植物的生长发育常常受到干旱、盐度等非生物胁迫的影响[1]。转录因子调控下游基因的表达,是植物适应非生物胁迫的关键因子[2]。NF-Y转录因子可通过差异表达、选择性剪接、细胞氧化还原电位等相互作用,来调节其活性[3]。NF-YC含有组蛋白折叠基序(HFMs),并且通过 HFMs相互作用首尾相接组装形成异二聚体,再与NF-YA相互作用形成NF-Y转录因子。在DNA和NF-Y转录的结合中都发挥重要的作用[4]。NF-YC蛋白的保守域中含有1个与H2A蛋白结构类似的HFM结构域,在蛋白-蛋白和蛋白-DNA的互作中发挥重要作用。
NF-Y被称为血红素激活蛋白(HAP)或CCAAT结合因子(CBF),是所有真核生物中存在的三聚体转录因子[5]。在植物中,其生物学功能主要表现在开花进程、胚胎发育、叶绿体发育、应激反应等多方面的调控[6]。已证实,番茄NF-Y因子在调节果实成熟中起重要作用,不同的NF-Y因子在番茄果实成熟过程中的作用可能不同[7]。另外,有研究表明,NF-Y基因过表达会增强小麦的耐旱性[8]。1995年,Albani等[9]从拟南芥中分离出了第1个NF-YC家族成员AtNF-YC2。AtNF-YC2亚基的过表达加速了植物的开花过程并提高了植物的转录水平[10]。1998年Edwards等[11]首次鉴定出拟南芥中有13个NF-YC亚基。此外,E Z等[12]研究表明,NF-Y可能在单子叶植物中分化以调节胚乳发育。NF-YC亚基的过表达会增强水稻植株的抗盐性。Chen等[13]研究表明,NO、H2O2和ABA参与盐胁迫诱导的NF-YC基因的表达,当没有H2O2、NO分子或者ABA合成受阻时,NF-YC基因的表达终止。2006年,Ben-Naim等[14]研究表明,CCT存在于多数开花相关蛋白中,拟南芥中的NF-YC与CCT保守域互作,从而调控植株开花时间,番茄中的NF-YC也参与开花时间调节子的调节。AtNF-YC与AtNF-YB结合成二聚体,参与到光周期开花途径中[15]。云杉中的NF-YC亚基过表达时促进花粉管的发育[16-17]。此外,NF-YC参与小麦中有关光合作用相关基因表达的调控;在水稻中,NF-Y转录因子丧失功能后,叶绿体退化,降低了叶绿素含量[18]。
本研究从山西师范大学生命科学学院基因工程实验室前期的试验中获得1条马铃薯EST序列[19],使用电子克隆方法获得马铃薯NF-YC基因的全长cDNA,对其进行生物信息学分析。关于马铃薯青枯菌植病互作产生的NF-YC基因的研究鲜见报道。因此,分离和鉴定马铃薯与青枯菌互作诱导产生的NF-YC基因,通过相关生物信息学软件对其生物学功能和作用机制的预测和研究,旨在为后期的基因功能研究奠定理论基础。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验材料
供试植物材料选用的是青枯菌高抗基因型ED13,由中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所提供,青枯菌选用的是菌株PO41、生理小种3号(race3)、生化变种2号(biovar2)。取九叶期至十叶期试管苗,参照He等[20]伤根灌菌接种法接种青枯菌。
1.2 试验方法及电子克隆
山西师范大学生命科学学院基因工程实验室前期试验中得到1条马铃薯EST序列,长度为796 bp,通过NCBI BlastN同源比对检索,以马铃薯NFYC-1-Like(XM_015310514.1)为参考序列,运用电子克隆方法进行比对、拼接,直到序列能完整翻译,进而获得NF-YC全长序列。将其与马铃薯全基因组序列数据库中可用的序列进行比对[21]。
1.3 马铃薯NF-YC基因的生物信息学分析
马铃薯NF-YC基因的核酸及氨基酸组成、编码蛋白的理化性质、开放阅读框(Open reading frame)的翻译与寻找分别采用Bioedit、Prot-Param和ProtScale服务器及ORF dinder等在线工具完成。亲、疏水性、蛋白质的磷酸化位点和亚细胞定位、信号肽和跨膜区分析利用在线工具ProtScale、NetPhos 3.1、TargetP 1.1、SignalP 4.1、TMHMM 2.0软件完成。保守结构域通过在线工具NCBI中的CDD(Conserved Domain Database)预测。蛋白质二级和三级结构预测通过SOPMA和CPH Models 3.2 Server等在线工具完成,三级结构用 Accelrys DS Visualise软件显示结果。N-J(Neighbor-Joining)法系统发育树使用MEGA软件[22]完成(表1)。
表1 生物信息学分析所用的在线分析工具
Tab.1 The online tools used in bioinformatics analysis

