低温、干旱、盐碱等非生物胁迫是限制作物持续高产和稳产的主要逆境因子[1]。因此,从作物中筛选和分离抗性基因,并在作物自身中进行抗性基因功能发挥相关的代谢网络调控机制研究,将为进一步开展作物抗逆分子育种奠定重要基础[2-3],为我国乃至整个世界粮食安全提供保障。
一些富含脯氨酸/甘氨酸的蛋白家族已被证实在植物生长发育和逆境适应中扮演着十分重要的角色[4-6]。这些富含脯氨酸/甘氨酸的蛋白家族种类较多,包括GRP(Glycine-rich protein)、PRP(Proline-rich protein)和GPRP(Glycine-and proline-rich protein)等[4,7-8]。其中,一些GRP 和PRP 蛋白是组成植物细胞壁的重要结构蛋白,在植物病虫害防御、耐旱和抗冷等方面具有重要的作用[9-11]。GPRP 则是与上述2类植物细胞壁蛋白(GRP 和PRP)明显不同的一类,同时是富含脯氨酸和甘氨酸的新型蛋白,它与细胞膜密切相关[7,12],可能属于跨膜蛋白[4],但其在植物生长发育和逆境适应中的生物学功能还有待进一步研究。
根据前人报道的结果[4,7],并利用生物信息学分析,我们获得了3个候选的水稻OsGPRP基因家族成员LOC_Os05g02780、LOC_Os03g60470和LOC_Os05g02770。本研究拟利用RT-PCR和测序等方法克隆这3个水稻OsGPRP基因的cDNA序列,进而分析其编码蛋白的保守结构域;同时,在分析这3个水稻OsGPRP家族基因启动子顺式作用元件的基础上,进一步分析了水稻幼苗中3个OsGPRP基因在RNA转录水平上对干旱和低温胁迫的响应模式,为深入研究这些基因在水稻逆境适应中的功能及其功能发挥的分子机理奠定基础,也为水稻和其他作物分子育种提供理论依据。
1 材料和方法
1.1 材料种植、逆境处理和取样
选取饱满、健壮的粳稻中花11种子,用75%的酒精和5%的NaClO消毒在28 ℃浸种发芽后,于光照培养箱中水培培养,培养的光周期是16 h光照和8 h黑暗,光照和黑暗培养的温度分别为28,20 ℃。生长25 d的幼苗,用于胁迫处理。参考Kim等[13]和Liu等[14]的方法,用纱布吸去幼苗根部水分于相同的光照培养箱中进行干旱处理至明显卷叶取样;参考Liu等[14]和Perez-Diaz等[15]的方法,在同样的另一光照培养箱中8 ℃处理48 h取样。干旱和低温胁迫处理取样均分为地上部(包括叶、茎和鞘,即Shoot)和地下部(根,即Root),取3次生物学重复的样品,取样后立即用液氮速冻于-80 ℃冰箱中保存。
1.2 总RNA提取和cDNA获得
参考孙利军等[16]的方法,主要采用TRIzol法提取冻存的各种水稻组织中的总RNA,利用TaKaRa公司的AMV反转录试剂盒合成获得水稻各种组织的cDNA。
1.3 水稻OsGPRP基因的cDNA克隆和编码蛋白保守结构域分析
