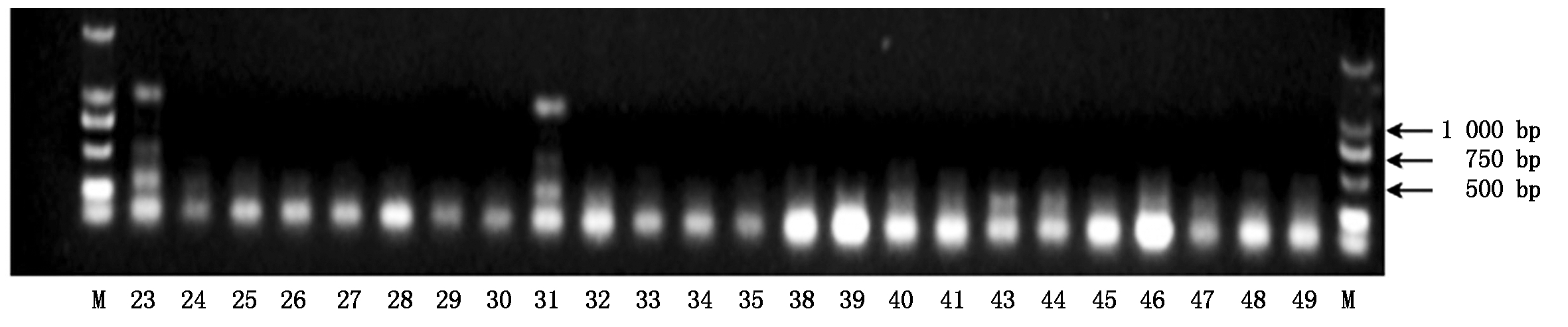
图3 疫病抗性基因特异性引物Phy-6的检测结果
Fig.3 Detection results of Phytophthora blight resistance gene using specific primer Phy-6
2.2 抗病性结果统计
利用6个STS标记对40份材料进行抗疫病鉴定,筛选出Phy-1、Phy-4 和Phy-6共3个STS标记具有目标条带,其余3对引物未呈现多态性标记。Phy-1、Phy-4 和Phy-6共鉴定出抗疫病材料18份,感病材料2份。其中,引物Phy-1筛选出抗病材料14个,Phy-4筛选出抗病材料7份,含有2个抗疫病基因的材料3份,引物Phy-6筛选出来的感病性材料2份(表2)。
表2 抗病性结果统计
Tab.2 Statistics of disease resistance results
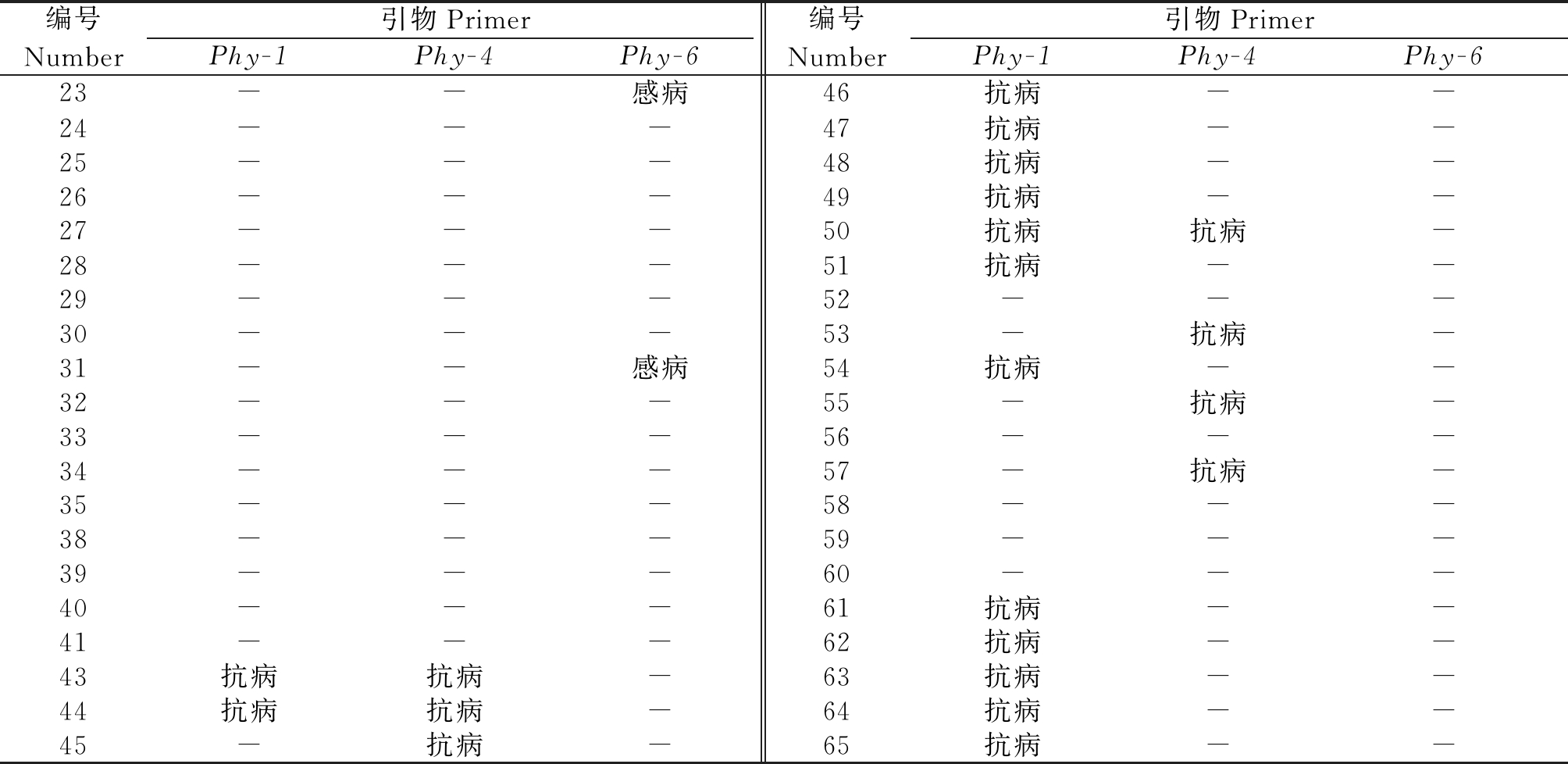
注:-.未扩增出特异性条带。
Note:-.No specific bands have been amplified.