分析项目Items分析工具Softwares开放阅读框分析ORF analysishttp://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html理化性质Physicochemical propertyhttp://web.expasy.org/protparam/亲、疏水性 Pro-hydrophobicityhttps://web.expasy.org/protscale/磷酸化位点 Phosphorylation sitehttp://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/亚细胞定位 Subcellular localizationhttp://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TargetP/信号肽 Signal peptidehttp://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/跨膜区 Transmembrane regionhttp://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/保守结构域 Conserved domainhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi二级结构 Secondary structurehttps://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html三级结构 Tertiary structurehttp://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/CPHmodels/
2 结果与分析
2.1 马铃薯NF-YC基因cDNA全长的获取
在本实验室前期得到1条马铃薯EST序列,以马铃薯NFYC-1-Like(XM_015310514.1)为参考序列,在NCBI BlastN中通过同源比对,同源性达到99%。通过电子克隆方法,经过比对、拼接,获得NF-YC全长cDNA序列,长度为1 132 bp。通过与马铃薯全基因组数据库比对,将其命名为StNF-Y。GenBank登录号(Accession No.) :MH 919392.1。
2.2 马铃薯StNF-Y理化性质预测
利用ExPasy在线工具中的ProtParam预测马铃薯StNF-Y蛋白的理化性质[23],结果如表2所示,该蛋白不稳定系数为63.54,大于40,说明该蛋白为不稳定蛋白;平均疏水性为-0.503,初步判断该基因为亲水性蛋白。由图1 可知,该蛋白在第100-140个氨基酸之间出现最大疏水值2.2,在第100-120个氨基酸之间出现最小亲水值-2.833,且峰值分布在0 以下比分布在0以上的多,再次证明该蛋白为亲水性蛋白。在马铃薯StNF-Y氨基酸组成中,含量最高的为Asn(97个,占42.17%),含量最低的为Cys(1个,占0.43%)。
表2 StNF-Y蛋白一级结构预测
Tab. 2 Predicting primary structure of StNF-Y protein

名称Name数值Numerical value氨基酸数目 Number of amino acid230相对分子质量/ku Molecular weight 25 289.53等电点 Isoelectric point5.37负电荷残基数 Asp+Glu Total number of negatively charged residues Asp+Glu 26分子式 FormulaC1112H1735N317O339S10不稳定系数Ⅱ The instability indexⅡ63.54脂肪系数 Molecular weight Aliphatic index73.13平均疏水性 Theoretical pI Grand average of hydropathicity-0.503正电荷残基数Arg+Lys Total number of positively charged residues Arg+Lys20
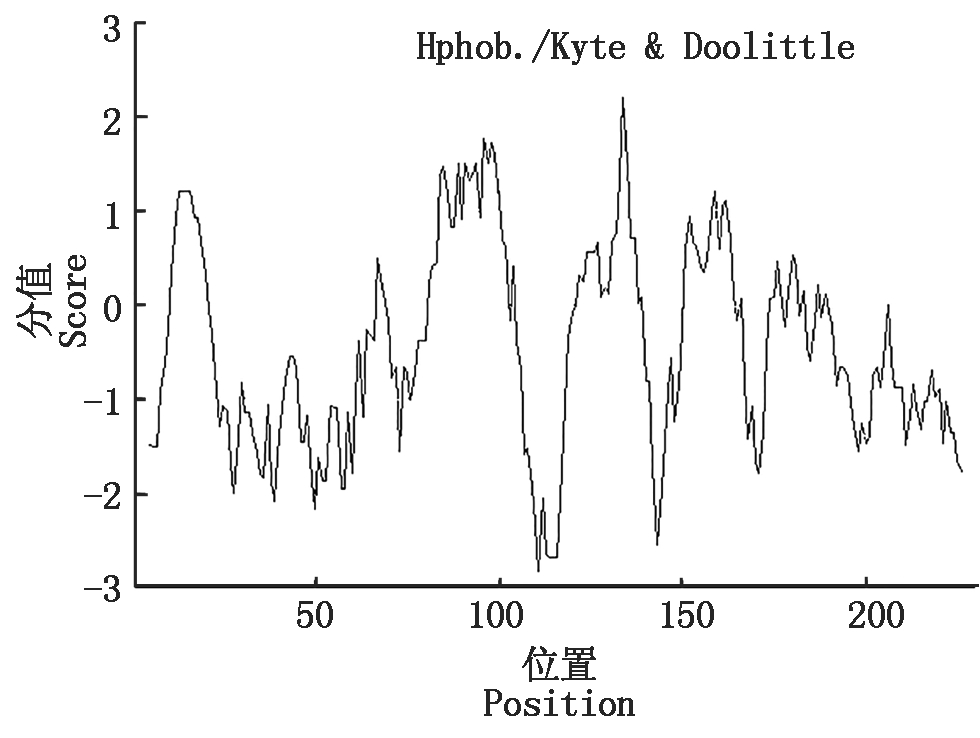
图1 StNF-Y蛋白亲水性/疏水性预测
Fig.1 Prediction of hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity of StNF-Y protein
2.3 马铃薯StNF-Y基因全长cDNA及氨基酸序列分析
利用BioEdit软件分析,马铃薯StNF-Y的全长cDNA长度为1 132 bp,终止密码子为TAA,编码230个氨基酸(图2)。
2.4 保守域预测及氨基酸同源序列比对分析
使用NCBI保守结构域数据库(Conserved Domain Database,CDD)[24],分析马铃薯StNF-Y蛋白的保守结构域结果显示(图3),该蛋白含有多个保守结构域,主要属于BUR6 superfamily家族,该结构域位于第44-141个氨基酸。提交NF-YC基因的氨基酸序列,BlastP搜索StNF-Y的同源氨基酸序列。DNAMAN软件用于马铃薯StNF-Y蛋白和其他物种NF-YC蛋白的氨基酸序列的多重比对[25],利用Blast P对StNF-Y基因编码的氨基酸同源性进行检

上排为cDNA 序列,下排为氨基酸序列;ATG 为起始密码子,*代表终止密码子;下划线标注的为BUR6 superfamily结构域。
The upper lines are cDNA sequences,the lower lines are amino acid sequences; ATG is the start codon,* is the stop codon; Underlined is the BUR6 superfamily domain.
