我国是世界农业大国,玉米作为农业中最为重要的农作物之一,在国民经济建设中有着举足轻重的作用[1],吉林省西部白城地区是玉米种植主产区[2],但是该地区多为盐渍化土壤,保水、保肥能力差,全年降雨量少且时间分布不均衡,加之当地时常高温,干旱经常发生,干旱缺水严重制约着玉米的増产[3-4]。土壤保水剂可以有效提升土壤保水保肥能力,缓解旱情。保水剂又称高吸水性树脂(Superabsorbent Polymers, SAPs),是一种具有三维网络结构、且能够吸收自身重量几百倍甚至几千倍水的高分子材料,具有良好的保水性能,可以反复吸水释水[5-7],目前广泛应用于土地荒漠化防治、农林抗旱保水等方面[8-10]。刘纪霜等[11]研究发现,土壤含水量和土壤孔隙度会因为施用保水剂而提高,进而改善土壤理化性状。李中阳等[12]研究表明,施用保水剂可显著提高小麦水分利用效率。迄今关于保水剂的研究较多,但其土壤多为壤土和黏土,对于半干旱地区盐渍化土壤施用保水剂研究较少,针对以上问题,本研究通过在白城地区盐渍化土壤设计田间试验,研究施用保水剂对玉米不同生育期土壤含水量、地上地下干物质重、光合性状、产量以及籽粒品质的影响。为半干旱地区盐渍化土壤抗旱增产,合理施用保水剂提供理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 试验地概况
试验地点吉林西部通榆县瞻榆镇向阳村(44°13′N,122°02′E),地处松辽平原西部,地势平坦,属北温带大陆性季风气候,平均海拔160 m,年均匀气温6.6 ℃,极端最低气温-25.9 ℃,极端最高气温40.5 ℃,无霜期162 d,年降雨量332.4 mm。土壤类型为盐渍化土壤,肥力较低。其表层(0~20)理化性质为: pH值8.5、有机质17.06 g/kg、碱解氮46.86 mg/kg、速效磷11.64 mg/kg、速效钾85.55 mg/kg。
1.2 试验设计
试验设置不施用保水剂(CK)、施用保水剂(SAP)2个处理,每个处理3次重复,每个小区垄长50 m共6垄、垄宽65 cm、株距15 cm、小区面积195 m2,试验采用随机区组试验排列。保水剂用量22.5~30.0 kg/hm2,与肥料一起施用到地里。施肥量根据当地的测土配方施肥的结果而定,具体无机肥料用量为N 231.2 kg/hm2、P2O5 85.9 kg/hm2、K2O 110 kg/hm2,秸秆用量为3 000 kg/hm2,磷钾肥秸秆做基肥一次性施用,氮肥的2/3做追肥。2018年5月3日播种,10月4日收获。2018年降雨量为356.6 mm,供试玉米为 领科128,保水剂为自制的保水剂。
1.3 测定项目与数据分析
采用质量烘干法测定含水率和玉米干物质重,用SPAD-502叶绿素仪测定玉米活体叶片叶绿素含量,使用LI-6400XT光合系统分析仪测定穗位叶光合速率、蒸腾速率和气孔导度,用1241型近红外谷物品质分析仪(丹麦FOOS公司产)测定籽粒淀粉、脂肪和蛋白质含量(干基%)。采用Excel 2016、SPSS 19.0等统计软件进行分析处理,结果用平均值表示,P<0.05为差异显著。
2 结果与分析
2.1 保水剂对玉米出苗率的影响
由表1可知,施用保水剂(SAP)处理的玉米出苗速度和出苗率均高于不施用保水剂(CK)。其中出苗速度比CK快2 d,而出苗率比CK提高了4.6百分点。
表1 保水剂对玉米种子出苗的影响