依据phytozome网站(https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html)上3个水稻OsGPRP1(LOC_Os05g02780)、OsGPRP2(LOC_Os03g60470)和OsGPRP3(LOC_Os05g02770)基因信息,设计特异引物(表1),以幼苗的根、茎、叶和幼穗的混合cDNA为模板,利用TOYOBO公司的KOD plus高保真酶进行PCR扩增3个OsGPRP基因的cDNA序列,PCR程序为:94 ℃预变性5 min;94 ℃变性30 s,退火(OsGPRP1为57 ℃退火30 s;OsGPRP2为58 ℃退火30 s;OsGPRP3为60 ℃退火30 s),72 ℃延伸45 s,28个循环;72 ℃延伸7 min。扩增结束后,将纯化的目的片段连接到TaKaRa Biotechnology公司的pMD18-T载体上,转化大肠杆菌,抗性筛选获得阳性克隆后摇菌并提取质粒,送上海生工进行测序分析。利用ClustalX program (ver 1.83)软件,参考Peng等[4]和Marty等[7]的报道,分析3个水稻OsGPRP基因cDNA所编码的蛋白保守结构域。
1.4 启动子顺式作用元件分析
在phytozome网站上下载获得3个水稻OsGPRP基因起始密码子上游2 kb的基因组序列,再利用PlantCARE database (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/)分析3个水稻OsGPRP基因启动子的顺式作用元件[14,17]。
1.5 荧光定量PCR分析
参考Liao等[18]和杜方等[19]的方法,设计3个水稻OsGPRP基因的荧光定量PCR引物(表1),以OsActin1(LOC_Os03g50885)为内参,在StepOnePlus PCR 仪(ABI,USA)上进行qRT-PCR反应,每个反应均设3 次重复。三步法qRT-PCR反应程序设为:95 ℃预变性3 min;40个循环反应(95 ℃变性15 s,60 ℃退火20 s,72 ℃延伸30 s);溶解曲线阶段(95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 1 min,以每秒上升0.3 ℃的速度升温到95 ℃,95 ℃ 15 s)。反应结束后确认荧光定量PCR的扩增曲线和溶解曲线,表达量分析采用2-ΔΔCt计算。
表1 水稻OsGPRP基因cDNA克隆和qRT-PCR扩增的引物和产物大小
Tab.1 Primers and amplicon sizes used for OsGPRP cDNA cloning and qRT-PCR