图2 StNF-Y cDNA序列以及推导的氨基酸序列
Fig.2 StNF-Y gene cDNA sequence and deduced amino acid sequence
索,马铃薯StNF-Y基因编码的氨基酸与番茄Solanum pennellii (XP_015070179.1)、辣椒Capsicum chinense(PHU23636.1)、马铃薯Solanum lycopersicum (NP_001234244.1)、烟草Nicotiana attenuata (XP_019248263.1)中的NF-YC蛋白的氨基酸序列具有较高的相似性,分别为94%,93%,84%,81%。结果显示(图4),StNF-Y结构域的氨基酸序列高度保守。
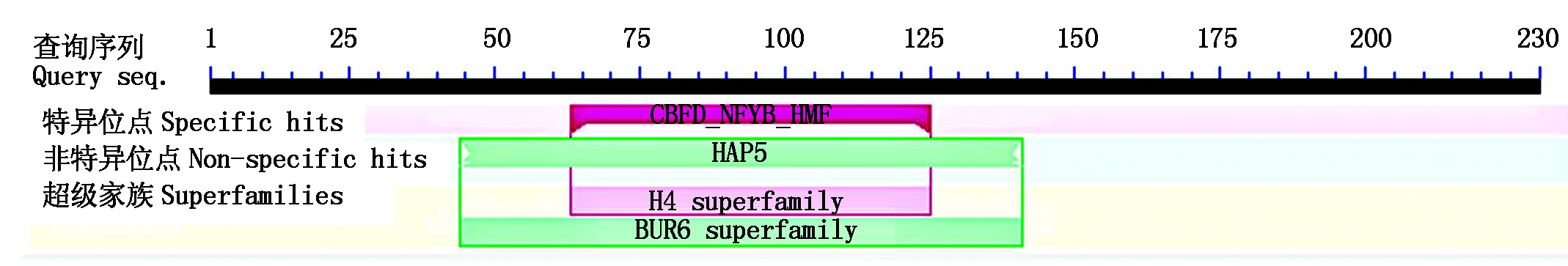
图3 StNF-Y蛋白的保守结构域分析
Fig.3 Conserved domain prediction of StNF-Y protein
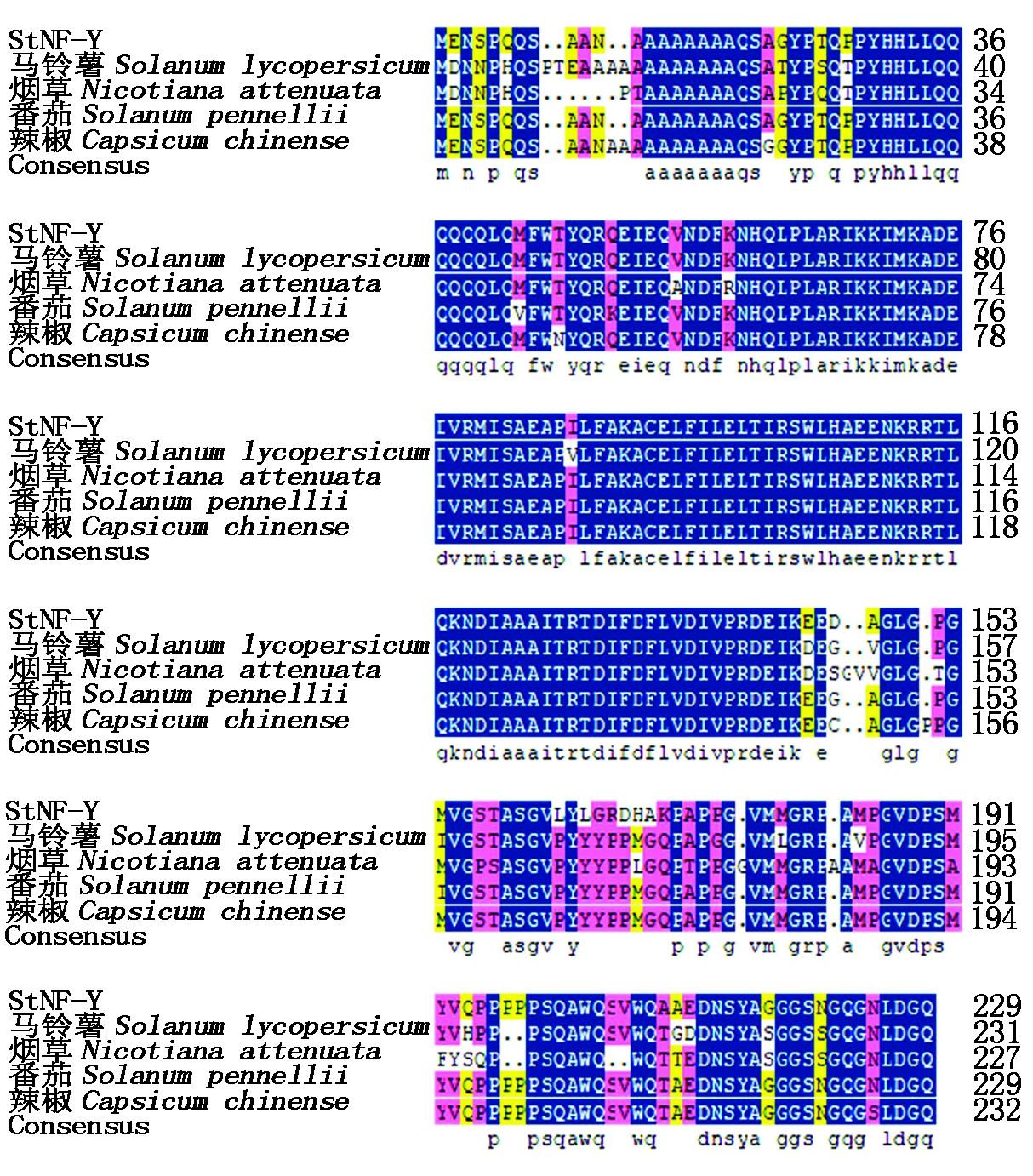
图4 马铃薯StNF-Y蛋白与其他植物 NF-YC蛋白的同源性比对
Fig.4 Homology comparison of potato StNF-Y protein with other plant NF-YC proteins
2.5 蛋白分子磷酸化位点分析
使用NetPhos 3.1 Server对该氨基酸进行磷酸化位点分析,结果显示,其共有13个磷酸化位点,Ser磷酸化位点6个,分别位于第82,157,190,200,205,214个氨基酸上;Thr磷酸化位点4个,分别在第26,101,115,158个氨基酸上;3个Tyr磷酸化位点位于第24,192,215个氨基酸上。据推测,StNF-Y蛋白的活性与功能可能通过这些位点的磷酸化反应来调节。
2.6 蛋白的信号肽、跨膜区、亚细胞定位分析
通过使用SignalP 4.1 Server预测蛋白质序列的信号肽,结果显示无信号肽段出现。使用TMHMM Server 2.0[26]预测蛋白质的跨膜区,结果显示该蛋白是一种膜外蛋白,没有跨膜区。使用TargetP 1.1 Server服务器[27]分析蛋白质亚细胞定位,结果显示StNF-Y转录因子主要位于胞质中的概率最大。
2.7 马铃薯StNF-Y转录因子二级结构分析
