云南省昭通市昭阳区烤烟种植历史悠久,是全市烤烟主产烟区,但受人均耕地面积少的制约和农业产业结构调整的影响,烤烟种植连作现象突出。长期的烤烟连作会导致土壤理化性状发生变化,造成土壤板结,土传病害增加,导致烤烟田间生长迟缓,植株矮小,产质量降低[1-5],进而影响烟叶内在化学成分协调性和香吃味等感官评吸质量。翻耕是农业生产的重要措施之一,翻耕的深度根据土壤质地、气候状况、翻耕时间及作物类别等多种因素而定。合理深耕能加厚耕层,疏松、熟化土壤,改善土壤的水、气、热状况和营养条件,建立良好土壤构造,提高土壤的有效肥力,消除杂草,降低病虫害,促进作物增产。通过开展翻耕深度试验,旨在为当地连作区域烤烟生产相关技术措施的改进提供参考依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 供试材料
供试品种:云烟85。供试肥料:烟草专用复合肥(N∶P2O5∶K2O =11∶15∶23)基施,KNO3(N∶K2O=14∶44)和50% K2SO4追施,施肥量为纯氮105 kg/hm2。
1.2 试验设计
2018年在云南省昭阳区布嘎乡花鹿坪村,东经 103°43′46″,北纬 27°13′17″,海拔高度1 964 m,选择土地平整,连作3年烟地,肥力中等、均匀,冬闲,土壤类型为黄壤。单因素随机区组试计,4个处理,分别为:对照(CK):翻耕深度15 cm、T1:翻耕深度20 cm、T2:翻耕深度25 cm、T3:翻耕深度30 cm。3次重复,共12个小区,每小区面积55.66 m2,行距110 cm,株距55 cm。4月11日采用膜下小苗方式移栽,田间管理严格按照当地优质烤烟生产技术标准进行操作。
1.3 测定项目及方法
1.3.1 土壤物理特性检测 分别于烤烟移栽前、旺长期、采烤前,按小区采集0~20 cm土壤耕层环刀土样,测定土壤容重、孔隙度、土壤水分含量。
1.3.2 烟株干物质积累测定 分别于烤烟团棵期、旺长期、采烤前,每小区采集2株烟株,烘箱105 ℃杀青后,85 ℃恒温烘干,测定根、茎、叶的干质量。
1.3.3 烤烟农艺性状调查 按照《YC/T142-2010 烟草农艺性状调查测定方法》,在成熟采烤前调查烤烟主要农艺性状。
1.3.4 烤烟根结线虫病调查 按照《GB/T23222-2008 烟草病虫害分级及调查方法》,在采烤结束后调查各处理烟株根系根结线虫发病情况,计算发病率和病情指数。
1.3.5 烤烟经济性状调查 按小区进行烟叶采烤,测定各处理产量、上等烟比例和中等烟比例。
1.4 数据统计分析
试验数据采用Microsoft Office Excel 2003和SPSS 17.0进行统计分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同处理对耕层土壤物理特性的影响
由表1可以看出,移栽前土壤含水量CK>T3>T1>T2,旺长期土壤含水量T2>T1>T3>CK,采烤前土壤含水量T3>CK>T1>T2。移栽前土壤容重T1、T2、T3均为1.16 g/cm3,CK为1.13 g/cm3;旺长期土壤容重T1(T3)>CK>T2,且T2与T1、T3在0.05水平有显著差异;采烤前土壤容重T2>T1(CK)>T3。移栽前土壤孔隙度CK>T3>T1>T2;旺长期土壤孔隙度T2>CK>T3>T1,且T1与T2在0.05水平有显著差异;采烤前土壤孔隙度T3>T1>CK>T2。
2.2 不同处理烟株干物质积累情况