基因Gene引物序列(5'-3')Primersequence产物/bpProductOsGPRP1F:CCTCGTCTTCAGGACTCAATTCGTCT653R:CGCATTACTTCCACTTCTTGAACTTGCOsGPRP2F:CAAGTCTTAGGTAGGTCACTGTTGGTGC665R:GCAGTGCAATTTAGTTTGCTTATCACTTCOsGPRP3F:ATGGGAGGGAGCAAGGATGAGC547R:GAACACGCCGTGCAACACGATOsGPRP1qF:CTTGATTGGGGTGGGTGACA122qR:TCCCTGGTGAGGAGGATACCOsGPRP2qF:AAGCGGTTACCCTGGTGCAT154qR:AGGGTAACCGCTTGGTGGATOsGPRP3qF:TCAGACGACGATGGGAGG239qR:GGTTACCGTGTTGGAATGGOsActin1qF:TCTCTCTGTATGCCAGTGGTCGT253qR:TCATAGTCCAGGGCGATGTAGG
2 结果与分析
2.1 水稻OsGPRP基因的cDNA克隆及保守结构域分析
以水稻幼苗根、茎、叶和幼穗的混合cDNA为模板,根据设计的特异引物(见材料与方法1.3),经RT-PCR扩增获得了大小约为653,665,547 bp的单一cDNA目的片段(图1),将这些片段回收后经TA克隆、测序和Blast软件分析发现,OsGPRP1、OsGPRP2和OsGPRP3分别包含197,180,170个氨基酸,且均具有3个保守结构域即N端的XYPP重复区域、中部富含A(丙氨酸)的疏水区(Hydro domain)和C端HGK重复序列(图2),因而属于典型的植物GPRP蛋白家族成员[4,7]。
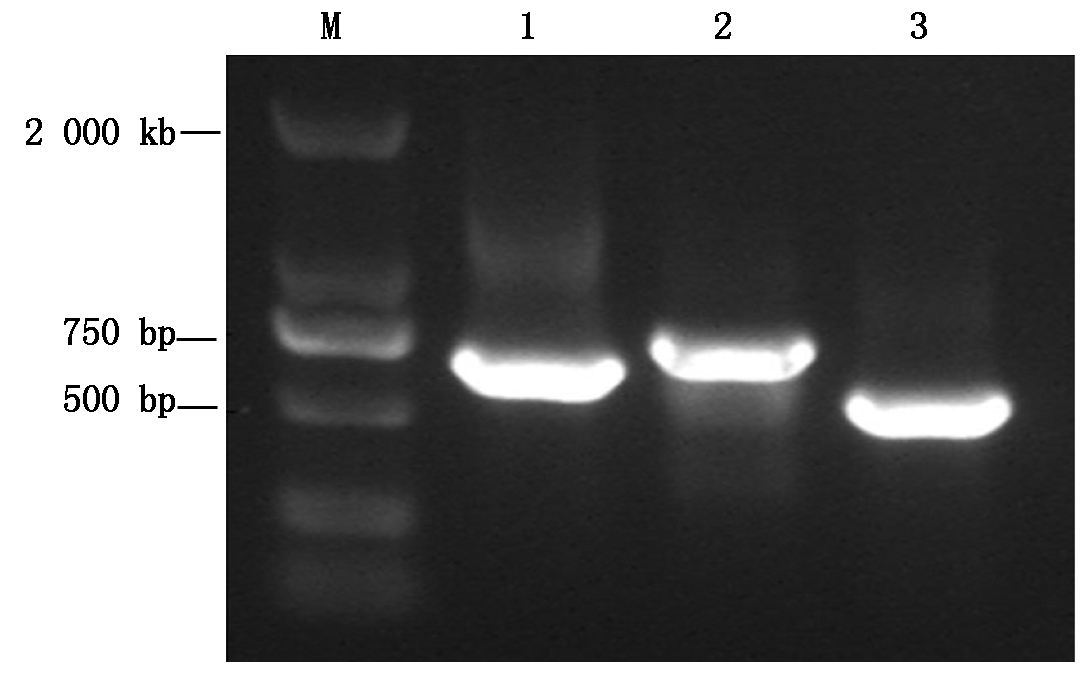
M.DNA Marker;1.OsGPRP1 PCR产物;2.OsGPRP2 PCR产物;3.OsGPRP3 PCR产物。
M.DNA Marker;1.PCR product of OsGPRP1;2.PCR product of OsGPRP2;3.PCR product of OsGPRP3。
图1 水稻OsGPRP基因的RT-PCR扩增
Fig.1 Amplification of rice OsGPRPs by RT-PCR
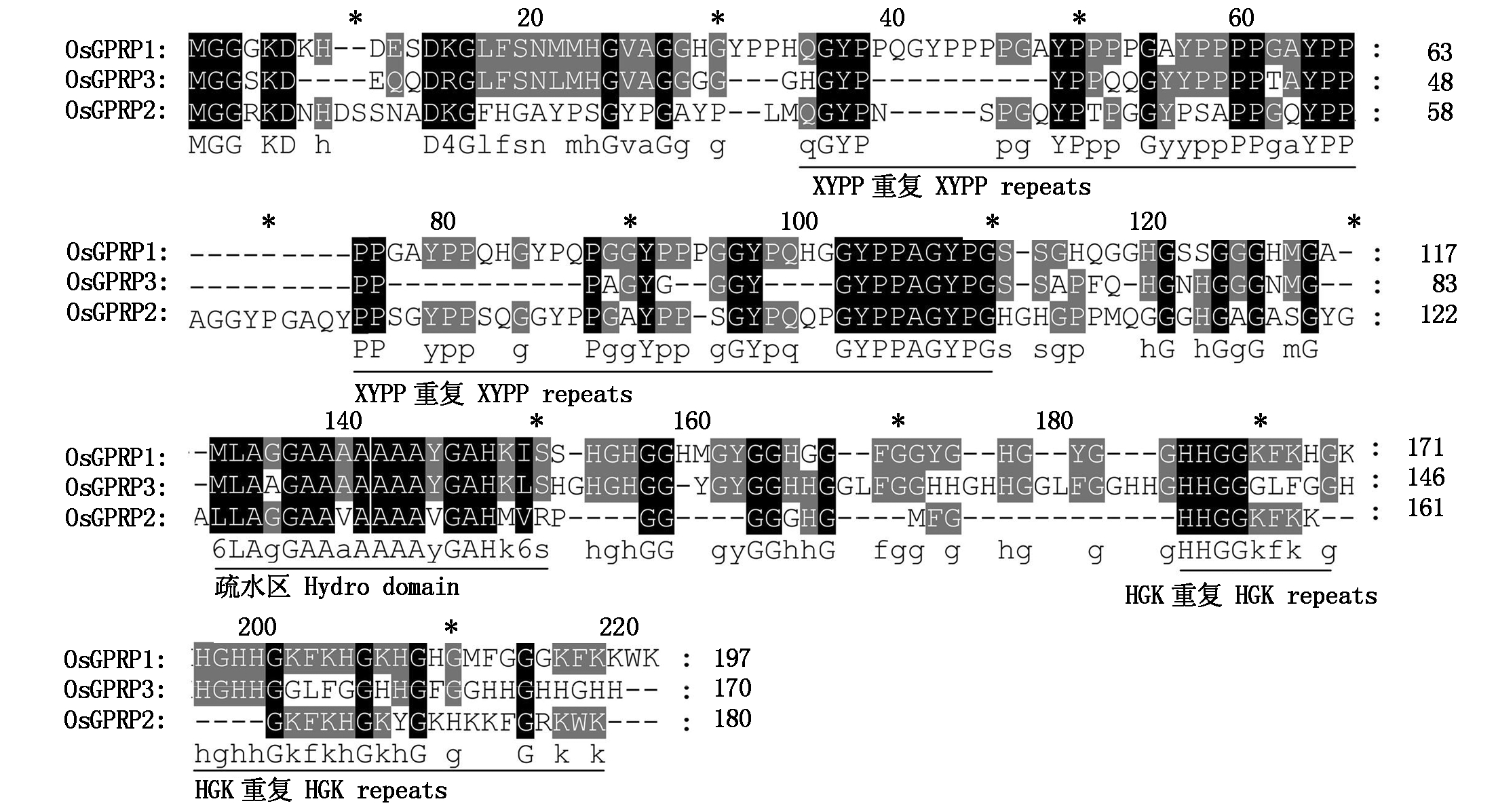
图2 水稻OsGPRP蛋白的保守结构域
Fig.2 Conserved motifs in the rice OsGPRPs
2.2 水稻OsGPRP基因的启动子顺式作用元件分析
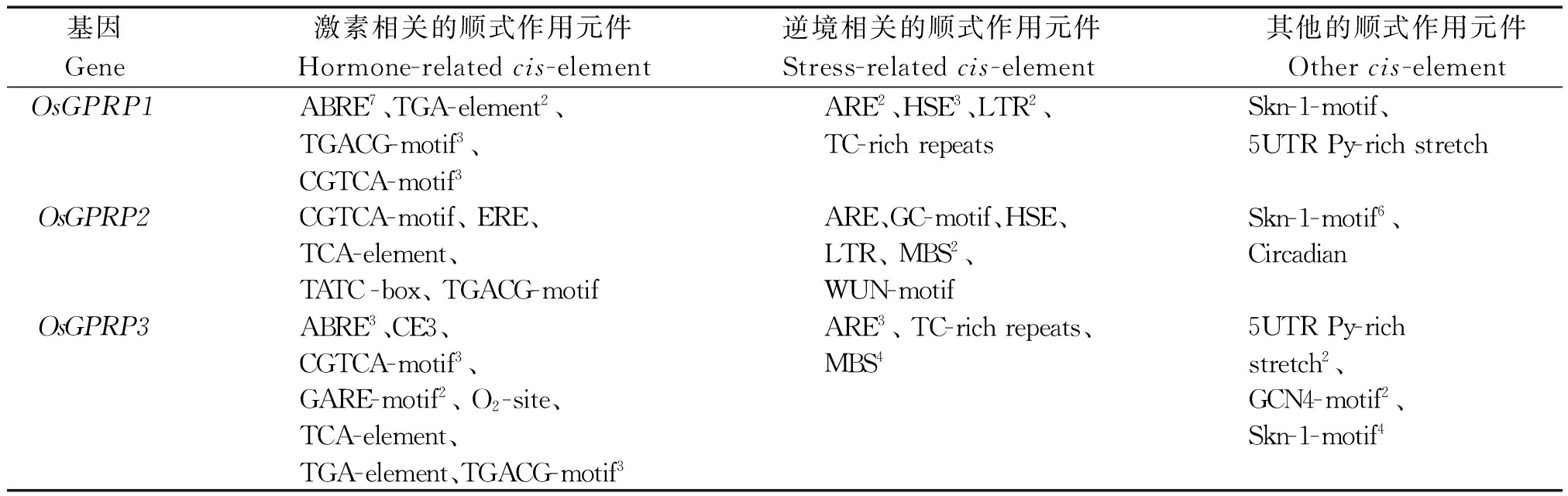
基因启动子顺式作用元件分析结果表明(表2),3个水稻OsGPRP基因启动子中除含有与植株生长发育和激素调控相关的顺式作用元件外,还含有许多与非生物胁迫响应相关的顺式作用元件,但3个水稻OsGPRP基因启动子所含的非生物胁迫相关的顺式作用元件种类和数目存在一定的差异;其中,OsGPRP1启动子中含有2个ARE、3个HSE、2个LTR和1个TC-rich repeats共4类作用元件;OsGPRP2启动子中含有1个GC-motif、1个HSE、1个ARE、1个LTR、1个WUN-motif和2个MBS共6类作用元件;OsGPRP3启动子中含有1个TC-rich repeats、4个MBS和3个ARE共3类作用元件,其中,ARE为3个水稻OsGPRP启动子所共有的非生物胁迫作用元件。由此表明,这些水稻OsGPRP基因在RNA转录表达水平上可能受到不同非生物胁迫的诱导。
