作者简介:王佳荣(1997—),女,河北保定人,在读硕士,主要从事分子植物病理学研究。
为了对40份来自国际玉米小麦改良中心(CIMMYT) 的小麦材料进行抗叶锈病基因鉴定,试验结合系谱分析、基因推导和分子标记检测等方法在苗期对36个已知抗病基因载体品种和供试的40份小麦材料接种17个具有毒性差异的叶锈菌生理小种,通过对比供试小麦材料与已知单基因载体品种侵染型,推导出供试小麦材料中可能携带的已知抗叶锈病基因,同时利用12个与已知抗病基因紧密连锁的标记对供试材料进行标记检测,检测结果与基因推导相互验证。进一步将40份供试品系分别种植于河北保定和河南周口试验田,接种叶锈菌混合小种进行田间成株期抗叶锈性鉴定。结果表明,7个供试小麦材料含有 Lr1,携带 Lr10的有9个品系,携带 Lr11和 Lr34的分别有10个品系,含有 Lr14a、 Lr15和 Lr26的分别有2,4,3个小麦品系;另外,经标记检测成株抗叶锈病基因 Lr37和 Lr46分别存在于22,39个小麦品系中,经田间鉴定有22个小麦品系表现成株抗性。
To identify leaf rust resistance genes in 40 wheat materials from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), combined with pedigree analysis, gene derivation and molecular marker detection, 36 known disease resistance gene vector varieties and 40 wheat materials were vaccinated with 17 physiological species of leaf rust bacteria with different toxicity.By comparing the infected types of the tested wheat lines and the known rust resistance genes,the possible known resistance genes in the tested wheat materials could be postulated.At the same time,12 markers closely linked with known resistance genes were used to detect the 40 CIMMYT lines,and the results could be verified with the gene postulation.Furthermore,40 tested lines were planted in Baoding,Hebei Province and Zhoukou,Henan Province,respectively,and inoculated with mixed Pt races for leaf rust evaluation at adult plant stage in the field.The results showed that 7 wheat lines contained Lr1, Lr10 was found in 9 lines,and each of Lr11 and Lr34 was present in 10 lines.Each of Lr14a, Lr15 and Lr26 was postulated to present in 2,4 and 3 lines,respectively.Each of Lr37 and Lr46 was identified in 22,39 wheat lines,respectively,by using molecular marker detection.In the field test 22 wheat lines showed adult plant resistance to leaf rust.
小麦叶锈病由叶锈菌侵染引起, 该病害可通过气流进行远距离传播, 在我国发生范围广, 传播速度快, 可对我国大范围小麦产区进行侵染。小麦叶锈病主要危害小麦叶片, 影响叶片光合作用, 通常会减产5%~15%, 大流行年份产量损失可达40%[1, 2]。我国是世界上小麦叶锈病的最大流行区之一, 主要发生在黄河和淮海流域[3], 因此, 选育和利用抗病品种至关重要。
根据小麦寄主对叶锈菌抗性不同可分为垂直抗病性和水平抗病性。垂直抗病性由主效基因控制, 表现为质量性状。垂抗品种能在叶锈菌侵入叶片后产生过敏性坏死反应(Hypersensitive reaction, HR), 阻止病原菌侵染并表现抗病性。垂直抗病性具有生理小种专化性, 当叶锈菌生理小种发生毒性变异时, 品种抗病性就会丧失[4]。水平抗病性又称为慢锈性(Slow rusting resistance), 由多个微效基因控制, 为数量性状抗性, 没有明显的生理小种专化性。具有慢锈抗性的小麦品种与叶锈菌表现亲和的非过敏性反应, 在田间表现潜伏期长、病斑小、发病率低和孢子量少等特点[1], 抗性较持久。
目前, 国内外定位的小麦抗叶锈病基因有100多个, 其中正式命名了80个[5], 这些基因大多为小种专化抗病基因, 非小种专化的慢锈基因只有Lr34[6]、Lr46[7]、Lr67[8]和Lr68[9]。由于我国叶锈菌小种变异频繁, 目前仅有Lr9、Lr19、Lr24、Lr38、Lr47、Lr51和Lr53等少数主效抗叶锈病基因仍具有有效抗性[10]。