在Expasy的SOPMA服务器[28]中在线预测马铃薯StNF-Y转录因子的二级结构,结果如图5所示,105个氨基酸可形成α-螺旋,占氨基酸总数的45.65%;13个氨基酸可形成延伸链,占氨基酸总数的5.65%;104个氨基酸可形成无规则卷曲,占氨基酸总数的45.22%。8个氨基酸形成β-转角,占氨基酸总数的3.48%。
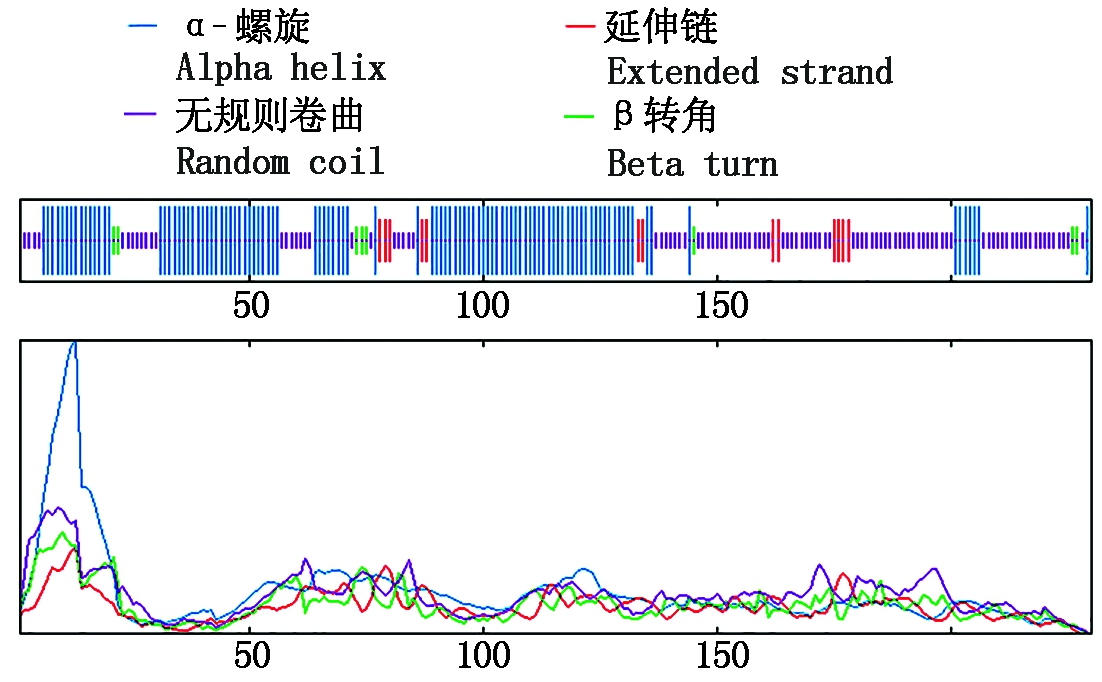
图5 StNF-Y蛋白的二级结构预测
Fig.5 Secondary structure prediction of StNF-Y protein
2.8 马铃薯StNF-Y转录因子三级结构分析
利用CPHmodels 3.2 Server预测StNF-Y的三级结构发现,目前PDB数据库中尚未有全长氨基酸序列匹配的模板,只能构建其保守序列的3D模型(图6),完整的StNF-Y三级结构由α-螺旋、β-转角和无规则卷曲形成,在C端是α-螺旋,在N端有一个较短的伸展肽段(EP)。
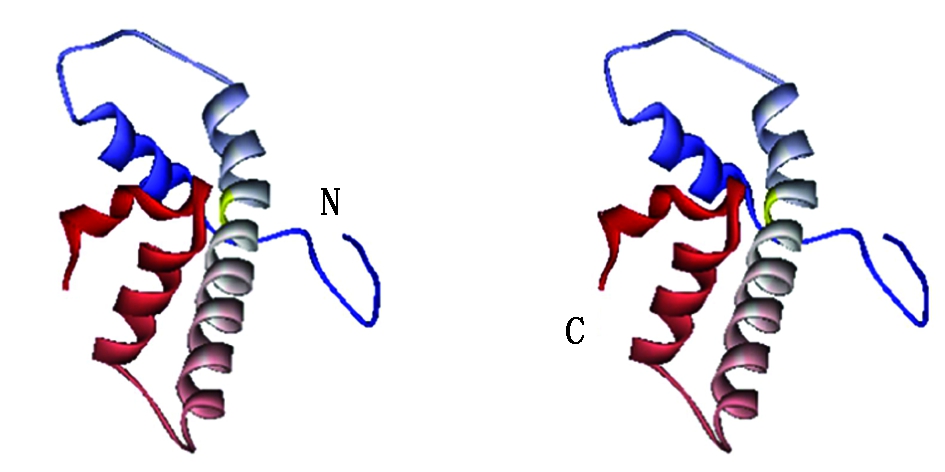
图6 StNF-Y保守序列(48-140)的三级结构
Fig.6 3D structure of the conserved domain (48-140)of the predicted amino acids
2.9 系统进化树构建
通过NCBI上的BlastP获得氨基酸序列的同源序列,使用MEGA 4.0软件,采用N-J法构建系统进化树(时间截止到2018年11月15日),结果如图7所示,系统发育树分析表明,马铃薯StNF-Y转录因子编码的氨基酸序列与番茄亲缘关系最近,与辣椒亲缘关系次之,与棉花亲缘关系最远。
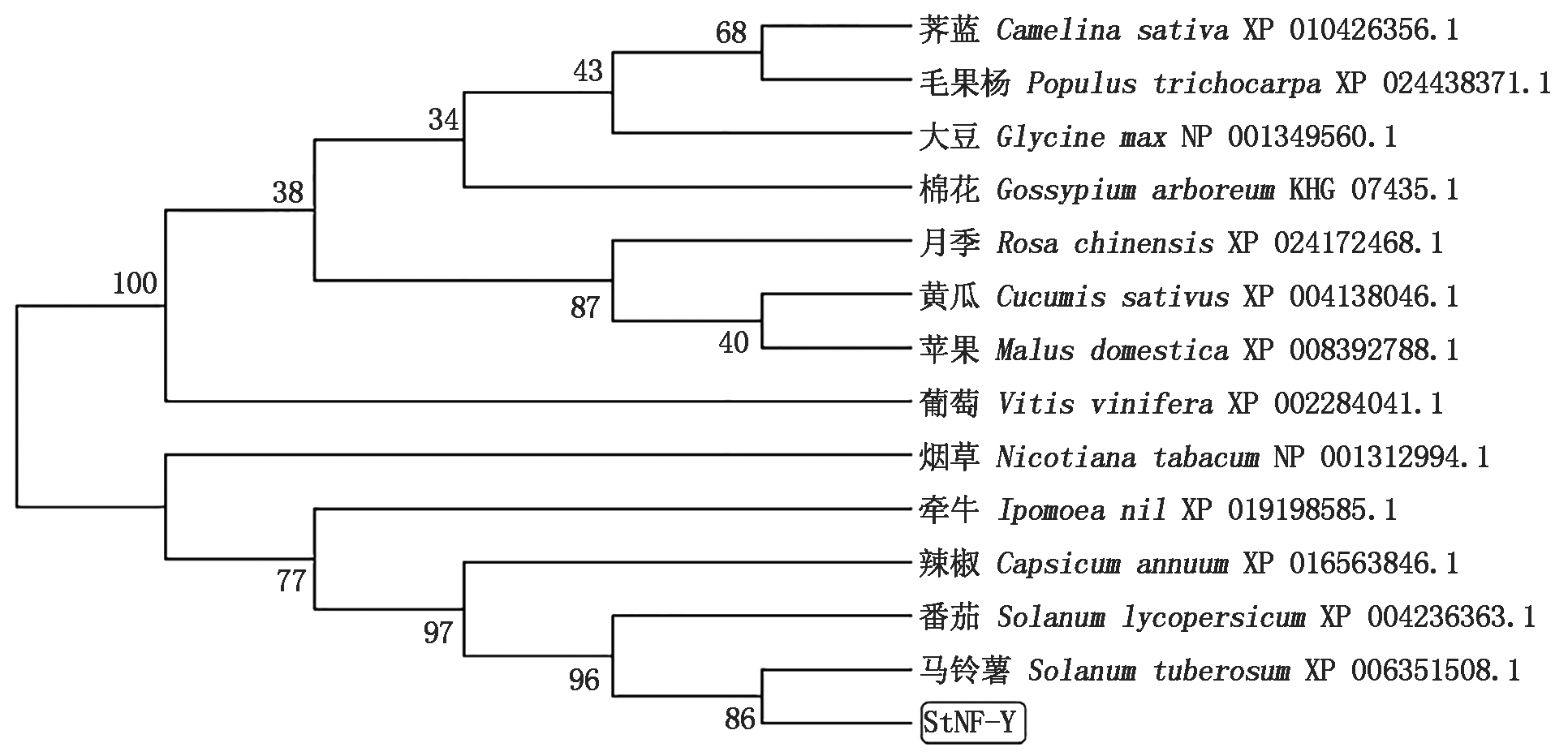
图7 基于StNF-Y蛋白氨基酸序列的系统进化树
Fig.7 Phylogenetic tree based on amino acid sequence of StNF-Y protein
3 结论与讨论
本研究在山西师范大学生命科学学院基因工程实验室前期工作中利用电子克隆技术拼接,获得了马铃薯StNF-Y基因的全长序列,并通过生物信息学方法对该基因的结构特征、功能属性和表达性质等方面进行了系统分析,其核苷酸和氨基酸序列都高度保守,核苷酸序列在茄科植物中保守性高达95%~100%,表明StNF-Y在进化上很保守,这可能与其重要功能有关。马铃薯StNF-Y转录因子全长1 132 bp,编码230个氨基酸,磷酸化位点有13个,StNF-Y是亲水性氨基酸,无信号肽。