表2 水稻OsGPRP基因的启动子顺式作用元件
Tab.2 cis-elements in the promoters of rice OsGPRPs
基因Gene激素相关的顺式作用元件Hormone-relatedcis-element逆境相关的顺式作用元件Stress-relatedcis-element其他的顺式作用元件Othercis-elementOsGPRP1ABRE7、TGA-element2、ARE2、HSE3、LTR2、Skn-1-motif、TGACG-motif3、TC-richrepeats5UTRPy-richstretchCGTCA-motif3OsGPRP2CGTCA-motif、ERE、ARE、GC-motif、HSE、Skn-1-motif6、TCA-element、LTR、MBS2、CircadianTATC-box、TGACG-motifWUN-motifOsGPRP3ABRE3、CE3、ARE3、TC-richrepeats、5UTRPy-richCGTCA-motif3、MBS4stretch2、GARE-motif2、O2-site、GCN4-motif2、TCA-element、Skn-1-motif4TGA-element、TGACG-motif3
注:顺势作用元件上的数字上标代表该基因中包含该类顺式作用元件的数量,没有数字上标代表该基因中仅包含有一个该类顺式作用元件。ABRE.脱落酸响应元件;TGA-element.植物激素响应元件;CGTCA-motif、TGACG-motif.茉莉酸甲酯调控元件;ERE.乙烯反应元件;TCA-element.水杨酸响应元件;TATC-box、GARE-motif.赤霉素响应元件;CE3.ABA和VP1响应元件;O2-site.新陈代谢调控元件;ARE.厌氧感应调控元件;HSE.热应激调控元件;LTR.低温响应元件;TC-rich repeats.胁迫响应元件;MBS.参与干旱诱导的MYB结合位点;GC-motif.增强诱发厌氧反应;WUN-motif.创伤响应元件;GCN4-motif、Skn-1-motif.胚乳表达调控元件; 5UTR Py-rich stretch.调控高转录水平元件; Circadian.生理周期调控元件。
Note:The superscript numbers of the cis-element represents the number of the cis-element pesent in the promoter,cis-element with no superscript are the only cis-element present in the promoter.ABRE.cis-acting element involved in the abscisic acid responsiveness; TGA-element.Auxin-responsive element; CGTCA-motif and TGACG-motif.cis-acting regulatory element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness; ERE.Ethylene-responsive element; TCA-element.cis-acting element involved in salicylic acid responsiveness; TATC-box and GARE-motif.cis-acting element involved in gibberellin-responsiveness; CE3.cis-acting element involved in ABA and VP1 responsiveness; O2-site.cis-acting regulatory element involved in zein metabolism regulation; ARE.cis-acting regulatory element essential for the anaerobic induction; HSE.cis-acting element involved in heat stress responsiveness; LTR.cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness; TC-rich repeats.cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness; MBS.MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility; GC-motif.Enhancer-like element involved in anoxic specific inducibility; WUN-motif.Wound-responsive element; GCN4-motif and Skn-1-motif.cis-regulatory element involved in endosperm expression; 5UTR Py-rich stretch.cis-acting element conferring high transcription levels; Circadian.cis-acting regulatory element involved in circadian control.
