水稻白叶枯病是由革兰氏阴性菌黄单孢菌(Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae,Xoo)侵染引起的一类细菌性维管束病害,是对水稻产量最具破坏性的病害之一。利用抗病基因培育抗病品种是控制白叶枯病最经济有效的手段[1]。目前,已经鉴定了将近40个白叶枯病抗性基因,9个(Xa1[2]、Xa3/Xa26[3]、xa5[4-5]、Xa10[6]、xa13[7]、Xa21[8]、Xa23[9]、xa25[10]和Xa27[11])已经被克隆。只有7个抗病基因Xa21、xa5、Xa7、Xa10、Xa27、Xa23和Xa27相应的无毒基因(avr基因)被分离。有意思的是,其中的5个avr基因(avrxa5、avrXa7、avrXa10[6]、avrXa23[12]和avrXa27[11])都属于TAL效应子(Effector),它是由黄单胞菌通过细菌Ⅲ型分泌系统分泌的一类细菌蛋白质,作为转录因子,通过结合目标基因的启动子区来激活植物基因的表达[13]。由于水稻宿主和致病菌的协同进化,在植物抗病基因与病原菌avr基因的互作压力下,病原菌通过伪装、多样化avr基因或获得额外的效应子来避免相应的抗病基因的识别,从而使得单个抗病基因提供的抗性很容易被克服[14]。例如,Xa4大面积长期应用后,导致白叶枯菌小种进化,抗病品种已经丧失了抗性[15];xa5对含有TAL效应基因pthXo1的菌株无效[16];P6小种不能感染携带Xa21的抗病品种,但是在P6的raxX基因缺失或raxST基因突变后能够克服Xa21介导的抗病反应[17]。
基因聚合是培育具有持久和广谱抗性等优良性状后代的有效策略。例如Xa21+xa13的聚合系抗性明显高于仅含有一个抗病基因的水稻[18]。Xa7和Xa21[19],Xa21、Xa4和Xa23[20],xa5、xa13和Xa21[21]等白叶枯抗病基因累加后,抗性增加,抗谱拓宽。不仅如此,白叶枯病抗性基因与其他基因聚合后,可增加对其他病虫害的额外抗性。例如含Xa23与稻瘟病抗病基因的基因聚合水稻系同时获得了对白叶枯病和稻瘟病的抗性[22]。含Xa23与细菌性条斑病抗性基因Rxol的基因聚合水稻系同时抗白叶枯病和细菌性条斑病[23]。Xa21、Bt基因与几丁质酶基因的三基因聚合系IR72则同时抗白叶枯病、纹枯病和虫害[24]。抗病基因组合后呈现正向的抗性累加效应是育种家所期望的,然而,并非所有的抗病基因组合都能获得正向的抗性叠加效应。比如,Xa27介导的抗性在xa5和Xa27双基因纯合系中大大减弱[25];同样,在xa5和 Xa10双基因纯合植株中,依赖于avrXa10的Xa10的表达和Xa10介导的对PXO99A的抗性都被部分抑制[6];在xa5和Xa23双基因纯合植株中,avrXa23诱导的Xa23表达完全丧失,Xa23介导的抗性水平也降低[26]。