通过更进一步的预测发现,StNF-Y蛋白含有BUR6保守功能结构域,属于BUR6 superfamily家族,并且对蛋白质的结构和功能都至关重要。该蛋白质的二级结构有4种结构形式:α-螺旋、延伸链、β-转角和无规则卷曲,这为实现其功能提供了结构基础。通过氨基酸多序列比对及构建系统进化树,发现该蛋白与马铃薯、番茄、辣椒、烟草、牵牛花中的核转录因子亲缘关系较近,说明StNF-Y蛋白在生物进化过程中高度保守。
近年来,已经分离和鉴定了越来越多的植物NF-Y基因,其中包括拟南芥[29]、大豆[30]、甘蓝型油菜[31]、葡萄[32]、柑橘[33]等。目前,关于拟南芥中的NF-Y基因研究的较多,其次是番茄、小麦、水稻等。NF-Y由NF-YA、NF-YB和NF-YC亚类TF组成,已被证明参与植物许多生长发育过程的调节和对各种环境胁迫刺激的反应[34]。最新的研究发现,NF-YC转录因子在糖异生过程和植物胚乳发育中起重要作用。Zhang等[35]研究结果表明,NF-Y基因通过上调糖异生基因Pck1和G6pc来控制葡萄糖代谢的生理功能。此外,NF-Y基因也参与植物对非生物胁迫的反应[36]。拟南芥NF-YC3/4/9与ABI 5启动子的CCAAT元件结合,激活其在种子萌发过程中的表达及整合GA和ABA信号转导途径[37]。已证实,NF-Ys参与了植物响应干旱反应的ABA信号传递[38]。前几年,有研究表明,NF-Y转录因子能引起植物对干旱胁迫的反应,主要是通过影响叶绿素含量、光合作用、开花进程等对植物生理过程进行调控。这与本试验所用的原始序列来源相一致,初步推测,其可能同以往发现的其他植物的NF-YC转录因子一样参与相关防御反应。
进一步确定马铃薯StNF-Y蛋白在植株中实际的功能表达,还需要具体的分子生物学试验来验证。有必要针对该基因表达的精细细胞定位和信号调控进行进一步的深入研究,这对于解释早期马铃薯与青枯病的植病互作机制、进行马铃薯育种乃至为今后青枯病的控制提供新的目标具有重要的理论意义。
[1] Wu X L,Shi H F,Guo Z F. Overexpression of a NF-YC gene results in enhanced drought and salt tolerance in transgenic seashore paspalum [J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2018,9:1355. doi:10.3389/fpls.2018.01355.
[2] Singh K B,Foley R ![]()
 nchez L. Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2002,5(5):430-436. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00289-3.
nchez L. Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses [J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2002,5(5):430-436. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00289-3.
[3] Matuoka K,Chen K Y. Nuclear factor Y(NF-Y)and cellular senescence [J]. Experimental Cell Research,1999,253(2):365-371. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4605.
[4] Ly L L,Yoshida H,Yamaguchi M. Nuclear transcription factor Y and its roles in cellular processes related to human disease [J]. American Journal of Cancer Research,2013,3(4):339-346.
[5] Quan S W,Niu J X,Zhou L,Xu H,Ma L,Qin Y. Identification and characterization of NF-Y gene family in walnut(Juglans regia L.)[J]. BMC Plant Biology,2018,18(1):255. doi:10.1186/s12870-018-1459-2.
[6] 宋秋明,李大勇,张慧娟,宋凤鸣. 植物NF-Y转录因子的生物学功能及其研究进展 [J]. 植物生理学报,2015(5):623-632. doi:10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2015.0186.