编号Number引物PrimerPhy-1Phy-4Phy-6编号Number引物PrimerPhy-1Phy-4Phy-623--感病46抗病--24---47抗病--25---48抗病--26---49抗病--27---50抗病抗病-28---51抗病--29---52---30---53-抗病-31--感病54抗病--32---55-抗病-33---56---34---57-抗病-35---58---38---59---39---60---40---61抗病--41---62抗病--43抗病抗病-63抗病--44抗病抗病-64抗病--45-抗病-65抗病--
3 讨论
辣椒抗疫病基因的遗传规律比较复杂,不同辣椒试材携带的抗疫病基因的遗传规律不同,一般认为辣椒疫病的抗病性是由单基因遗传、寡基因遗传或多基因遗传[14-17],如N1345疫病抗性基因由2对加性-显性-上位性主基因控制,两主基因加性效应、显性效应均相等[18]。PI201234抗性基因是由一个CaPhyto的显性基因控制[9]。CM334抗性基因是由2个非连锁的隐性基因共同控制[19]。
国内外的研究学者已对辣椒疫病基因进行了系列QTL定位或连锁标记研究,但得到的结论有所差异,本试验利用已报道的6个抗疫病分子标记对40份辣椒材料进行了抗病性鉴定,只有3个标记能筛选出目标条带,可能是由于辣椒材料的水平抗性和垂直抗性并存,而辣椒疫霉菌不同生理小种的致病力存在差异有关[20],所以前人开发的分子标记并不适用于所有辣椒材料的抗疫病鉴定。因此,针对具体育种材料进行定位与标记的筛选,可有效提高辣椒抗疫病分子育种的进程,为加快辣椒抗疫病新品种选育及产业发展奠定了基础。
[1] Parra G,Ristaino J B.Resistance to mefenoxam and metalaxyl among fieldi solates of Phytophthora blight of bell pepper[J].Plant Dis,2001,85:1069-1075.doi:10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.10.1069.
[2] Obata T S,Witt S,Lisec J,Palacios R N,Florez S I,Yousfi S.Metabolite profiles of maize leaves in drough the atand combined stress field trials reveal there lation ship between metabolism and grainyield[J].Plant Physiol,2015,169:2665-2683.doi:10.1104/pp.15.01164.
[3] Wang J E,Li D W,Zhang Y L,Zhao Q,He Y M,Gong Z H.Defence responses of pepper(Capsicum annuum L.)infected with in compatible and compatible strains of Phytophthora capsici[J].Plant Pathol,2013,136:625-638.doi:10.1007/s10658-013-0193-8.
[4] Reyes T,Alfredo,Castro R,Arturo,Rodrguez A,Gerardo P S,Martha E,Lamour K L,John F P,Sylvia P.Virulence phenotypes on chili pepper for Phytophthora capsici isolates from Michoac n Mexico[J].Hort Science,2019,54(9):1526-1531.doi:10.21273/HORTSCI13964-19.
n Mexico[J].Hort Science,2019,54(9):1526-1531.doi:10.21273/HORTSCI13964-19.
[5] Wang P Y,Wang L R,Guo J J,Yang W C,Shen H L.Molecular mapping of agene conferring resistance to Phytophthora capsici Leonian race 2 inpepper line PI201234(Capsicum annuum L.)[J].Mol Breeding,2016,36:66.doi:10.1007/s11105-009-0178-0.
[6] Liu W Y,Kang J H,Jeong H S,Choi H J,Yang H B,Kim K T,Choi D,Choi G J,Jahn M,Kang B C.Combined use of bulked segregant analysis and microarrays reveals SNP markers pinpointing a major QTL for resistance to Phytophthora capsici in pepper[J].Theor Appl Genet,2014,127(11):2503-2513.doi:10.1007/s00122-014-2394-8.