通过分子标记辅助回交选育的含单抗病基因和基因组合的近等基因系(NILs),为研究抗病基因的功能提供了珍贵的材料。前期研究中,揭示了xa5和Xa21单基因抗病系和基因累加系的抗性正向叠加效应,本研究继续报道了xa3、Xa23单基因抗病系以及xa5、Xa4、Xa21和xa13等基因聚合系的抗谱。通过比较分析8个致病菌对这些抗病系的致病性,揭示了单个抗病基因和基因组合后的抗病效应的不确定性以及致病菌的毒性变异。研究结果为水稻抗病系培育和水稻种植布局提供了理论基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 水稻材料
本研究所用的水稻材料包括对白叶枯菌敏感的粳稻品种TP309和籼稻品种IR24,单基因抗病系IRBB3、IRBB5、IRBB21、CBB23,多抗病基因聚合系IRBB50、IRBB54和IRBB59。所有IR系列水稻的遗传背景都是IR24。IRBB3、IRBB5、IRBB21是分别含Xa3、xa5和Xa21的单抗病基因近等基因系[27];IRBB50、IRBB54和IRBB59是分别含Xa4+xa5、Xa21+xa5、Xa21+xa5+xa13基因组合的多抗病基因近等基因系[28-29]。CBB23是以感病籼稻品种JG30为轮回亲本,通过5代回交选育的携带Xa23基因的单抗病基因系[30]。
1.2 革兰氏阴性菌黄单孢菌的培养和水稻抗谱鉴定
将江汉大学保存的8个来自菲律宾的白叶枯菌小种(P1:PXO61、P2:PXO86、P3:PXO79、P4:PXO7、P6:PXO99、P7:PXO145、P8:PXO280和P10:PXO124)在PSA培养基(土豆300 g/L、蔗糖 15 g/L、Na2HPO4·12H2O 2 g/L、Ca(NO3)2·4H2O 0.5 g/L、琼脂15 g/L)上活化,刮取活化后的菌斑用无菌水制备成浓度约为109个细胞/mL的菌液用于水稻品种的抗性鉴定。在水稻生长的高分蘖期,用剪叶法[31]进行接种。每个小种接种5株,每株接种3~5个叶片。接种12 d后,对病斑长度进行测量,每个小种至少测量10个叶片。病斑长度用于评价抗病系的抗性水平,根据标准病害分级系统,病斑长度≤3 cm表示抗病(R),3~6 cm 表示中度抗病(MR),6~10 cm表示中度感病(MS),≥10 cm 表示感病(S)[32]。
1.3 抗性基因的分子标记检测