由表2可知,不同处理在不同时期烟株的根、茎、叶干物质积累T2较大,其次为T3和T1,CK最差。方差分析结果表明,团棵期,处理T1与T3叶、T2与CK根、T2与T3茎在0.05水平有显著性差异,处理T2与CK茎、叶在0.01水平有极显著差异。旺长期,处理T1与CK茎,T2、T3与CK叶在0.05水平有显著性差异;处理T2与T1、CK根、茎,与T3茎在0.01水平有极显著差异;处理T3与T1、CK根在0.05水平有显著性差异,茎在0.01水平有极显著差异。采烤前,处理T1与CK根、茎,T1与T3茎,T3与CK根在0.05水平有显著性差异;处理T2与CK根、茎、叶,与T1茎、叶,与T3茎在0.01水平有极显著差异;处理T3与T1叶,与CK茎、叶在0.01水平有极显著差异。
表1 不同处理不同时期耕层土壤物理特性
Tab.1 The arable layer soil physical properties of different treatment in different periods
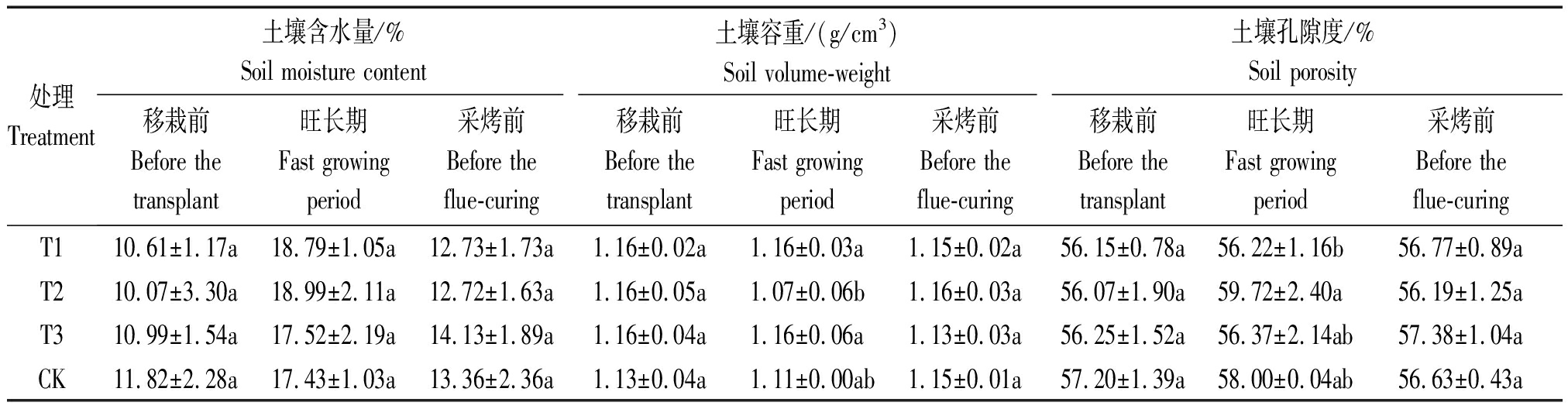
处理Treatment土壤含水量/%Soil moisture content土壤容重/(g/cm3)Soil volume-weight土壤孔隙度/%Soil porosity移栽前Before the transplant旺长期Fast growing period采烤前Before the flue-curing移栽前Before the transplant旺长期Fast growing period采烤前Before the flue-curing移栽前Before the transplant旺长期Fast growing period采烤前Before the flue-curingT110.61±1.17a18.79±1.05a12.73±1.73a1.16±0.02a1.16±0.03a1.15±0.02a56.15±0.78a56.22±1.16b56.77±0.89aT210.07±3.30a18.99±2.11a12.72±1.63a1.16±0.05a1.07±0.06b1.16±0.03a56.07±1.90a59.72±2.40a56.19±1.25aT310.99±1.54a17.52±2.19a14.13±1.89a1.16±0.04a1.16±0.06a1.13±0.03a56.25±1.52a56.37±2.14ab57.38±1.04aCK11.82±2.28a17.43±1.03a13.36±2.36a1.13±0.04a1.11±0.00ab1.15±0.01a57.20±1.39a58.00±0.04ab56.63±0.43a
注:数据为平均值±标准差;每组数据后小写字母不同表示在0.05水平有显著差异,大写字母不同表示在0.01水平有极显著差异。表2-5同。
Note:The data were mean ± standard deviation;Different lowercase letters following the data in each group indicate a significant difference at 0.05 level, different capital letters indicate a significant difference at 0.01 level. The same as Tab.2-5.