Tab.1 Effect of water retaining agent on
emergence of corn seed
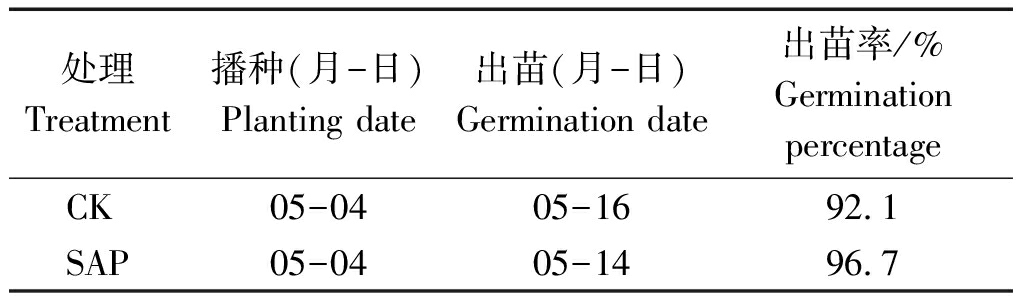
处理Treatment播种(月-日)Planting date出苗(月-日)Germination date出苗率/%GerminationpercentageCK05-0405-1692.1SAP05-0405-1496.7
2.2 保水剂对土壤含水量的影响
由表2可知,在玉米整个生育期,抽雄期和乳熟期土壤含水率低于苗期和完熟期。与不施用保水剂(CK)相比,施用保水剂(SAP)处理能显著(P<0.05)提高玉米不同生育期不同土层土壤含水量,其中抽雄期提高效果最为明显,不同土层增幅为9.67% ~16.06%。表层土壤(0~20)含水量由于受外界环境影响,水分蒸发损失较大,增幅较低。
表2 保水剂对玉米不同生育期含水量的影响
Tab.2 Effect of water retaining agent on moisture content of corn in different growth stages cm
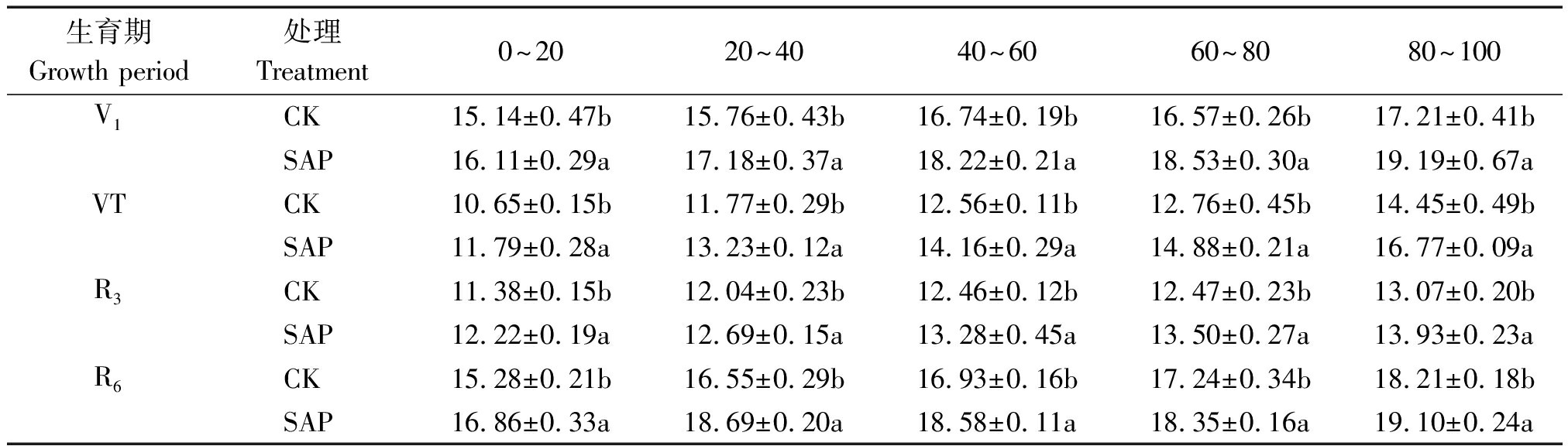
生育期Growth period处理Treatment0~2020~4040~6060~8080~100V1CK15.14±0.47b15.76±0.43b16.74±0.19b16.57±0.26b17.21±0.41bSAP16.11±0.29a17.18±0.37a18.22±0.21a18.53±0.30a19.19±0.67aVTCK10.65±0.15b11.77±0.29b12.56±0.11b12.76±0.45b14.45±0.49bSAP11.79±0.28a13.23±0.12a14.16±0.29a14.88±0.21a16.77±0.09aR3CK11.38±0.15b12.04±0.23b12.46±0.12b12.47±0.23b13.07±0.20bSAP12.22±0.19a12.69±0.15a13.28±0.45a13.50±0.27a13.93±0.23aR6CK15.28±0.21b16.55±0.29b16.93±0.16b17.24±0.34b18.21±0.18bSAP16.86±0.33a18.69±0.20a18.58±0.11a18.35±0.16a19.10±0.24a
注:V1.苗期;VT.抽雄期;R3.乳熟期;R6.完熟;表中数据后不同小写字母表示相同土层相同生育期不同处理差异达显著水平P<0.05。表3-6同。
Note: V1.Seedling stage; VT. Tasseling stage; R3.Milk-ripe stage;R6.Physiological maturity; Different lowercase letters a and b after the data in the table indicate that there are significant differences between different treatments in the same soil layer during the same growth period(P<0.05).The same as Tab.3-6.