为了确保所种植的抗病系含有相应的抗病基因,对抗病系IRBB3、IRBB5、IRBB21、IRBB50、IRBB54和IRBB59所含有的抗病基因进行了分子标记辅助检测。对xa5的检测采用的是CAPS标记xa5-Xho Ⅰ F/R[33],Xa21使用的是Gao等[34]开发的一个功能标记U1/I2,Xa3使用的是功能标记BB3-RF/R[35],特异的在抗性材料里扩增;Xa4使用的是紧密连锁的SSR标记RM224[36],Xa23使用的是共分离标记Lj74[37]。具体的引物序列和预期的PCR产物长度见表1。
表1 抗病基因分子标记检测引物
Tab.1 List of primers for resistance gene detection
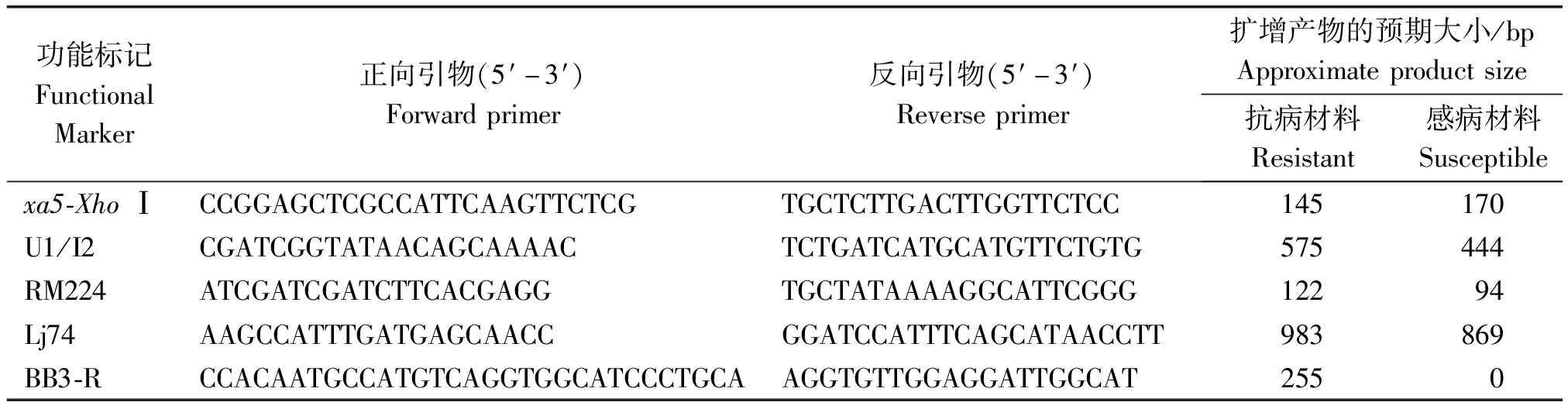
功能标记FunctionalMarker正向引物(5′-3′)Forwardprimer反向引物(5′-3′)Reverseprimer扩增产物的预期大小/bpApproximateproductsize抗病材料Resistant感病材料Susceptiblexa5-XhoⅠCCGGAGCTCGCCATTCAAGTTCTCGTGCTCTTGACTTGGTTCTCC145170U1/I2CGATCGGTATAACAGCAAAACTCTGATCATGCATGTTCTGTG575444RM224ATCGATCGATCTTCACGAGGTGCTATAAAAGGCATTCGGG12294Lj74AAGCCATTTGATGAGCAACCGGATCCATTTCAGCATAACCTT983869BB3-RCCACAATGCCATGTCAGGTGGCATCCCTGCAAGGTGTTGGAGGATTGGCAT255 0
2 结果与分析
2.1 接种试验检测8个小种的有效致病性
为了保证接种的有效性,在进行接菌试验时,对不含有以上抗病基因的受体品种IR24和另外一个感病粳稻品种TP309同时进行了接种。IR24的接种结果在之前的研究中已经报道[34]。IR24对8个小种都表现出明显的感病表型,其中被P8感染后的叶片病斑长度最长,有20~25 cm,而P6的病斑长度最短,仅有3~6 cm(图1-B和文献[34]的表1,S1)。TP309在受到8个小种侵染后,被P8侵染后的叶片病斑最长,平均长约19 cm,被P6侵染后的叶片病斑长度最短(图1)。对TP309和IR24的接种结果表明,8个小种都具备致病性,且P8小种的致病力最强,这8个小种可以用于抗性品种的抗谱分析。
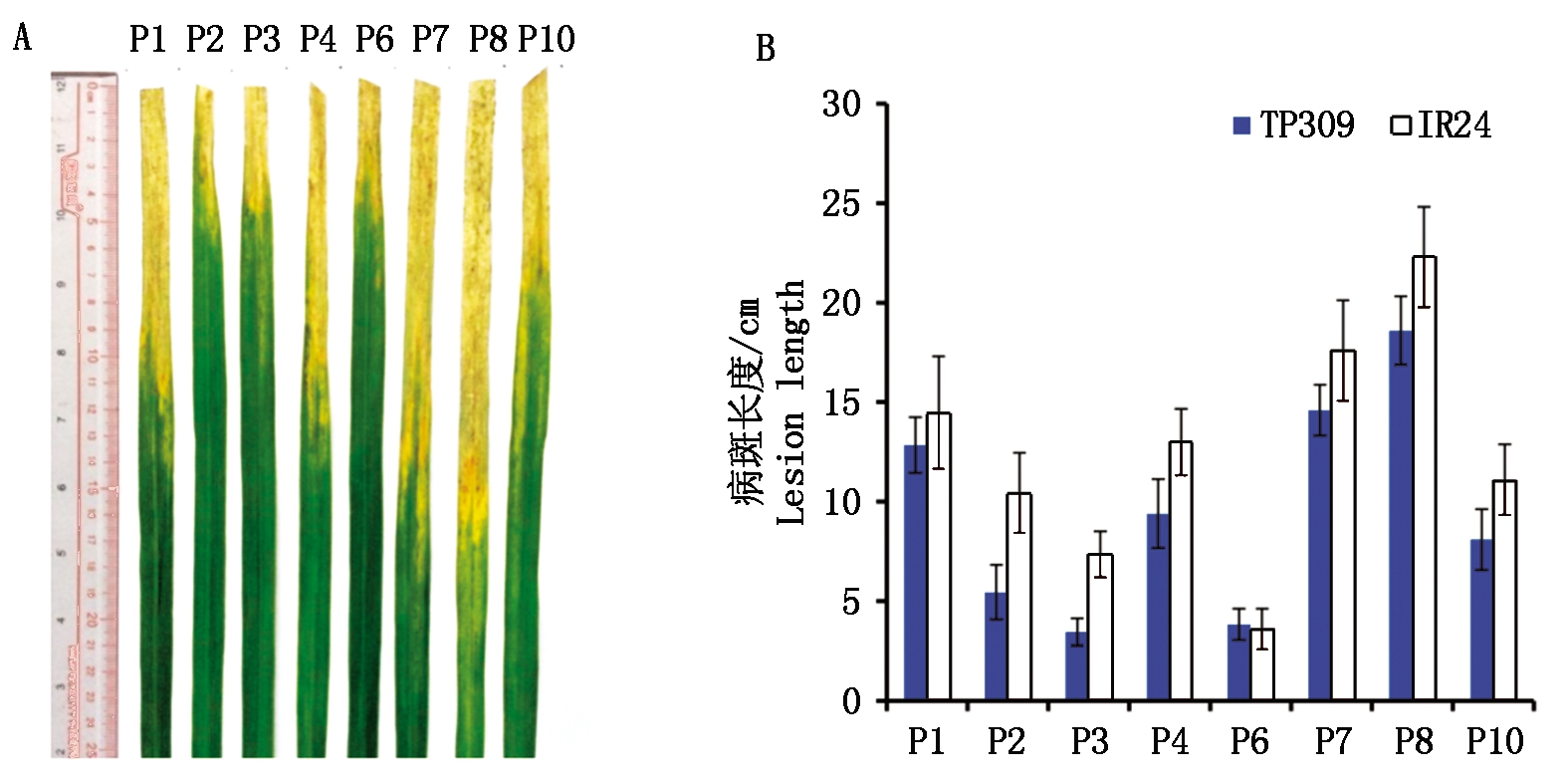
A.8个小种在TP309上致病的图像;B.8个小种在TP309和IR24上诱导的病斑长度。P1-P10.Xoo 小种。
A.Pathogenic images of 8 strains on TP309; B.Leison length induced by 8 strains on TP309.P1-P10.Xoo strains.