表2 不同处理不同时期根、茎、叶干物质积累情况
Tab.2 The different treatment dry matter accumulation of tobacco plants roots, stems and leaves in different periods
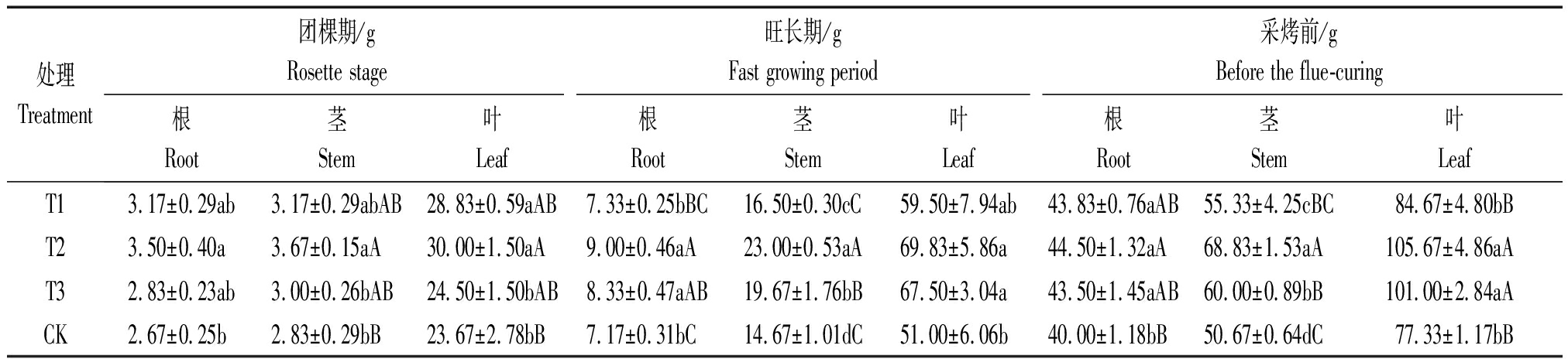
处理Treatment团棵期/gRosette stage旺长期/gFast growing period采烤前/gBefore the flue-curing根Root茎Stem叶Leaf根Root茎Stem叶Leaf根Root茎Stem叶LeafT13.17±0.29ab3.17±0.29abAB28.83±0.59aAB7.33±0.25bBC16.50±0.30cC59.50±7.94ab43.83±0.76aAB55.33±4.25cBC84.67±4.80bBT23.50±0.40a3.67±0.15aA30.00±1.50aA9.00±0.46aA23.00±0.53aA69.83±5.86a44.50±1.32aA68.83±1.53aA105.67±4.86aAT32.83±0.23ab3.00±0.26bAB24.50±1.50bAB8.33±0.47aAB19.67±1.76bB67.50±3.04a43.50±1.45aAB60.00±0.89bB101.00±2.84aACK2.67±0.25b2.83±0.29bB23.67±2.78bB7.17±0.31bC14.67±1.01dC51.00±6.06b40.00±1.18bB50.67±0.64dC77.33±1.17bB
2.3 不同处理烟株根结线虫发生情况
对根结线虫发生情况调查表明(表3),CK根结
表3 不同处理烟株根结线虫发生情况
Tab.3 The root-knot nematode occurrence
of different treatment
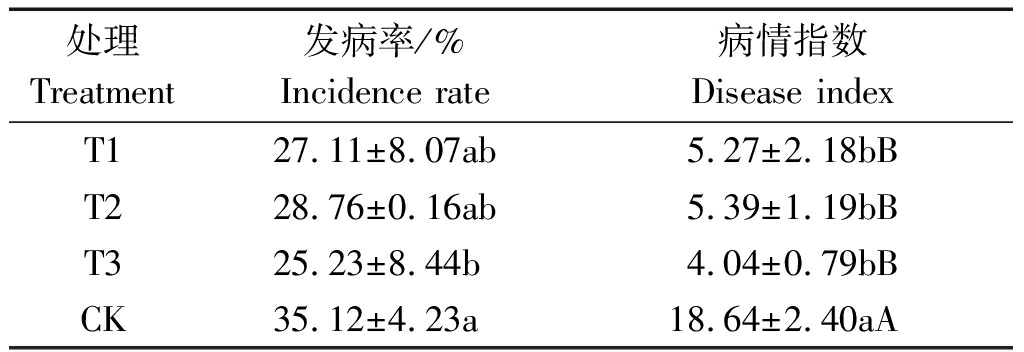
处理Treatment发病率/%Incidence rate病情指数Disease indexT127.11±8.07ab5.27±2.18bBT228.76±0.16ab5.39±1.19bBT325.23±8.44b4.04±0.79bBCK35.12±4.23a18.64±2.40aA
线虫发病较重,发病率为35.12%,病情指数为18.64;其他3个处理发病较轻,病情指数在4.04~5.39。方差分析表明,CK发病率与T3在0.05水平有显著差异,病情指数与其他3个处理在0.01水平有极显著差异。
2.4 不同处理对烤烟农艺性状的影响
从表4可以看出,处理T2烟株株高112.85 cm,叶面积系数3.09,且在0.05水平显著高于CK。处理T3茎围12.07 cm,在0.05水平显著大于CK;节距和有效叶数各处理间无显著差异。
表4 不同处理烤烟农艺性状