[7] 刁卫平,王述彬,刘金兵,潘宝贵,郭广君,戈伟,高长洲.辣椒疫病抗性相关,NAC基因的鉴定及表达分析[J].分子植物育种,2018(16):5183-5191.doi:10.13271/j.mpb.016.005183.
Diao W P,Wang S B,Liu J B,Pan B G,Guo G J,Ge W,Gao C Z.Identification and expression analysis of NAC gene related to phytoph-thora blight resistance in pepper[J].Molecular Plant Breeding,2018(16):5183-5191.
[8] 王博,左星,李永新,巩振辉,李大伟.辣椒抗疫病相关基因的RGA-STS标记的开发[J].西北农业学报,2010,19(10):124-127.
Wang B,Zuo X,Li Y X,Gong Z H,Li D W.Development of a sequence tagged sites marker derived from resistance gene analog(RGA-STS)associated with resistance to Phytophthora capsici in pepper(Capsicum annuum L.)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2010,19(10):124-127.
[9] Muhammad A Z,Muhammad S U H,Mukhtar A,Abdul M K,Kashif A,Hidayat U,Abid K Gang,Lu Z H.The Ca ChiVI2 gene of Capsicum annuum L.confers resistance agains the at stress and in fection of Phytophthora capsici[J].Frontiersin Plant Science,2020(19):1-16.doi:10.3389/fpls.2020.00219.
[10] 王博,李永新,巩振辉,李大伟.辣椒疫病抗性相关的共显性RGA-STS标记的开发及应用[J].西北农业学报,2011,20(6):123-127.
Wang B,Li Y X,Gong Z H,Li D W.Development of a sequence tagged sites marker derived from resistancegene analog(RGA-STS)associated with resistance to Phytophthora capsici in pepper(Capsicum annuum L.)[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2011,20(6):123-127.
[11] 巩振辉,刘珂珂,逯明辉,李大伟.一种利用分子标记淘汰辣椒感疫病材料的方法,中国,ZL200910021240.9[P].2011-04-06.
Gong Z H,Liu K K,Lu M H,Li D W.a method of using molecular markers to eliminate the pestilential materials of pepper,China,ZL200910021240.9[P].2011-04-06.
[12] Qririn E A,Ogundiwin E A,Prince J P.Development of sequence characterized amplified region(SCAR)primers for the detection of Phyto.5.2 a major QTL for resistance to Phytophtho racapsici Leoninpepper[J].Theor Appl Genet,2005(110):605-612.doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1874-7.
[13] 王得元,安康,李颖.一种辣椒抗疫病育种的分子标记辅助选择方法[P].中国专利:CN1970790,2007-05-30.
Wang D Y,An K,Li Y.A molecular marker assisted selection method for pepper disease resistance breeding[P].Chinese patent:CN1970790,2007-05-30.
[14] 马寿宾,孙艳,王琛.分子标记辅助选择辣椒抗疫病新种质研究[J].北方园艺,2013(10):107-110.
Ma S B,Sun Y,Wang C.Molecular marker assisted selection of pepper materials with resistance to Phytophthora blight[J].Northern Horticulture,2013(10):107-110.
[15] Pflieger S,Palloix A,Caranta C.Defense response genescolocalize with quantitative disease resistance loci in pepper[J].Theor Appl Genet,2001(103):920-929.doi:10.1007/s001220100726.
[16] Thabuis A,Lefebvre V,Bernard G.Phenotypic and molecular evaluation of a recurrent selection program for a polygenic resistance to Phytophthora capsici in pepper[J].Theor Appl Genet,2004(109):342-351.doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1633-9.
[17] Thabuis A,Palloix A,Pflieger S.Comparative mapping of Phytophthora resistance loci in pepper germplasm:evidence forconserved resistance loci across solanceae and for a large genetic diversity[J].Theor Appl Genet,2003(106):1473-1485.doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1206-3.
[18] 张晓芬,韩华丽,陈斌,耿丽华,耿三省.甜椒疫病抗性遗传及相关基因分子标记研究[J].园艺学报,2011,38(7):1325-1332.
Zhang X F,Han H L,Chen B,Geng L H,Geng S S.Genetic and molecular marker analysis of resistance to Phythophtora capsici in sweet pepper[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2011,38(7):1325-1332.
[19] Kim B S,Kwon Y S.Inheritance of resistance to bacterial spot and Phytophhora blight in pepper[J].Journal of Korean Society for Horticultural Science,1991,7:17-24.doi:10.1590/S1982-56762010000300002.
[20] 张爱民,蓬桂华,梁传静,袁圆,熊世娟,涂祥敏,王兰.贵州地方辣椒材料疫病抗性鉴定的分子标记引物筛选[J].贵州农业科学,2017,45(11):10-14.
Zhang A M,Peng G H,Liang C J,Yuan Y,Xiong S J,Tu X M,Wang L.Molecular marker primers screening of identification on local pepper with Phytophthora blight resistance in Guizhou[J].Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2017,45(11):10-14.