图1 8个小种在感病品种TP309和IR24上的致病性检测
Fig.1 Pathogenicity test of eight strains on TP309 and IR24
2.2 分子标记辅助检测抗病系的真实性
采用xa5-Xho Ⅰ F/R、U1/I2、BB3-RF/RR、RM224和Lj74引物,分别对单基因系和聚合基因系中的xa5、Xa21、Xa3、Xa4和Xa23进行分子标记检测。检测结果如图2所示,以不含目标抗病基因的IR24为对照,IRBB3中能检测到Xa3基因,IRBB5、IRBB50、IRBB54和IRBB59均能检测到xa5基因,IRBB50中能检测到Xa4基因,IRBB21、IRBB54和IRBB59中均能检测到Xa21基因;而以不含Xa23基因的C418为对照,CBB23中能检测到Xa23基因。分子标记的检测结果证明了试验材料的真实可靠。
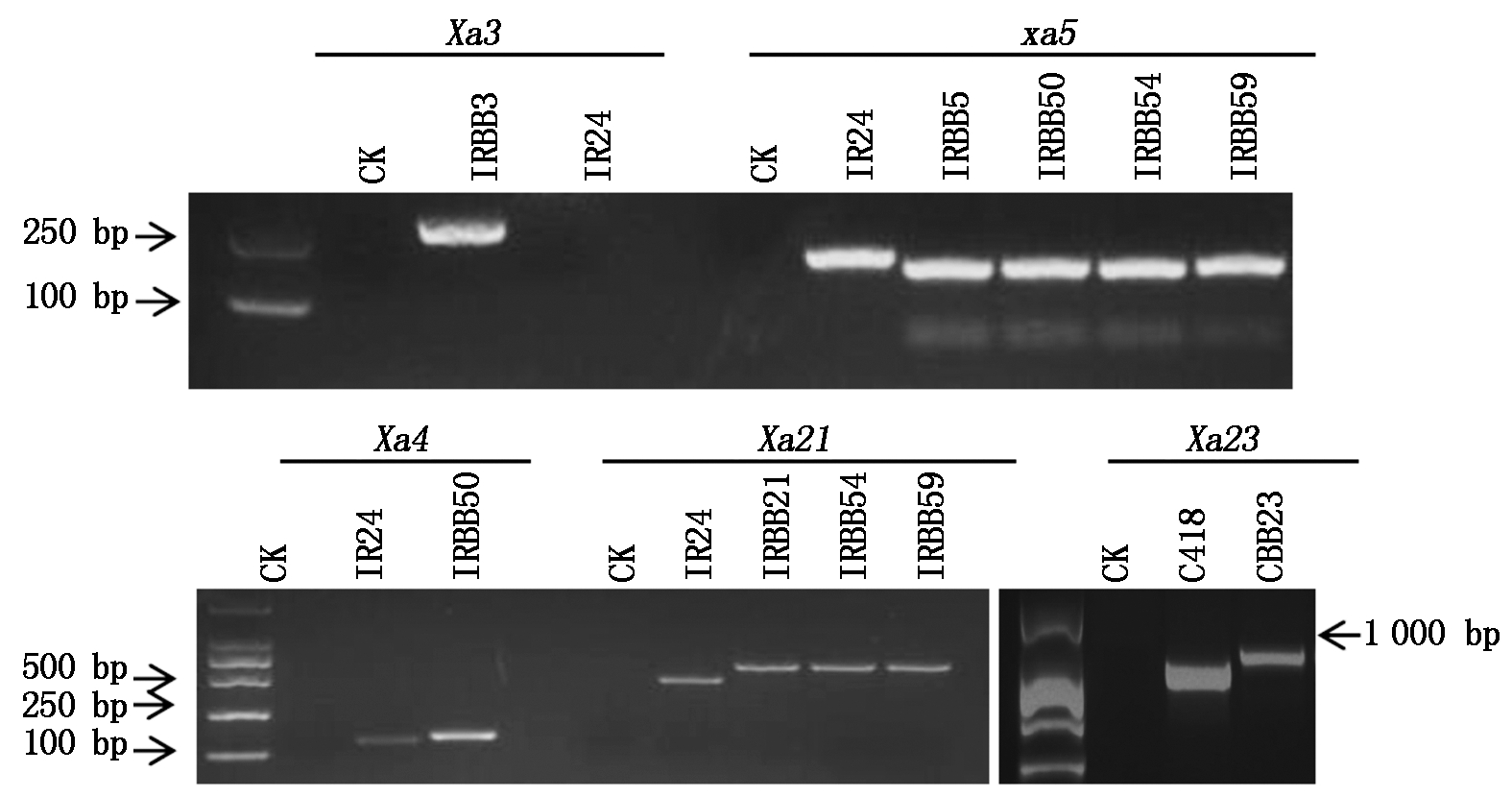
CK.双蒸水为模板。IR24、C418.阴性对照;IRBB3、IRBB5、IRBB21、CBB23、IRBB50、IRBB54和IRBB59.抗病近等基因系。
CK.Double steamed water as template.IR24, C418.Negative control; IRBB3, IRBB5, IRBB21, CBB23, IRBB50, IRBB54 and IRBB59.Resistant near-isogenic lines.