2.3 水稻OsGPRP家族成员对干旱的响应
以水稻OsActin1为内参,未处理为空白对照组,干旱胁迫下OsGPRP家族成员在水稻地上部和地下部的表达变化情况如图3所示。其中,OsGPRP1在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部的表达量略有上升,但差异均不显著;OsGPRP2在水稻幼苗地上部的表达量上升差异不显著,而在地下部的表达量则呈极显著上升;OsGPRP3在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部的表达量均为极显著上升。
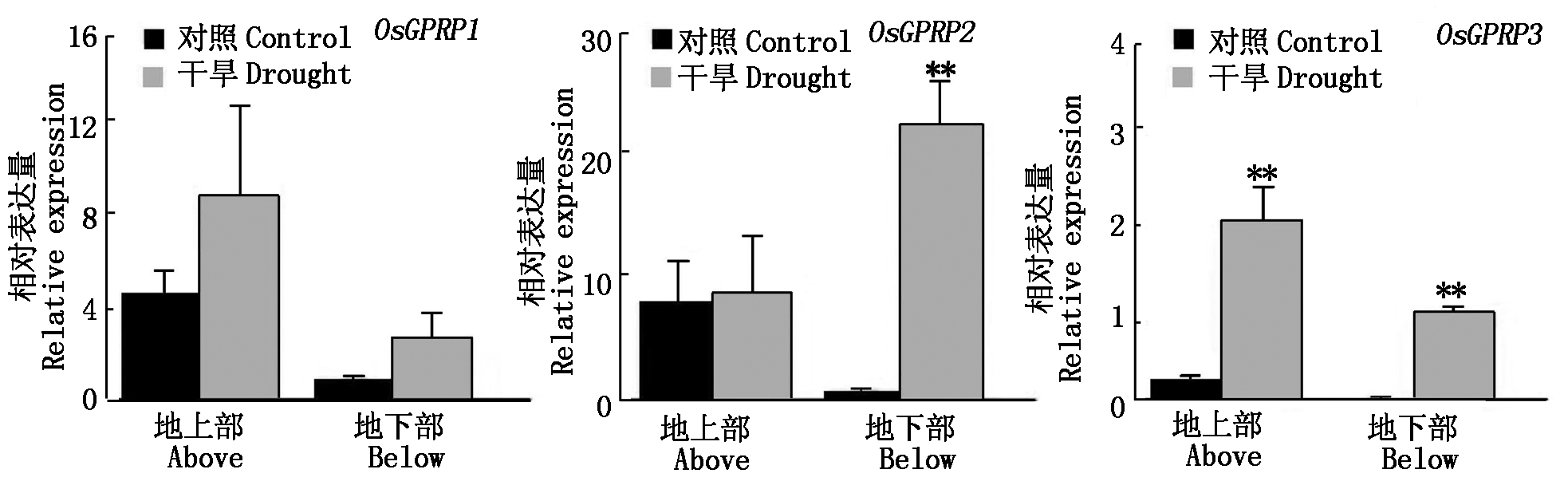
** .P < 0.01水平上差异极显著。
**.Indicates significant difference at level of P < 0.01.
图3 干旱对水稻OsGPRP家族成员表达的影响
Fig.3 Effects of drought on expressions of rice OsGPRP family members
2.4 水稻OsGPRP家族成员对低温的响应
以水稻OsActin1为内参,未处理为空白对照组,经低温处理后发现,3个水稻OsGPRP家族成员在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部中的表达量均具有不同程度的变化(图4);其中,OsGPRP1在水稻幼苗地上部的表达量略有上升但差异不显著,而在地下部的表达量则显著上升;OsGPRP2在水稻幼苗地上部的表达量极显著降低,而在地下部的表达量则极显著上升;OsGPRP3在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部的表达量均为极显著上升。
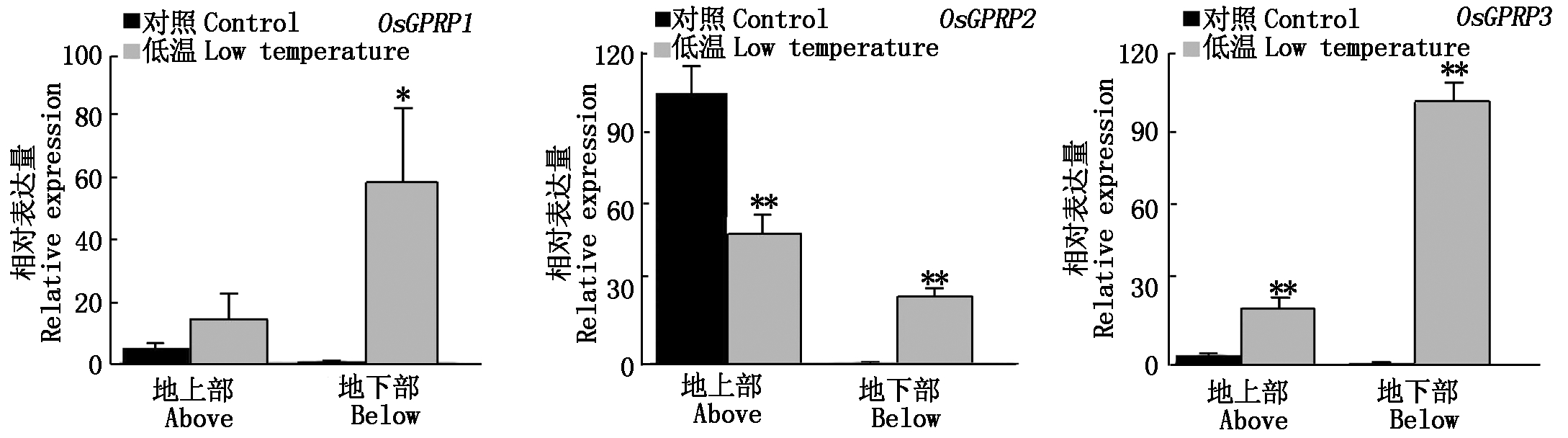
* 和 **分别表示P<0.05和P<0.01水平上的显著和极显著差异。
* and ** .Indicate significant differences at level of P<0.05 and P<0.01,respectively.
图4 低温对水稻OsGPRP家族成员表达的影响
Fig.4 Effects of low temperature on expressions of rice OsGPRP family members
3 讨论