2.3 保水剂对玉米不同生育期光合性状的影响
表3结果表明,施用保水剂(SAP)处理能显著(P<0.05)提高抽雄期和灌浆期玉米叶绿素含量、净光合速率、气孔导度和蒸腾速率。其中抽雄期SAP处理玉米叶绿素含量、净光合速率、气孔导度和蒸腾速率与不施用保水剂(CK)相比分别提高了13.68,19.53,22.56,12.94百分点,灌浆期SAP处理玉米叶绿素含量、净光合速率、气孔导度和蒸腾速率与CK相比分别提高了11.09,33.31,15.27,23.65百分点。
表3 保水剂对玉米光合性状的影响
Tab.3 Effect of water retaining agent on photosynthetic characteristics of maize
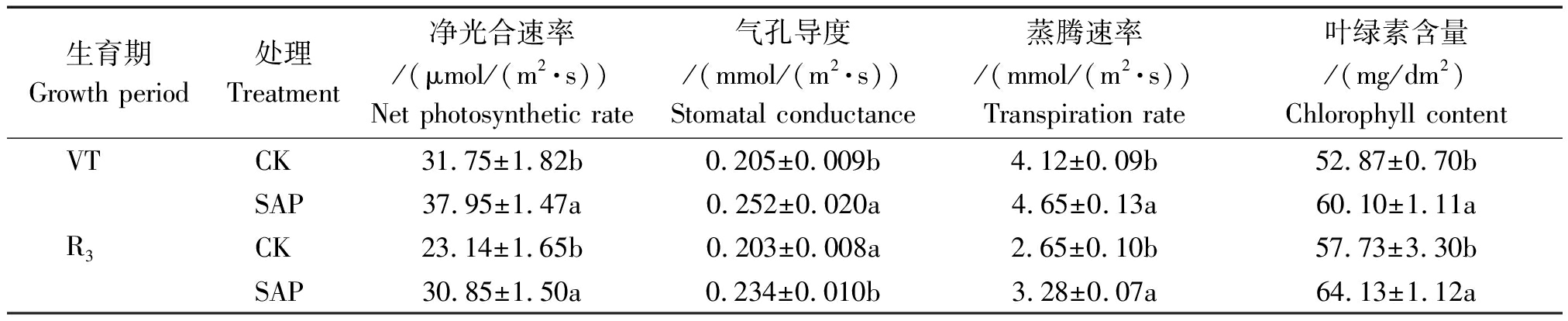
生育期Growth period处理Treatment净光合速率/(μmol/(m2·s))Net photosynthetic rate气孔导度/(mmol/(m2·s))Stomatal conductance蒸腾速率/(mmol/(m2·s))Transpiration rate叶绿素含量/(mg/dm2)Chlorophyll contentVTCK31.75±1.82b0.205±0.009b4.12±0.09b52.87±0.70bSAP37.95±1.47a0.252±0.020a4.65±0.13a60.10±1.11aR3CK23.14±1.65b0.203±0.008a2.65±0.10b57.73±3.30bSAP30.85±1.50a0.234±0.010b3.28±0.07a64.13±1.12a
2.4 保水剂对玉米干物质质量的影响
由表4可知,施用保水剂(SAP)处理各生育期地上干物质质量和地下干物质质量均显著(P<0.05)高于不施用保水剂(CK)。不同生育期SAP处理对地上干物质质量和地下干物质质量的影响有所不同,与CK相比,不同生育期SAP处理对地上干物质质量的增幅为V6>V12>VT>R3>R6,其中拔节期(V6)增幅达到了32.52%。地下干物质质量的增幅为V6>VT>V12>R3>R6,其中拔节期(V6)和抽雄期(VT)增幅为30.14%,29.46%。
表4 保水剂对玉米干物质质量的影响
Tab.4 Effect of water retaining agent on the dry weight of corn g
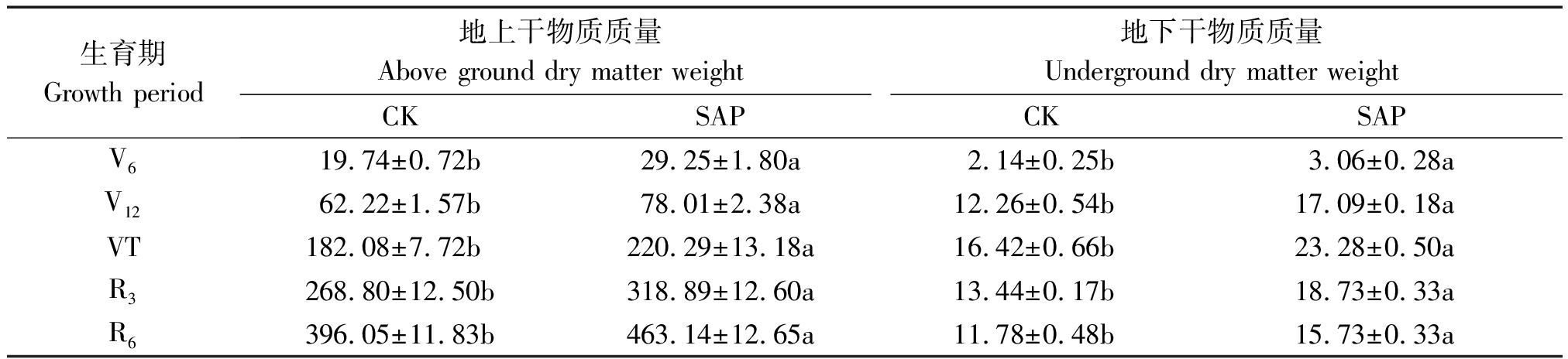