Tab.4 The flue-cured tobacco agronomic traits of different treatment
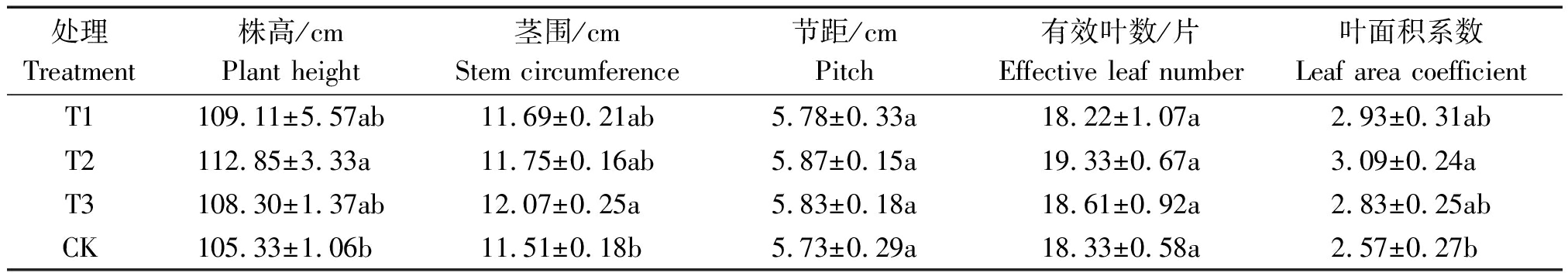
处理Treatment株高/cmPlant height茎围/cmStem circumference节距/cmPitch有效叶数/片Effective leaf number叶面积系数Leaf area coefficientT1109.11±5.57ab11.69±0.21ab5.78±0.33a18.22±1.07a2.93±0.31abT2112.85±3.33a 11.75±0.16ab5.87±0.15a19.33±0.67a3.09±0.24aT3108.30±1.37ab12.07±0.25a5.83±0.18a18.61±0.92a2.83±0.25abCK105.33±1.06b11.51±0.18b5.73±0.29a18.33±0.58a2.57±0.27b
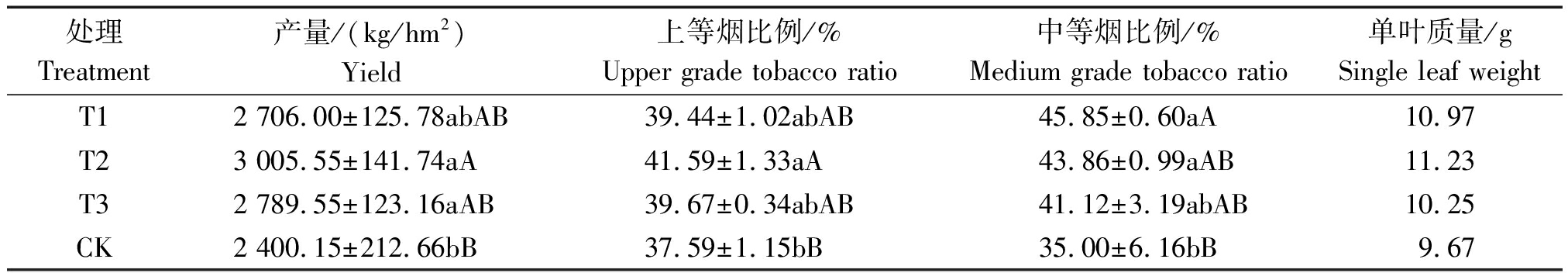
2.5 不同处理对烤烟经济性状的影响
从表5可知,处理T2烤烟经济性状最好,其次为处理T3和T1,CK烤烟经济性状最差。处理T2产量为3 005.55 kg/hm2,上等烟比例为41.59%,在0.01水平均显著高于CK;中等烟比例43.86%,在0.05水平显著高于CK。处理T3产量为2 789.55 kg/hm2,在0.05水平显著高于CK。处理T1中等烟比例为45.85%,在0.01水平显著高于CK。
3 讨论与结论
各种研究表明,深耕措施能改善土壤物理结构,提高土壤蓄水储熵能力,减少土传病害,促进作物生长发育,达到提质增产的目的[6-23]。郭海斌等[10-14]研究认为,深耕处理后,土壤容重下降、含水量增加。崔建平等[15]研究认为,土壤容重随翻耕深度增加而下降,其中表层土壤容重降幅大于深层土壤容重,土壤剖面含水率0~20 cm>20~40 cm>40~60 cm,随翻耕深度增加,0~20 cm土壤含水率呈上升趋势,20~40 cm土壤含水率变幅不大,40~60 cm土壤含水率则显著下降。童文杰等[16]研究认为,深耕处理显著降低亚表层20~40 cm土壤容重,同时显著增加该土层土壤总孔隙度和土壤毛管孔隙度。这与本研究中烤烟旺长期得到的结果基本一致,与烤烟移栽前得到的结果则相反,分析原因,这可能与当地的气候条件有关,一般来说,耕地深,耕层厚,土层松软,有利于贮水保墒。但是在某些条件下,如在多风、高温、干旱地区或季节,深耕会加剧水分丢失。因此,翻耕的适宜深度,应视作物、土壤条件与气候特点而定[17]。昭阳区本年度烤烟移栽时月平均气温15.1 ℃,比常年增加2.3 ℃,降水量7.60 mm,比常年减少75%,气温偏高,降水偏少,造成了深耕水分的加剧散失。
表5 不同处理烤烟经济性状
Tab.5 The flue-cured tobacco economic traits of different treatment