图2 分子标记检测近等基因系中的抗病基因
Fig.2 Detection of resistance genes in near-isogenic lines by molecular markers
2.3 单基因抗谱揭示病原菌毒性变异
在前期的研究中,报道了xa5和Xa21基因对8个小种的抗性,xa5对所有8个小种表现出抗性,而Xa21对P2、P3、P4和P6表现出抗性,对P1、P7和P10中度感病,对P8则完全敏感[34]。本研究中,进一步报道了Xa3和Xa23单基因抗病系的抗谱。结果如图3所示,单基因抗病系中,IRBB3的整体抗性最弱,对P1、P2、P3、P4、P6和P10中度感病,对P7和P8完全感病;而8个小种在CBB23叶片上诱导的病斑长度都不足1 cm,CBB23对白叶枯菌表现出了明显的广谱高抗性。值得注意的是,在之前的报道中,发现P8打破了Xa21基因介导的抗性,在IRBB21上诱导超过10 cm长的病斑[34]。本研究中,P8在2个感病对照TP309和IR24,以及单基因抗病系IRBB3上诱导的病斑长度都是8个小种中最长的,表现出最强的致病性。这个结果表明,在长期的病原菌和寄主互作中,P8克服了多个抗病基因介导的抗性,同样地,其他小种也有可能发生致病性的变化,因此,有必要对常用小种的致病性进行鉴定,以便及时发现毒性变异的致病菌。
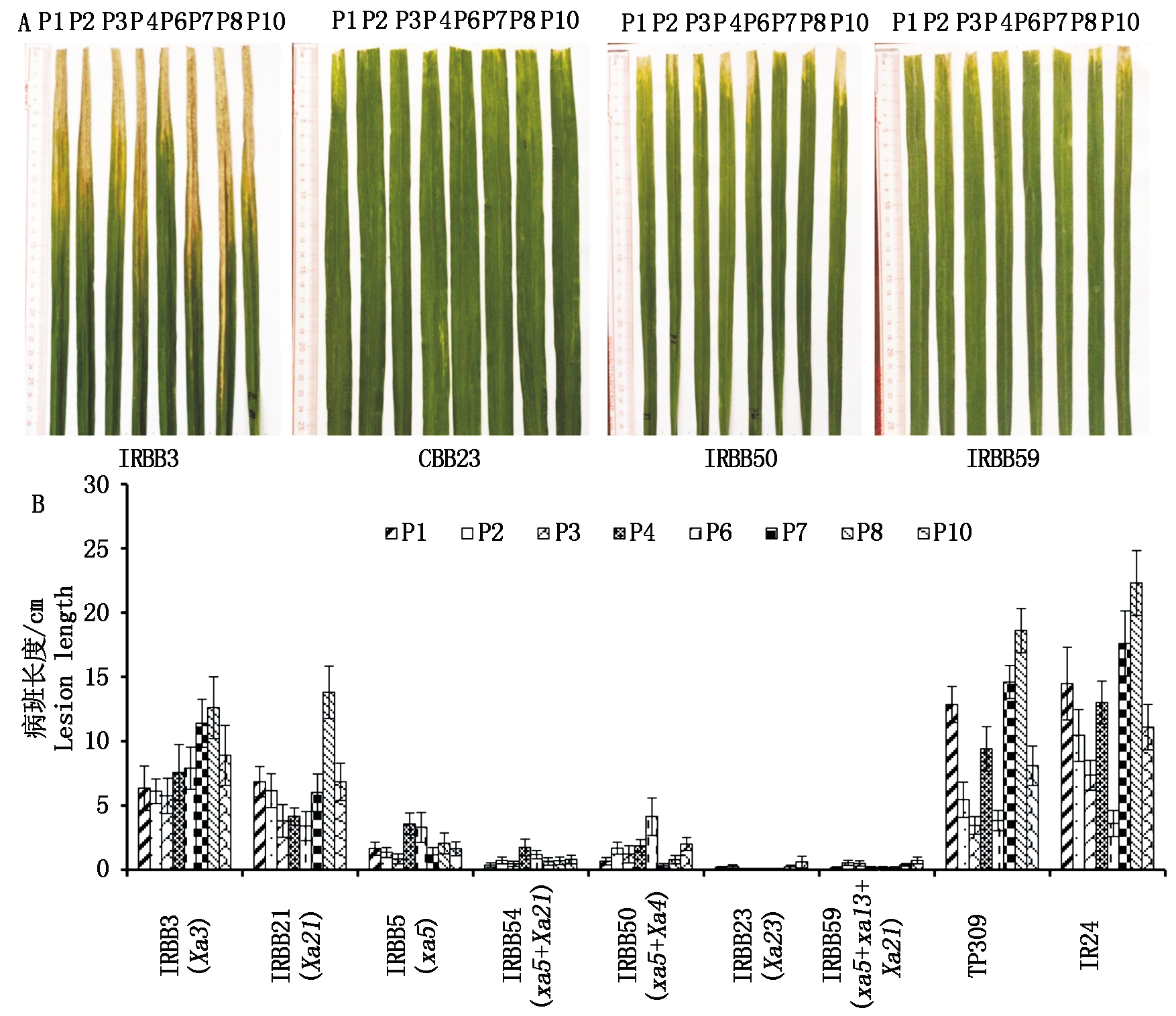
A.8个小种在近等基因系上致病的图像;B.8个小种在近等基因系上诱导的病斑长度。P1,P2,P3,P4,P6,P7,P8,P10.Xoo小种。TP309和IR24.感病对照; IRBB3、IRBB21、IRBB5、CBB23.单基因抗病系;IRBB54、IRBB50和IRBB59.多基因抗病系。
A.Pathogenic images of 8 strains on near-isogenic lines; B.Lesion length induced by 8 strains on near-isogenic lines.P1, P2, P3, P4, P6, P7, P8, P10.Xoo strains.TP309 and IR24.Susceptible control; IRBB3, IRBB21, IRBB5 and CBB23.Single gene resistant line; IRBB54, IRBB50 and IRBB59.Multi-genes resistant line.