生育期Growth period地上干物质质量Above ground dry matter weight地下干物质质量Underground dry matter weightCKSAPCKSAPV619.74±0.72b29.25±1.80a2.14±0.25b3.06±0.28aV1262.22±1.57b78.01±2.38a12.26±0.54b17.09±0.18aVT182.08±7.72b220.29±13.18a16.42±0.66b23.28±0.50aR3268.80±12.50b318.89±12.60a13.44±0.17b18.73±0.33aR6396.05±11.83b463.14±12.65a11.78±0.48b15.73±0.33a
注:V6.拔节期;V12.大喇叭口期。
Note: V6.Jointing stage; V12. Trumpet stage.
2.5 保水剂对玉米产量性状的影响
从表5可以看出,与不施用保水剂(CK)相比,施用保水剂(SAP)处理能显著(P<0.05)提高玉米株高、单穗质量、千粒质量和产量。其中株高增加了29.72 cm,单穗质量增加了16.04 g,千粒质量增加了7.52 g,产量提高了8.14百分点。穗长、轴粗和行粒数与CK相比虽增加不显著,但均有不同程度的提高。
表5 保水剂对玉米产量及其构成因子的影响
Tab.5 Effect of water retaining agent on corn yield and its constituent factors
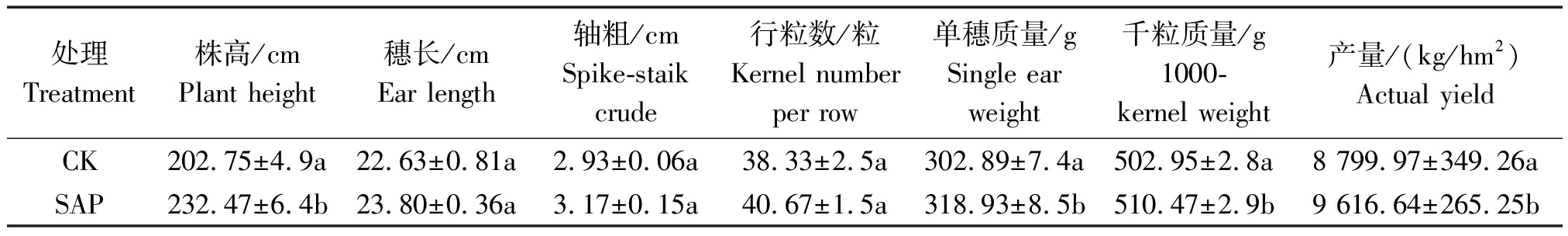
处理Treatment株高/cmPlant height穗长/cmEar length轴粗/cmSpike-staik crude行粒数/粒Kernel numberper row单穗质量/gSingle earweight千粒质量/g1000-kernel weight产量/(kg/hm2)Actual yieldCK202.75±4.9a22.63±0.81a2.93±0.06a38.33±2.5a302.89±7.4a502.95±2.8a8 799.97±349.26aSAP232.47±6.4b23.80±0.36a3.17±0.15a40.67±1.5a318.93±8.5b510.47±2.9b9 616.64±265.25b
2.6 保水剂对玉米籽粒品质的影响
表6结果表明,施用保水剂(SAP)能显著(P<0.05)提高玉米籽粒蛋白、脂肪和淀粉干基含量。其中与不施用保水剂(CK)相比,蛋白、脂肪和淀粉干基分别提高了10.65,3.97,0.99百分点。施用保水剂对玉米籽粒蛋白干基影响较大,而对脂肪和淀粉干基影响较小。