处理Treatment产量/(kg/hm2)Yield上等烟比例/%Upper grade tobacco ratio中等烟比例/%Medium grade tobacco ratio单叶质量/gSingle leaf weightT12 706.00±125.78abAB39.44±1.02abAB45.85±0.60aA10.97T23 005.55±141.74aA41.59±1.33aA43.86±0.99aAB11.23T32 789.55±123.16aAB39.67±0.34abAB41.12±3.19abAB10.25CK2 400.15±212.66bB37.59±1.15bB35.00±6.16bB9.67
童文杰等[16]进一步对烟田深耕增产增效机理进行了系统研究,认为深耕处理不仅显著增加烤烟根系绝对量,还促进根系向深层土壤生长,提高烤烟根系根深指数;并总结了深耕措施首先作用于土壤容重、孔隙等物理结构,然后影响烟田土壤蓄水储熵,促进烤烟早生快发,优化烤烟根系空间分布构型,进而作用于地上部形态建成,最终影响烟叶产量产值。战秀梅等[18-19]研究认为,深翻可以显著提高春玉米的产量、花后干物质的积累量,促进根系发育。杨章明等[20-23]研究了烟地深翻对烤烟生长发育、土传病害发生和烤烟产质量的影响,认为烟地深翻可有效提高烟株农艺性状,促进烟株长势均衡,明显改善土传病害发生情况,显著提高烟叶产质量。这与试验研究得到的结果基本相似或一致,深耕处理的烟株根、茎、叶均比对照有显著增加,且根结线虫发病显著低于对照,产量、上等烟比例等经济性状显著高于对照。
对连作烟地进行翻耕,翻耕深度25~30 cm可以改善土壤物理性状,降低根结线虫病的发生,促进烟株生长发育,改善烟株株高、茎围、叶面积系数等田间农艺性状,提高烟叶产量和上等烟比例等经济性状。
[1] 邓阳春,黄建国.长期连作对烤烟产量和土壤养分的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报,2010,16(4):840-845.
Deng Y C,Huang J G. Effect of long continuous cropping on the yields of flue-cured tobacco and nutrients in soils[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2010,16(4):840-845.
[2] 晋艳,杨宇虹,段玉琪,龙玉华,叶成碧.烤烟连作对烟叶产量和质量的影响研究初报[J].烟草科技,2002(1):41-45. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-0861.2002.01.016.
Jin Y, Yang Y H, Duan Y Q, Long Y H, Ye C B. Influence of continuous cropping on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Tobacco Science & Technology, 2002(1): 41-45.