图3 8个小种在近等基因系上的致病性检测
Fig.3 Pathogenicity test of eight strains on near-isogenic lines
2.4 基因聚合后的抗性叠加效应
xa5+Xa21基因聚合后对8个小种都表现出正向的抗性叠加效应[34]。而xa5与Xa4基因聚合后正向的抗性叠加效应不明显(图3)。基因聚合系中抗性正向叠加效应最显著的是含xa5+Xa21+xa13三基因组合的IRBB59。IRBB59和CBB23一样,8个小种在IRBB59叶片上诱导的病斑长度都不足1 cm,表现出明显的广谱高抗性(图3)。xa5+Xa21、xa5+Xa4、xa5+Xa21+xa13的基因组合对P8的抗性都达到高抗病的水平,表明了上述基因组合能有效抵御P8的侵染,也说明了基因聚合策略对选育持久广谱抗性水稻品种的有效性。
3 讨论与结论
Zhang等[30]报道显示IRBB21对10个菲律宾小种中的P10敏感,对其余9个小种都具有抗性。而在我们的之前研究中,IRBB21对P10中度感病,对P8则完全敏感[34]。本研究的结果发现IRBB3对P1、P2、P3、P4达到了中度感病的水平,而Xiang等[38]的报道显示,携带Xa3的水稻品种对P1、P2、P3、P4、P5和P9都表现出抗性的表型。这些结果表明,不同实验室保存命名的相同的小种在致病性上不一定完全相同,这种情况或是由于培养条件的不同,使得小种在保存的过程中发生了突变,亦或是在培养过程中出现了操作失误,导致常用的小种混淆或是污染等,可以在后续的研究中继续关注。
P8对Xa21介导抗性的突破以及其他抗病基因,比如Xa4[15]抗性被突破的事实,提示育种家关注单个抗病基因抵御水稻病害的时效性。由于植物和病原菌的协同进化,大面积长时间的种植含单个基因的抗性品系容易导致抗性丧失,聚合育种是增加抗性、减缓抗性丧失的有效手段。单基因系IRBB21对4个菲律宾小种(P1、P7、P8和P10)的抗性已明显减弱,而Xa21在和xa5聚合后对以上4个小种的抗性明显提高[34]。Xa21+xa5+xa13的组合更是对所有小种产生了高抗性,病斑长度均不足1 cm。但是,在进行基因组合时,还是要充分考虑2个基因的作用机制。xa5和Xa21、xa13聚合后,表现出了正向的抗性叠加效应,是育种家所期望的。而在之前的报道中,xa5和Xa23/Xa10/Xa27基因聚合后,聚合系的抗性都出现了一定程度的弱化[6,25-26]。根据本研究和前人研究结果,Xa23单基因已经可以对常用的白叶枯菌提供广谱高抗性[30],和xa5的聚合反而弱化了Xa23的功能。推测其原因,Xa23、Xa10和Xa27基因的一个共同特点是相应的avr基因都是TAL效应子。TAL效应子是由黄单胞菌通过细菌Ⅲ型分泌系统分泌的一类细菌蛋白质,作为转录因子,通过结合植物基因的启动子区来激活植物基因的表达,Xa23、Xa10和Xa27的表达都依赖于其相应的avr基因。以Xa27基因为例,AvrXa27结合在Xa27的启动子区,诱导其表达使植株产生抗病性,AvrXa27诱导的Xa27的表达需要显性Xa5的参与。在隐性xa5和Xa27双基因纯合聚合系中,隐性xa5不能行使显性Xa5的功能,Xa27的激活被弱化,从而使Xa27介导的抗病反应减弱[25]。xa5和Xa21的基因聚合后,2个基因在聚合系IRBB54中的表达都要高于单基因系[34]。xa5和Xa21基因聚合后的抗性增强效应可能也与Xa21和Xa27不同的抗病机制有关。Xa21属于组成型表达基因,表达不依赖于显性Xa5的功能。因此,为提高抗性、拓宽抗谱、延缓抗性丧失,聚合育种最好选择具有不同抗病机制的基因进行组合。
本研究调查了多个单基因抗病系和基因组合抗病系对8个常用的白叶枯病小种的抗性水平,研究结果一方面鉴定了各个抗病系的抗谱,另一方面也揭示了常用致病菌的毒性变异以及基因聚合策略在应付致病菌毒性变异的有效性和可能出现的拮抗效应,在水稻白叶枯病的理论研究和应用研究中应充分考虑这些因素。
[1] Ogawa T.Methods and strategy for monitoring race distribution and identification of resistance genes to bacterial leaf blight(Xanthomonas campestris pv.oryzae)in rice(Oryza sativa)[J].Jarq, 1993, 27(2):71-80.
[2] Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang Z X, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T.Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1998, 95(4):1663-1668.doi:10.1073/pnas.95.4.1663.
[3] Sun X L, Cao Y L, Yang Z F, Xu C G, Li X H, Wang S P, Zhang Q F.Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein[J].Plant J, 2004, 37(4):517-527.doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01976.x.
[4] Iyer A S, McCouch S R.The rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 encodes a novel form of disease resistance[J].Mol Plant Microbe Interact, 2004, 17(12):1348-1354.doi:10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.12.1348.
[5] Jiang G H, Xia Z H, Zhou Y L, Wan J, Li D Y, Chen R S, Zhai W X, Zhu L H.Testifying the rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5 by genetic complementation and further analyzing xa5(Xa5)in comparison with its homolog TFIIAγ1[J].Mol Genet Genomics, 2006, 275(4):354-366.doi:10.1007/s00438-005-0091-7.
[6] Tian D S, Wang J X, Zeng X, Gu K Y, Qiu C X, Yang X B, Zhou Z Y, Goh M L, Luo Y C, Murata-Hori M, White F F, Yin Z C.The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum[J].The Plant Cell, 2014, 26(1):497-515.doi:10.1105/tpc.113.119255.