表6 保水剂对玉米籽粒品质的影响
Tab.6 Effect of water retaining agent
on corn grain quality %
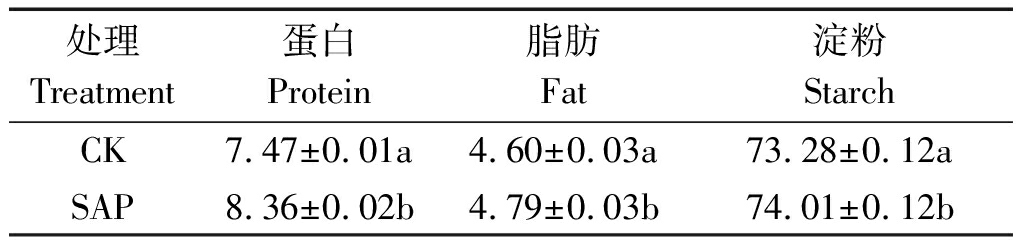
处理Treatment蛋白Protein脂肪Fat淀粉StarchCK7.47±0.01a4.60±0.03a73.28±0.12aSAP8.36±0.02b4.79±0.03b74.01±0.12b
3 结论与讨论
本研究结果表明,利用保水剂的保水和吸盐性能,在播种期墒情不好的情况下,施用保水剂能提高半干旱地区盐渍化土壤玉米出苗时间和出苗率。这与许紫峻等[13]研究结果一致。由于保水剂能在雨水或灌溉水量较少的时候迅速吸收水分,在土壤墒情不好时缓慢释放水分以提供作物吸收利用,所以当土壤水分亏缺时,作物生长发育不会受到限制[14]。在本试验中,施用保水剂能显著提高玉米不同生育期不同土层含水量,其中抽雄期提高效果最为显著,不同土层增幅为9.67%~16.06%。与对照组不施用保水剂(CK)相比,施用保水剂(SAP)能显著提高地上和地下干物质质量,尤其是地下干物质质量,这表明保水剂对根系的促进作用较大,进而促进玉米生长发育。
叶绿素含量的消长规律是反映叶片生理活性变化的重要指标之一,同时也反映叶片光合作用的强弱[15-17],而光合产物的积累与产量密切相关。本研究结果表明,SAP处理能显著提高抽雄期和灌浆期玉米叶绿素含量、净光合速率、气孔导度和蒸腾速率。这可能是由于施用保水剂的作物能够获得比较充足的水分,可以减少干旱胁迫所产生的自由基对叶绿素及光合电子传递系统的伤害,进而提高了叶片的光合速率[18-19]。玉米籽粒品质是衡量玉米营养和经济价值的重要指标之一[20],与对照组CK相比,SAP能显著提高玉米籽粒蛋白、脂肪和淀粉干基含量。其中对玉米籽粒蛋白干基影响较大,而对脂肪和淀粉干基影响较小。本研究产量分析结果表明,SAP处理能显著提高玉米株高、单穗质量、千粒质量和产量。这与张丽华等[21]研究结果一致。
综上所述,通过在半干旱地区盐渍化土壤施加保水剂,能提高玉米出苗率,改善水分亏缺期土壤含水量、提高地上地下部分干物质质量、光合性状,促进玉米生长发育,改善产量构成因素,进而提高玉米产量和籽粒品质。
[1] 丁仕英, 汪经壮. 玉米种植现状与新技术应用的效率[J]. 吉林农业, 2016(5):64-64. doi:10.14025/j.cnki.jlny.2016.05.013.