Song Q M,Li D Y,Zhang H J,Song F M. Biological function and research progress of plant NF-Y transcription factors [J]. Plant Physiology Journal,2015(5):623-632.
[7] 李珊,许蕙金兰,朱本忠,罗云波. 番茄NF-Y转录因子生物信息学分析及其与RIN共同调控果实成熟研究 [J]. 食品科学,2017,38(22):1-7. doi:10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201722001.
Li S,Xu H J L,Zhu B Z,Luo Y B. Bioinformatics analysis of tomato NF-Y transcription factor and its co-regulation of fruit ripening with RIN [J]. Food Science,2017,38(22):1-7.
[8] Stephenson T J,McIntyre C L,Collet C,Xue G P. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y family of transcription factors in Triticum aestivum [J]. Plant Molecular Biology,2007,65(1/2):77-92. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9200-9.
[9] Albani D,Robert L S. Cloning and characterization of a Brassica napus gene encoding a homologue of the B subunit of a heteromeric CCAAT-binding factor [J]. Gene,1995,167(1/2):209-213. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00680-X.
[10] Hackenberg D,Keetman U,Grimm B. Homologous NF-YC2 subunit from Arabidopsis and tobacco is activated by photooxidative stress and induces flowering [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2012,13(3):3458-3477. doi:10.3390/ijms13033458.
[11] Edwards D,Murray J A,Smith A G. Multiple genes encoding the conserved CCAAT-box transcription factor complex are expressed in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology,1998,117(3):1015-1022. doi:10.1104/pp.117.3.1015.
[12] E Z G,Li T T,Zhang H Y,Liu Z H,Deng H,Sharma S,Wei X F,Wang L,Niu B X,Chen C. A group of nuclear factor Y transcription factors are sub-functionalized during endosperm development in monocots [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2018,69(10):2495-2510. doi:10.1093/jxb/ery087.
[13] Chen M,Zhao Y J,Zhuo C L,Lu S Y,Guo Z F. Overexpression of a NF-YC transcription factor from bermudagrass confers tolerance to drought and salinity in transgenic rice [J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal,2015,13(4):482-491. doi:10.1111/pbi.12270.
[14] Ben-Naim O,Eshed R,Parnis A,Teper-Bamnolker P,Shalit A,Coupland G,Samach A,Lifschitz E. The CCAAT binding factor can mediate interactions between CONSTANS-like proteins and DNA [J]. Plant Journal,2006,46(3):462-476. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02706.x.
[15] Tiwari S B,Shen Y,Chang H C,Hou Y L,Harris A,Ma S F,McPartland M,Hymus G J,Adam L,Marion C,Belachew A,Repetti P P,Reuber T L,Ratcliffe O J. The flowering time regulator CONSTANS is recruited to the FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter via a unique cis-element [J]. New Phytologist,2010,187(1):57-66. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03251.x.
[16] Yu Y L,Li Y Z,Huang G X,Meng Z D,Zhang D,Wei J,Yan K,Zheng C C,Zhang L G. PwHAP5,a CCAAT-binding transcription factor,interacts with PwFKBP12 and plays a role in pollen tube growth orientation in Picea wilsonii [J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2011,62(14):4805-4817. doi:10.1093/jxb/err120.
[17] Qu B Y,He X,Wang J,Zhao Y Y,Teng W,Shao A,Zhao X Q,Ma W Y,Wang J Y,Li B,Li Z S,Tong Y P. A wheat CCAAT-box binding transcription factor increases grain yield of wheat with less fertilizer input [J]. Plant Physiology,2015,167(2):411-423. doi:10.1104/pp.114.246959.
[18] Warpeha K M,Upadhyay S,Yeh J,Hawkins A S,Lapik Y R,Anderson M B,Kaufman L S. The GCR1,GPA1,PRN1,NF-Y signal chain mediates both blue light and abscisic acid responses in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Physiology,2007,143(4):1590-1600. doi:10.1104/pp.106.089904.
[19] 郜刚,任彩虹,金黎平,谢开云,屈冬玉. 马铃薯非特异性脂质转移蛋白基因StLTPa1的克隆和表达 [J]. 作物学报,2008,34(9):1510-1517. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1006.2008.01510.
Gao G,Ren C H,Jin L P,Xie K Y,Qu D Y. Cloning,expression and characterization of a non-specific lipid transfer protein gene StLTPa1 from potato [J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2008,34(9):1510-1517.
[20] He L Y,Sequeira L,Kelman A. Characteristics of strains of Pseudomonas solanacearum from China [J]. Plant Disease,1983,67(12):1357-1361. doi:10.1094/pd-67-1357.
[21] Lingle S E,Dyer J M. Cloning and expression of sucrose synthase-1 cDNA from sugarcane [J]. Journal of Plant Physiology,2001,158(1):129-131. doi:10.1078/0176-1617-00266.
[22] Tamura K,Dudley J,Nei M,Kumar S. MEGA4:molecular evolutionary genetics analysis(MEGA)software version 4.0 [J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution,2007,24(8):1596-1599.doi:10.1093/molbev/msm092.
[23] 苏丽艳.番茄SlETR6基因的克隆及非生物胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 华北农学报,2019,34(1):19-25. doi:10.7668/hbnxb.201751117.
Su L Y. Cloning and expression analysis of SlETR6 gene in tomato under abiotic stress [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2019,34(1):19-25.