[7] Chu Z H, Fu B Y, Yang H, Xu C G, Li Z K, Sanchez A, Park Y J, Bennetzen J L, Zhang Q F, Wang S P.Targeting xa13, a recessive gene for bacterial blight resistance in rice[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 112(3):455-461.doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0145-6.
[8] Song W Y, Wang G L, Chen L L, Kim H S, Pi L Y, Holsten T, Gardner J, Wang B, Zhai W X, Zhu L H, Fauquet C, Ronald P.A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21[J].Science, 1995, 270(5243):1804-1806.doi:10.1126/science.270.5243.1804.
[9] Wang C L, Zhang X P, Fan Y L, Gao Y, Zhu Q L, Zheng C K, Qin T F, Li Y Q, Che J Y, Zhang M W, Yang B, Liu Y G, Zhao K J.Xa23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice[J].Mol Plant, 2015, 8(2):290-302.doi:10.1016/j.molp.2014.10.010.
[10] Liu Q S, Yuan M, Zhou Y, Li X H, Xiao J H, Wang S P.A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice[J].Plant,Cell and Environ, 2011, 34(11):1958-1969.doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02391.x.
[11] Gu K Y, Yang B, Tian D S, Wu L F, Wang D J, Sreekala C, Yang F, Chu Z Q, Wang G L, White F F, Yin Z C.R gene expression induced by a type-Ⅲ effector triggers disease resistance in rice[J].Nature, 2005, 435(7045):1122-1125.doi:10.1038/nature03630.
[12] Wang C L, Qin T F, Yu H M, Zhang X P, Che J Y, Gao Y, Zheng C K, Yang B, Zhao K J.The broad bacterial blight resistance of rice line CBB23 is triggered by a novel transcription activator-like(TAL)effector of Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae[J].Mol Plant Pathol, 2014, 15(4):333-341.doi:10.1111/mpp.12092.
[13] Boch J, Bonas U.Xanthomonas AvrBs3 family-type Ⅲ effectors: discovery and function[J].Annu Rev Phytopathol, 2010,48:419-436.doi:10.1146/annurev-phyto-080508-081936.
[14] Jones J D G, Dangl J L.The plant immune system[J].Nature, 2006, 444(7117):323-329.doi:10.1038/nature05286.
[15] 章琦.中国杂交水稻白叶枯病抗性的遗传改良[J].中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(2):111-119.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2009.02.001.
Zhang Q.Genetics and improvement of resistance to bacterial blight in hybrid rice in China[J].Chin J Rice Sci, 2009, 23(2):111-119.
[16] Huang S, Antony G, Li T, Liu B, Obasa K, Yang B, White F F.The broadly effective recessive resistance gene xa5 of rice is a virulence effector-dependent quantitative trait for bacterial blight[J].Plant J, 2016, 86(2):186-194.doi:10.1111/tpj.13164.
[17] Ronald P C.The role of RaxST, a prokaryotic sulfotransferase, and RaxABC, a putative type I secretion system, in activation of the rice XA21-mediated immune response[J].Scientifica, 2014, 2014:532816-532818.doi:10.1155/2014/532816.
[18] Pandey M K, Rani N N, Sundaram R M, Laha G S, Madhav M S, Rao K S, Sudharshan I, Hari Y, Varaprasad G S, Rao L V S, Suneetha K, Sivaranjani A K P, Viraktamath B C.Improvement of two traditional Basmati rice varieties for bacterial blight resistance and plant stature through morphological and marker-assisted selection[J].Molecular Breeding, 2013,31:239-246.doi:10.1007/s11032-012-9779-7.
[19] 闫成业, 刘艳, 牟同敏.分子标记辅助选择改良杂交水稻金优207的白叶枯病抗性[J].中国水稻科学, 2013, 27(5):52-59.doi:10.16267/j.cnki.1005-3956.2013.05.021.
Yan C Y, Liu Y, Mou T M.Improvement of rice bacterial blight resistance of hybrid rice jinyou 207 by molecular marker assisted selection[J].Chin J Rice Sci, 2013, 27(5): 52-59.
[20] 邓其明, 周宇爝, 蒋昭雪, 万映秀, 赵斌, 杨莉, 李平.白叶枯病抗性基因 Xa21, Xa4 和 Xa23 的聚合及其效应分析[J].作物学报, 2005, 31(9):1241-1246.doi:10.3321/j.issn:0496-3490.2005.09.025.
Deng Q M, Zhou Y J, Jiang Z X, Wan Y X, Zhao B, Yang L, Li P.Pyramiding bacterial blight(BB)resistance genes(Xa21, Xa4 and Xa23)into rice and its effect analysis[J].Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2005, 31(9):1241-1246.
[21] Singh S, Sidhu J S, Huang N, Vikal Y, Li Z, Brar D S, Dhaliwal H S, Khush G S.Pyramiding three bacterial blight resistance genes(xa5, xa13 and Xa21)using marker-assisted selection into indica rice cultivar PR106[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2001, 102(6-7):1011-1015.doi:10.1007/s001220000495.
[22] 潘晓飚, 陈凯, 张强, 黄善军, 谢留杰, 李美, 孟丽君, 徐正进, 徐建龙, 黎志康.分子标记辅助选育水稻抗白叶枯病和稻瘟病多基因聚合恢复系[J].作物学报, 2013, 39(9):1582-1593.doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2013.01582.