Ding S Y, Wang J Z. Current situation of maize cultivation and efficiency of new technology application[J]. Agriculture of Jilin, 2016 (5): 64-64.
[2] 王寅, 张馨月, 高强, 李翠兰, 焉莉, 冯国忠. 吉林省农田耕层土壤pH的时空变化特征[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(2):387-391. doi:10.19336/j.cnki.trtb.2017.02.19.
Wang Y, Zhang X Y, Gao Q, Li C L, Yan L, Feng G Z. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of soil pH in farmland topsoil of Jilin Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(2):387-391.
[3] 赵刚, 王淑英, 樊廷录, 党翼, 王磊, 张建军, 李尚中, 程万莉. 西北旱塬区不同株型玉米增密对产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2018,36(4):101-108. doi:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2018.04.15.
Zhao G, Wang S Y, Fan T L, Dang Y, Wang L, Zhang J J, Li S Z, Cheng W L. Effects of planting density of different plant type maize on yield in northwest dry highland of loess plateau[J]. Agricultural Research in Arid Areas, 2018,36(4): 101-108.
[4] 刘慧, 于楠. 吉林省西部半干旱地区玉米高产限制因素探究[J].吉林农业, 2015(14):45-45. doi:10.14025/j.cnki.jlny.2015.14.009.
Liu H, Yu N. Exploration on the restrictive factors of maize high yield in semi-arid areas of western Jilin Province[J].Agriculture of Jilin, 2015 (14): 45-45.
[5] 范如芹, 罗佳, 刘海琴, 严少华, 唐玉邦, 张振华. 淀粉基高吸水性树脂对基质理化性质及小青菜生长的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2015, 38(4):617-623. doi:10.7685/j.issn.1000-2030.2015.04.014.
Fan R Q, Luo J, Liu H Q, Yan S H, Tang Y B, Zhang Z H. The effects of a starch-based super absorbent polymer on characteristics of soilless growth media and the growth of Chinese cabbage[J].Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015, 38(4): 617-623.
[6] 虞利俊, 徐磊, 唐玉邦. 功能型保水剂在江苏丘陵山区生态修复中的应用展望[J].江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(5):473-474. doi:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2016.05.135.
Yu L J, Xu L, Tang Y B. Application prospects of functional water retaining agents in ecological restoration of Hilly and mountainous areas in Jiangsu[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(5): 473-474.
[7] 崔英德, 郭建维, 阎文峰,易国斌, 康正. SA-IP-SPS型保水剂及其对土壤物理性能的影响[J].农业工程学报, 2003, 19(1):28-31. doi:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2003.01.007.
Cui Y D, Guo J W, Yan W F, Yi G B, Kang Z. SA-IP-SPS water retaining agent and its effect on soil physical properties[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2003, 19(1): 28-31.
[8] 金英, 李凤芹, 薛镇海. 保水剂在柞蚕步甲科害虫药物防治上的应用[J]. 吉林农业, 2017(12):80-81. doi:10.14025/j.cnki.jlny.2017.12.038.
Jin Y, Li F Q, Xue Z H. Application of water-retaining agent in medicinal control of tussah carapace insects[J]. Agriculture of Jilin, 2017 (12): 80-81.
[9] 武毅, 孙保平, 张建锋,宋双双, 申豪杰, 陈串, 何艳. 保水剂对4种木本植物生长及根系形态的影响[J].中国水土保持科学, 2018, 16(1):96-102. doi:10.16843/j.sswc.2018.01.012.
Wu Y, Sun B P, Zhang J F, Song S S, Shen H J, Chen C, He Y. Effects of water-retaining agents on growth and root morphology of four woody plants[J].Soil and Water Conservation Science of China, 2018, 16(1): 96-102.
[10] Yang L X, Yang Y, Chen Z, Guo C X, Li S C. Influence of super absorbent polymer on soil water retention, seed germination and plant survivals for rocky slopes eco-engineering[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 62(1):27-32. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2013.10.019.
[11] 刘纪霜, 罗兴录, 樊吴静,黄冬飞, 杨鑫, 曾文丹. 保水剂对土壤理化性状和木薯产量影响研究[J].中国农学通报, 2013, 29(33):253-258. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2013.33.044.