GRPR 蛋白含有4 个保守结构域,近N 端的XYPP 重复和中部富含A(丙氨酸)的疏水区(Hydro domain)是所有GPRP 蛋白所共有的,而另外2个结构域(N 端G-rich 区和C 端HGK重复)只存在于部分GPRP 蛋白中[4,7]。本研究克隆的3个水稻OsGPRP基因编码的蛋白序列中均包含了近N端的XYPP重复区域、中部多A 疏水区和C端HGK重复序列3个保守结构域,说明这3个水稻OsGPRP基因是典型的植物GPRP家族成员。
在前人研究的基础上进一步利用生物信息学进行同源蛋白基因搜索分析发现,GPRP蛋白基因广泛分布于高等植物中[4,7]。目前,在拟南芥、玉米、大豆和鹰嘴豆中报道的GPRP基因数分别仅有5,3,6,4个[4,7];本研究在生物信息学分析的基础上,利用RT-PCR等方法也只分离到了3个水稻OsGPRP蛋白编码基因的cDNA序列。由此表明,GPRP这类基因在高等植物中应属于数量少的小基因家族。
前人研究结果已经表明,拟南芥、大豆、鹰嘴豆和蚕豆等植物中GPRP基因的表达会受到各种生物和非生物胁迫的调控[4,7,20]。本研究发现,3个水稻OsGPRP基因的表达也分别受到干旱和低温的影响,只是3个OsGPRP基因对干旱和低温胁迫响应的模式存在一定的差异。例如,干旱胁迫下,OsGPRP1在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部的上升表达量变化均不显著;OsGPRP3在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部的表达量均极显著上升;而OsGPRP2只在水稻幼苗地下部的表达量极显著上升,在地上部的上升表达差异不显著。低温胁迫下,OsGPRP1只在水稻幼苗地下部的表达量显著上升,在地上部的表达量差异不显著;OsGPRP3在水稻幼苗地上部和地下部的表达量均为极显著上升;而OsGPRP2在水稻幼苗地上部的表达量极显著下降,但在地下部的表达量则极显著上升。由此表明,在干旱、低温等胁迫下,这些OsGPRP家族成员可能既存在协同作用,也可能存在功能分化;类似的基因家族成员存在功能冗余和分化的现象在拟南芥、大豆和水稻等中均有报道[4,18,21]。
参考文献:
[1] Shen G X,Wei J,Qiu X Y,et al.Co-overexpression of AVP1 and AtNHX1 in cotton further improves drought and salt tolerance in transgenic cotton plants[J].Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2015,33(2):167-177.