[3] 晋艳,杨宇虹,段玉琪,孔光辉.烤烟轮作、连作对烟叶产量质量的影响[J].西南农业学报,2004,17(S1):267-271. doi: 10.16213/j.cnki.scjas.2004.s1.063.
Jin Y, Yang Y H, Duan Y Q, Kong G H. Effect of rotational cropping and continuous cropping on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2004,17(S1):267-271.
[4] 高群,孟宪志,于洪飞.连作障碍原因分析及防治途径研究[J].山东农业科学,2006(3):60-63.doi:10.14083/j.issn.1001-4942.2006.03.023.
Gao Q,Meng X Z,Yu H F. Reason analysis and control methods of succession cropping obstacle[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2006(3):60-63.
[5] 张翼,张长华,王振民,黄建国.连作对烤烟生长和烟地土壤酶活性的影响[J].中国农学通报,2007,23(12):211-215. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2007.12.048.
Zhang Y,Zhang C H,Wang Z M,Huang J G. The effects on the yields of flue-cured tobacco and activities of main soil enzymes[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2007,23(12):211-215.
[6] 邹文秀,陆欣春,韩晓增,王凤仙.耕作深度及秸秆还田对农田黑土土壤供水能力及作物产量的影响[J]. 土壤与作物,2016,5(3):141-149. doi:10.11689/j.issn.2095-2961.2016.03.003.
Zou W X,Lu X C,Han X Z,Wang F X. The impact of tillage depth and straw incorporation on crop yield and soil water supply in arable black soil[J]. Soils and Crops,2016,5(3):141-149.
[7] 胡心意,傅庆林,刘琛,丁能飞,林义成.秸秆还田和耕作深度对稻田耕层土壤的影响[J].浙江农业学报,2018,30(7):1202-1210. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2018.07.14.