Liu J S, Luo X L, Fan W J, Huang D F, Yang X, Zeng W D. Effects of water retaining agent on the physical and chemical biological character of soil and the root tubers yield of cassava[J]. China Agricultural Bulletin, 2013, 29 (33): 253-258.
[12] 李中阳,吕谋超, 樊向阳, 杜臻杰, 胡超. 不同类型保水剂对冬小麦水分利用效率和根系形态的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(12):3753-3758. doi:10.13287/j.1001-9332.20151016.007.
Li Z Y, Lü M C, Fan X Y, Du Z J, Hu C. Effects of different types of water retaining agents on water use efficiency and root morphology of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(12): 3753-3758.
[13] 许紫峻, 汪溪远, 师庆东,陈娇, 李浩, 徐婉婷, 王伟. 不同材质保水剂对玉米生长综合效率的DEA模型分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017, 24(6):160-166. doi:10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2017.06.023.
Xu Z J, Wang X Y, Shi Q D, Chen J, Li H, Xu W T, Wang W. DEA model analysis of comprehensive efficiency of maize growth with different water retaining agents[J]. Soil and Water Conservation Research, 2017, 24(6): 160-166.
[14] 张运涛. 保水剂在玉米节水高产中的应用[J]. 吉林农业, 2017(9):45-45. doi:10.14025/j.cnki.jlny.2017.09.013.
Zhang Y T. Application of water-retaining agent in water-saving and high yield of maize[J]. Agriculture of Jilin, 2017(9): 45-45.
[15] 滕守振, 汪海, 梁海生, 辛红佳, 李圣彦, 郎志宏. 玉米叶片叶绿素含量的全基因组关联性分析[J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(4):98-103. doi:10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2017.04.013.
Teng S Z, Wang H, Liang H S, Xin H J, Li S Y, Lang Z H. Genome-wide association analysis of chlorophyll content in maize leaves[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(4): 98-103.
[16] 张丽光,李丹, 刘磊, 王蕾, 孙志梅, 彭正萍, 薛世川. 不同施肥种植模式对玉米光合特性、养分效率及产量性状的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2013, 27(2):115-119. doi:10.13870/j.cnki.stbcxb.2013.02.048.
Zhang L G, Li D, Liu L, Wang L, Sun Z M, Peng Z P, Xue S C. Effects of different fertilization and planting patterns on photosynthetic characteristics, nutrient efficiency and yield traits of maize[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 27(2): 115-119.
[17] 李长志, 李欢, 刘庆,史衍玺. 不同生长时期干旱胁迫甘薯根系生长及荧光生理的特性比较[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016, 22(2):511-517. doi:10.11674/zwyf.14513
Li C Z, Li H, Liu Q, Shi Y X. Comparison of root development and fluorescent physiological characteristicsof sweet potato exposure to drought stress in different growth stages[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2016, 22 (2): 511-517.
[18] 赵敏. 保水剂对玉米某些生理特性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2001, 1(3):12-13. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7283.2001.03.006
Zhao M. The effect of high absorbing water resin on physiological characteristics of maize[J]. Crop Journal, 2001, 1(3): 12-13.
[19] 任迎虹, 尹福强, 刘松青,祁伟亮. 不同桑品种在干旱胁迫下叶绿素、水分饱和亏及丙二醛的变化规律研究[J].西南农业学报, 2016, 29(11):2583-2587. doi:10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2016.11.013.
Ren Y H, Yin F Q, Liu S Q, Qi W L. Changes of chlorophyll, water saturation deficit and malondialdehyde in different mulberry varieties under drought stress[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 29 (11): 2583-2587.
[20] 张晓林, 徐韦, 李坦,吕远大, 赵涵. 玉米籽粒主要性状与蛋白质含量的相关性[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014, 42(12):104-106. doi:10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2014.12.033.
Zhang X L, Xu W, Li T, Lü Y D, Zhao H. Correlation between main grain traits and protein content of maize[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014, 42(12): 104-106.
[21] 张丽华, 边少锋, 孙宁, 闫伟平, 赵洪祥, 谭国波, 方向前, 孟祥盟, 冯艳春. 保水剂不同粒型及施用量对玉米产量和光合性状的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2017,25(1):153-156. doi:10.13597/j.cnki.maize.science.20170125
Zhang L H, Bian S F, Sun N, Yan W P, Zhao H X, Tan G B, Fang X Q, Meng X M, Feng Y C. Effects of water-retaining agents on yield and photosynthetic characteristics of maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2017, 25(1): 153-156.