[24] 梁倩,李璐,安茜,周雅莉,王计平.紫苏脂肪酸去饱和酶基因PfFAD2的生物信息学及表达特性分析 [J]. 山西农业科学,2018,46(3):316-319. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2018.03.02.
Liang Q,Li L,An Q,Zhou Y L,Wang J P. Bioinformatics and expression analysis of perilla fatty acid desaturase gene PfFAD2 [J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(3):316-319.
[25] 王萍,于月华,白玉翠,郭坤鹏,康嘉楠,倪志勇. 大豆GmNAC23基因的克隆及特征分析[J]. 华北农学报,2019,34(1):46-53. doi:10.7668/hbnxb.201751084.
Wang P,Yu Y H,Bai Y C,Guo K P,Kang J N,Ni Z Y. Cloning and characterization of soybean GmNAC23 gene [J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2019,34(1):46-53.
[26] 卫永乐,温志芳,刘芳,张杰伟,黄武刚,兰彦平,程丽莉,曹庆昌,胡广隆. 榛属ycf1基因生物信息学分析 [J]. 山西农业科学,2018,46(8):1244-1247,1333. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2018.08.04.
Wei Y L,Wen Z F,Liu F,Zhang J W,Huang W G,Lan Y P,Cheng L L,Cao Q C,Hu G L. Bioinformatics analysis of ycf1 gene in corylus [J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(8):1244-1247,1333.
[27] 张宁,温银元,王金荣,贺美林,兰敏.苦参8-异戊烯基转移酶基因蛋白家族生物信息学分析 [J]. 山西农业科学,2018,46(5):692-695,772. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2018.05.06.
Zhang N,Wen Y Y,Wang J R,He M L,Lan M. Bioinformatics analysis of sophora flavescens 8-isopentenyltransferase gene protein family [J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(5):692-695,772.
[28] 高嵩,吕庆雪,何欢,张建新,张志军,宋广树,刘伟. 玉米中绒毡层发育调控基因ZmUdt1克隆的生物信息学分析[J]. 华北农学报,2018,33(1):52-59. doi :10.7668/hbnxb.2018.01.009.
Gao S,Lü Q X,He H,Zhang J X,Zhang Z J,Song G S,Liu W. Bioinformatics analysis of ZmUdt1 cloning of tapetum development regulation gene in maize(Zea mays L.)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2018,33(1):52-59.
[29] Siefers N,Dang K K,Kumimoto R W,Bynum W E,Tayrose G,Holt B F. Tissue-specific expression patterns of Arabidopsis thaliana NF-Y transcription factors suggest potential for extensive combinatorial complexity [J]. Plant Physiology,2009,149(2):625-641. doi:10.1104/pp.108.130591.
[30] Quach T N,Nguyen H T,Valliyodan B,Joshi T,Xu D,Nguyen H T. Genome-wide expression analysis of soybean NF-Y genes reveals potential function in development and drought response [J]. Molecular Genetics and Genomics,2015,290(3):1095-1115. doi:10.1007/s00438-014-0978-2.
[31] Liang M X,Yin X Z,Lin Z Y,Zheng Q S,Liu G H,Zhao G M. Identification and characterization of NF-Y transcription factor families in canola(Brassica napus L.)[J]. Planta,2014,239(1):107-126. doi:10. 1 007/s00425-013-1964-3.
[32] Ren C,Zhang Z,Wang Y,Li S H,Liang Z C. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the NF-Y gene family in grape(Vitis vinifera L.)[J]. BMC Genomics,2016,17(1):605.doi:10.11 86/s 12864-0 16-2989-3.
[33] Pereira S L,Martins C P,Sousa A O,Camillo L R,Araújo C P,Alcantara G M,Camargo D S,Cidade L C,Almeida A F,Costa M G. Genome-wide characterization and expression analysis of citrus nuclear factor-Y(NF-Y)transcription factors identified a novel NF-YA gene involved in drought-stress response and tolerance [J]. PloS One,2018,13(6):e0199187. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0199187.
[34] Chu H D,Nguyen K H,Watanabe Y,Le D T,Pham T L,Mochida K,Tran L S. Identification,structural characterization and gene expression analysis of members of the nuclear factor-Y family in chickpea(Cicer arietinum L.)under dehydration and abscisic acid treatments [J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(11):3290. doi:10.3390/ijms19113290.
[35] Zhang Y J,Guan Q Y,Liu Y,Zhang Y W,Chen Y L,Chen J L,Liu Y L,Su Z G. Regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis by nuclear factor Y transcription factor in mice [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2018,293(20):7894-7904. doi:10.1074/jbc.RA117.000508.
[36] Yan D H,Xia X L,Yin W L. NF-YB family genes identified in a poplar genome-wide analysis and expressed in populus euphratica are responsive to drought stress [J]. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2013,31(2):363-370. doi:10.1007/s11105-012-0508-5.
[37] Liu X,Hu P W,Huang M K,Tang Y,Li Y G,Li L,Hou X L. The NF-YC-RGL2 module integrates GA and ABA signalling to regulate seed germination in Arabidopsis [J]. Nature Communications,2016,7:12768. doi:10.1038/ncomms12768.
[38] Bi C,Ma Y,Wang X F,Zhang D P. Overexpression of the transcription factor NF-YC9 confers abscisic acid hypersensitivity in Arabidopsis [J]. Plant Molecular Biology,2017,95(4/5):425-439. doi:10.1007/s 11 103-017-0661-1.