Hu X Y,Fu Q L,Liu C,Ding N F,Lin Y C. Effects of straw-returning and tillage depth on soil properties in plough layer of paddy soil[J].Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2018,30(7):1202-1210.
[8] 彭成林,袁家富,赵书军,佀国涵,贾平安,徐祥玉,徐大兵,李金华,吴鹏飞.不同耕作深度与施肥量对江汉平原稻田土壤紧实度和水稻产量的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2019,58(6):30-33. doi:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2019.06.008.
Peng C L,Yuan J F,Zhao S J,Si G H,Jia P A,Xu X Y,Xu D B,Li J H,Wu P F. Effects of different tillage depths and fertilizer rates on soil compaction and grain yield in paddy fields in Jianghan plain[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2019,58(6):30-33.
[9] 黄尚书,武琳,叶川,黄欠如,成艳红,张昆,吴昌强,周琦娜,杨小华,钟义军.耕作深度对红壤坡耕地花生根系生长及活力的影响[J].江西农业学报,2018,30(12):9-12.doi:10.19386/j.cnki.jxnyxb.2018.12.02.
Huang S S,Wu L,Ye C,Huang Q R,Cheng Y H,Zhang K,Wu C Q,Zhou Q N,Yang X H,Zhong Y J. Effects of tillage depth on root growth and activity of peanut in red soil slope field[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2018,30(12):9-12.
[10] 郭海斌,冀保毅,王巧锋,赵亚丽,穆心愿,薛志伟,李潮海,赵志杰.深耕与秸秆还田对不同质地土壤物理性状和作物产量的影响[J].河南农业大学学报,2014,48(4):505-511. doi:10.16445/j.cnki.1000-2340.2014.04.010.
Guo H B,Ji B Y,Wang Q F,Zhao Y L,Mu X Y,Xue Z W,Li C H,Zhao Z J. Effects of deep tillage and straw returning on soil physical properties and grain yield of different soil texture[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural University,2014,48(4):505-511.
[11] 潘金华,庄舜尧,曹志洪,蔡宪杰,程森.条状超深耕对皖南旱坡地土壤性状及烤烟产质量的综合效应[J].土壤,2016,48(3):559-564. doi:10.13758/j.cnki.tr.2016.03.022.
Pan J H,Zhuang S Y,Cao Z H,Cai X J,Cheng S. Effects of strip ultra-deep subsoiling on tobacco growth, yield and quality in uplands at South Anhui[J]. Soils,2016,48(3):559-564.
[12] 李晓龙,高聚林,胡树平,于晓芳,王志刚,苏治军,谢岷.不同深耕方式对土壤三相比及玉米根系构型的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2015(4):1-7,29. doi:10.7606/j.issn.1000-7601.2015.04.01.
Li X L,Gao J L,Hu S P,Yu X F,Wang Z G,Su Z J,Xie M. Effects of various cultivation approaches on the three-phase ratio of soil and root system structure of maize[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas,2015(4):1-7,29.
[13] 李小飞,孙永明,叶川,张昆,黄尚书,余跑兰,武琳,李昊.不同耕作深度对茶园土壤理化性状的影响[J].南方农业学报,2018,49(5):877-883. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2018.05.08.
Li X F,Sun Y M,Ye C,Zhang K,Huang S S,Yu P L,Wu L,Li H. Effects of various tillage depths on soil physical and chemical properties of tea plantation[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2018,49(5):877-883.
[14] 罗俊,林兆里,阙友雄,李诗燕,姚坤存,姜永,张华,陈建峰.耕作深度对蔗地土壤物理性状及甘蔗产量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(2):405-412. doi:10.13287/j.1001-9332.201902.010.
Luo J,Lin Z L,Que Y X,Li S Y,Yao K C,Jiang Y,Zhang H,Chen J F. Effect of subsoiling depths on soil physical characters and sugarcane yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2019,30(2):405-412.