[2] 万建民.中国水稻分子育种现状与展望[J].中国农业科技导报,2007,9(2):1-9.
[3] 朱义旺,林雅容,陈 亮.我国水稻分子育种研究进展[J].厦门大学学报:自然科学版,2016,55(5):661-671.
[4] Peng H,Feng Y M,Zhang H,et al.Molecular cloning and characterisation of genes coding for Glycine-and proline-rich proteins (GPRPs) in soybean[J].Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,2012,30(3):566-577.
[5] Boron A K,Van Orden J,Markakis M N,et al.Proline-rich protein-like PRPL1 controls elongation of root hairs in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2014,65(18):5485-5495.
[6] Fujino K,Obara M,Sato K.Diversification of the plant-specific hybrid glycine-rich protein (HyGRP) genes in cereals[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2014,5(1):489.
[7] Marty I,Monfort A,Stiefel V,et al.Molecular characterization of the gene coding for GPRP,a class of proteins rich in glycine and proline interacting with membranes in Arabidopsis thaliana[J].Plant Molecular Biology,1996,30(3):625-636.
[8] Kour A,Boone A M,Vodkin L O.RNA-Seq profiling of a defective seed coat mutation in glycine max reveals differential expression of Proline-rich and other cell wall protein transcripts[J].PLoS One,2014,9(5):e96342.
[9] Kim J Y,Kim W Y,Kwak K J,et al.Glycine-rich RNA-binding proteins are functionally conserved in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa during cold adaptation process[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2010,61(9):2317-2325.
[10] Yeom S I,Seo E,Oh S K,et al.A common plant cell-wall protein HyPRP1 has dual roles as a positive regulator of cell death and a negative regulator of basal defense against pathogens[J].Plant Journal,2012,69(5):755-768.
[11] Tan J,Zhuo C,Guo Z.Nitric oxide mediates cold-and dehydration-induced expression of a novel MfHyPRP that confers tolerance to abiotic stress[J].Physiologia Plantarum,2013,149(3):310-320.
[12] Schoofs L,Hamdaoui A,Devreese B,et al.The ovary of the desert locust Schistocerca gregaria contains a glycine-and proline-rich peptide that displays sequence similarities with a new class of GPRP proteins from plants[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,1998,243(2):390-394.
[13] Kim D Y,Kwon S I,Choi C,et al.Expression analysis of rice VQ genes in response to biotic and abiotic stresses[J].Gene,2013,529(2):208-214.
[14] Liu J L,Luo M S,Yan X,et al.Characterization of genes coding for galacturonosyltransferase-like (GATL) proteins in rice[J].Genes & Genomics,2016,38(10):917-929.
[15] Perez-Diaz J,Wu T M,Perez-Diaz R A,et al.Organ-and stress-specific expression of the ASR genes in rice[J].Plant Cell Reports,2014,33(1):61-73.
[16] 孙利军,黄 磊,李大勇,等.水稻OsWRKY转录因子对非生物胁迫响应的重叠表达特性分析[J].植物生理学报,2014,50(11):1651-1658.
[17] Lescot M,Dehais P,Thijs G,et al.PlantCARE,a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences [J].Nucleic Acids Research,2002,30(1):325-327.
[18] Liao P F,Huang J Q,Tong P G,et al.Characterization and expression analysis of inositolphosphorylceramide synthase family genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J].Genes & Genomics,2017,39(5):485-492.
[19] 杜 方,王 婷,樊俊苗,等.新铁炮百合朱丽叶器官差异基因表达分析[J].华北农学报,2017,32(5):25-30.
[20] Nakahara K S,Kitazawa H,Atsumi G,et al.Screening and analysis of genes expressed upon infection of broad bean with Clover yellow vein virus causing lethal necrosis[J].Virology Journal,2011,8:355.
[21] Lee B H,Henderson D A,Zhu J K.The Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its regulation by ICE1[J].Plant Cell,2005,17(11):3155-3175.