Pan X B, Chen K, Zhang Q, Huang S J, Xie L J, Li M, Meng L J, Xu Z J, Xu J L, Li Z K.Developing restorer lines pyramiding different resistant genes to blast and bacterial leaf blight by marker-assisted selection in rice[J].Acta Agron Sin, 2013, 39(9): 1582-1593.
[23] Zhou Y L, Xu J L, Zhou S C, Yu J, Xie X W, Xu M R, Sun Y, Zhu L H, Fu B Y, Gao Y M,Li Z L.Pyramiding Xa23 and Rxo1 for resistance to two bacterial diseases into an elite indica rice variety using molecular approaches[J].Mol Breeding, 2009, 23(2):279-287.doi:10.1007/s11032-008-9232-0.
[24] Datta K, Baisakh N, Thet K M, Tu J, Datta S.Pyramiding transgenes for multiple resistance in rice against bacterial blight, yellow stem borer and sheath blight[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2002, 106(1):1-8.doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1014-1.
[25] Gu K Y, Tian D S, Qiu C X, Yin Z C.Transcription activator-like type Ⅲ effector AvrXa27 depends on OsTFIIAγ5 for the activation of Xa27 transcription in rice that triggers disease resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv.oryzae[J].Molecular Plant Pathology, 2009, 10(6):829-835.doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00567.x.
[26] Yuan M, Ke Y G, Huang R Y, Ma L, Yang Z Y, Chu Z H, Xiao J H, Li X H, Wang S P.A host basal transcription factor is a key component for infection of rice by TALE-carrying bacteria[J].eLife, 2016, 5:e19605.doi:10.7554/eLife.19605.
[27] Ogawa T, Yamamoto T, Khush G S, Mew T W.Breeding of near-isogenic lines of rice with single genes for resistance to bacterial blight pathogen(Xanthomonas campestris pv.oryzae)[J].Jpn J Breed, 1991, 41(3):523-529.doi:10.1270/jsbbs1951.41.523.
[28] Huang N, Angeles E R, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Singh S, Zhang G, Kumaravadivel N, Bennett J, Khush G S.Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: marker-assisted selection using RFLP and PCR[J].Theor Appl Genet, 1997, 95(3):313-320.doi:10.1007/s001220050565.
[29] Yoshimura S, Yoshimura A, Iwata N, Mccouch S R, Abenes M L, Baraoidan M R, Mew T W, Nelson R J.Tagging and combining bacterial blight resistance genes in rice using RAPD and RFLP markers[J].Mol Breeding, 1995, 1(4):375-387.doi:10.1007/BF01248415.
[30] Zhang Q, Wang C L, Zhao K J, Yang W C, Qiao F, Zhou Y L, Jiang Q X, Liu G C.Development of near-isogenic line CBB23 with a new resistance gene to bacterial blight in rice and its application[J].Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2002, 16(3):206-210.doi:10.16819/j.1001-7216.2002.03.002.
[31] Kauffman H E, Reddy A P K, Hsieh S P Y, Merca S D.An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae[J].Plant Dis Rep, 1973, 57(6):537-541.
[32] IRRI: Standard evaluation system for rice[M].4th Edn.Manila: The Philippines, 1996.
[33] 夏志辉, 韩飞, 高利芬, 袁潜华, 翟文学, 刘迪, 罗越华.利用功能标记鉴定普通野生稻中的白叶枯病抗性基因[J].中国水稻科学, 2009, 23(6):653-656.doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7216.2009.06.15.
Xia Z H, Han F, Gao L F, Yuan Q H, Zhai W X, Liu D, Luo Y H.Application of functional marker to identify genes for bacterial blight resistance in Oryza rufipogon[J].Chin J Rice Sci, 2009, 23(6):653-656.
[34] Gao L F, Fang Z W, Zhou J F, Li L, Lu L, Li L L, Li T T, Chen L H, Zhang W X, Zhai W X, Peng H.Transcriptional insights into the pyramided resistance to rice bacterial blight[J].Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1):12358.doi:10.1038/s41598-018-29899-1.
[35] Hur Y J, Jeung J U, Kim S Y, Park H S, Cho J H, Lee J Y, Sohn Y B, Song Y C, Park D S, Lee C W, Sohn J G, Nam M H, Lee J H.Functional markers for bacterial blight resistance gene Xa3 in rice[J].Molecular Breeding, 2013, 31(4):981-985.doi:10.1007/s11032-012-9831-7.
[36] Sun X, Yang Z, Wang S, Zhang Q.Identification of a 47-kb DNA fragment containing Xa4, a locus for bacterial blight resistance in rice[J].Theor Appl Genet, 2003, 106(4):683-687.doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1117-8.
[37] Wang C L, Fan Y L, Zheng C K, Qin T F, Zhang X P, Zhao K J.High-resolution genetic mapping of rice bacterial blight resistance gene Xa23[J].Molecular Genetics and Genomics, 2014, 289(5):745-753.doi:10.1007/s00438-014-0848-y.
[38] Xiang Y, Cao Y L, Xu C G, Li X H, Wang S P.Xa3, conferring resistance for rice bacterial blight and encoding a receptor kinase-like protein, is the same as Xa26[J].Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 2006, 113(7):1347-1355.doi:10.1007/s00122-006-0388-x.