[15] 崔建平,田立文,郭仁松,林涛,徐海江,李发云.深翻耕作对连作滴灌棉田土壤含水率及含盐量影响的研究[J].中国农学通报,2014,30(12):134-139.
Cui J P,Tian L W,Guo R S,Lin T,Xu H J,Li F Y. Effect of deep tilling on soil moisture content and salinity content of drip irrigation cotton continuous cropping[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2014,30(12):134-139.
[16] 童文杰,邓小鹏,徐照丽,马二登,晋艳,李军营.不同耕作深度对土壤物理性状及烤烟根系空间分布特征的影响[J].中国生态农业学报,2016,24(11):1464-1472. doi:10.13930/j.cnki.cjea.160555.
Tong W J,Deng X P,Xu Z L,Ma E D,Jin Y,Li J Y. Effect of plowing depth on soil physical characteristics and spatial distribution of root system of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2016, 24(11): 1464-1472.
[17] 刘巽浩.耕作学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,1994:217.
Liu X H. Cultivation science[M].Beijing:China Agricultural Press,1994:217.
[18] 战秀梅,李秀龙,韩晓日,李亭亭,杨劲峰,刘小虎.深耕及秸秆还田对春玉米产量、花后碳氮积累及根系特征的影响[J].沈阳农业大学学报,2012,43(4):461-466. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-1700.2012.04.013.
Zhan X M,Li X L,Han X R,Li T T,Yang J F,Liu X H. Effects of subsoiling and straw-returning on yield and post-anthesis dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and root characteristics of spring maize[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University,2012,43(4):461-466.
[19] 隋凯强,付丽亚,韩伟,林少雯,刘树堂,皇甫呈惠.不同耕作深度下调控水肥对玉米生长状况的影响[J]. 华北农学报,2018,33(6):212-218. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.2018.06.029.
Sui K Q,Fu L Y,Han W,Lin S W,Liu S T,Huangfu C H. Effect of regulating water and fertilizer on maize growth under different tillage depth[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2018, 33(6): 212-218.
[20] 杨章明,常宁涛,杨艺炜,陈德鑫,张瑞萍.烟田深耕对攀枝花烟区烟叶质量的影响[J].南方农业,2017,11(18):25-27. doi:10.19415/j.cnki.1673-890x.2017.18.015.
Yang Z M,Chang N T,Yang Y W,Chen D X,Zhang R P. Effects of deep tillage on the quality of Panzhihua tobacco[J].South China Agriculture,2017,11(18):25-27.
[21] 潘金华,黄化刚,陈雪,庄舜尧.深耕与施肥对毕节烤烟生长及产质量的影响[J].中国烟草科学,2017,38(3):14-19. doi:10.13496/j.issn.1007-5119.2017.03.003.
Pan J H,Huang H G,Chen X,Zhuang S Y. Effects of deep tillage and associated fertilization on tobacco growth, yield and quality of Bijie City[J].Chinese Tobacco Science,2017,38(3):14-19.
[22] 郑建辉.不同翻耕深度对烤烟生产的影响[J].福建农业科技,2009(2):41-42. doi:10.13651/j.cnki.fjnykj.2009.02.023.
Zheng J H. Effects of different tillage depth on flue-cured tobacco production[J].Fujian Agricultural Science and Technology,2009(2):41-42.
[23] 范艺宽,毛家伟,孙大为,张翔,杨立均,李亮,司贤宗,吴俊林.耕作深度和秸秆还田互作对土壤团聚体组成和烟叶钾、氯含量的影响[J].河南农业科学,2018,47(1):32-36. doi:10.15933/j.cnki.1004-3268.2018.01.006.
Fan Y K,Mao J W,Sun D W,Zhang X,Yang L J,Li L,Si X Z,Wu J L. Effects of interaction between different plowing depths and straw return on soil aggregates and potassium and chlorine contents of flue-cured tobacco[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences,2018,47(1):32-36.