基因推导和分子标记技术具有耗时短、效率高的特点, 目前在小麦叶锈基因鉴定中应用广泛。王思曼等[11]在69份国外小麦材料中, 推导出Lr1、Lr10、Lr26等6个抗叶锈病基因。赵丽娜等[12]在23份中国小麦微核心种质中推导出Lr1、Lr2c、Lr16等9个抗叶锈病基因, 焦悦等[13]在50份国外小麦材料中推导出Lr1、Lr26、Lr34等6个抗叶锈病基因。Gao等[14]、Zhang等[15]和杨文香[16]分别对不同地区的小麦品种进行基因推导, 推导出Lr1、Lr2a、Lr9和Lr24等多个抗病基因。
利用已知基因进行合理的基因布局与基因聚合可延长抗病基因使用年限, 对国内外小麦品种进行抗性鉴定可以筛选抗病品种, 为我国的小麦抗叶锈病育种提供优良抗源。本试验利用我国小麦叶锈菌小种接种40份CIMMYT小麦品系进行抗叶锈基因鉴定, 同时利用已知基因的分子标记检测供试品系和抗性鉴定结果互相验证, 鉴定结果将为这些品系在抗性育种的利用奠定材料和理论基础。
试验材料包括40个国际玉米小麦改良中心(Centro Internacional de Mejoramientode Maizy Trigo, CIMMYT)小麦品系(中国农业科学院张学勇研究员馈赠, 系谱见表1)、36个含有已知抗病基因的载体品种、感病对照品种郑州5389和成株抗性对照品种SAAR; 基因推导所用的17个单孢纯化后的小麦叶锈菌生理小种(FGJQ、FHJQ①、FHJT、FHJR、TGPS、FHJQ②、THDB、PHTS、FHJQ③、FHSQ、FHGS①、FHDS、FHGS②、FHDQ、FHJS、FGJQ、FGDQ)和成株期使用的混合高毒性生理小种(THTT、THTQ、THTS、PHPS)均由河北农业大学小麦锈病实验室保存, 不同毒性的叶锈生理小种命名参照Long等[17]的四字母命名法。
| 表1 40个小麦品系的系谱及来源 Tab.1 The pedigrees and origins of the 40 wheat lines |
将所用36个载体品种、40个小麦供试品系和感病对照郑州5389在温室内种植17套穴盘。待小麦长至一心一叶时, 使用扫抹法将17种不同毒力的叶锈菌生理小种分别接种到17套供试材料, 将接种后的供试材料移入100% 湿度的接种桶, 并覆上塑胶膜黑暗保湿16 h, 后转入适合叶锈菌扩繁的23 ℃左右温室内培养大约14 d, 待感病对照品种5389完全发病, 按照Roelfs等[18]的6级分级标准对17套供试材料进行侵染型鉴定后, 根据Dubin等[19]提出的基因推导原则对40份小麦供试品系进行基因推导。
于2018— 2019年和2019— 2020年, 将40个CIMMYT小麦品系、感病材料5389和成株抗性对照品种SAAR分别种植于河南周口黄泛区农场试验田与河北保定河北农业大学试验田。供试品系行长0.8 m, 行距0.25 m, 每隔9行种植一行感病材料5389, 每行约40粒, 并在供试品系两侧垂直种植一列感病材料郑州5389作为诱发行, 在小麦试验田四周播种2列黑麦作为保护行, 防止小麦叶锈菌孢子扩散到其他区域。将4种高毒性生理小种(THTT、THTQ、THTS、PHPS)等量混合, 制成0.05% 吐温的孢子悬浮液, 在小麦拔节期喷施诱发行后用塑料薄膜覆盖保持密闭环境, 黑暗高湿条件下过夜。当感病材料5389病害严重度达到50% 时, 按照Li等[10]的方法进行病害严重度鉴定, 之后每间隔7 d鉴定一次, 直至田间小麦材料完全发病, 此时严重度达到最高值, 即为最终严重度(Final disease severity, FDS)。
本试验选用Sharp等[20]的CTAB法提取40份国外小麦品系及郑州5389小麦叶片DNA, 测定DNA浓度后将其稀释到40 ng/μ L。选用与已知10个抗叶锈病基因Lr1[21]、Lr9[22]、Lr10[23]、Lr19[24]、Lr20[25]、Lr21[26]、Lr26[27]、Lr34[28]、Lr37[29]、Lr46[30]紧密连锁的分子标记进行检测。PCR配置体系为10 μ L:模板1 μ L, 高保真Mix 5 μ L, ddH2O 3 μ L, 引物1 μ L; PCR扩增产物用1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测和分析。利用Lr46特异性标记csLV46G22检测时需将PCR产物进行酶切, 其体系为10 μ L:PCR产物7 μ L, NEBuffer 10× 1 μ L, Bsp Ⅰ 0.3 μ L, ddH2O 1.7 μ L, 酶切后用12%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳进行检测。
36个已知抗叶锈病基因的载体品种和40份供试小麦品系对17个小麦叶锈菌种的苗期侵染型、基因鉴定结果见表2, 3。结果表明, 9个抗叶锈基因Lr9、Lr19、Lr24、Lr28、Lr29、Lr42、Lr47、Lr51、Lr53对供试叶锈菌生理小种均表现高抗甚至免疫; 10个抗叶锈基因Lr2c、Lr3、LrB、Lr16、Lr3bg、Lr13、Lr14b、Lr23、Lr33和Lr39对所有供试叶锈菌生理小种均表现高感, 因此, 这19个抗叶锈病基因无法通过基因推导被推出, 其余17个基因Lr1、Lr2a、Lr26、Lr3ka、Lr11、Lr17、Lr30、Lr10、Lr14a、Lr18、Lr2b、Lr15、Lr20、Lr21、Lr36、Lr44和Lr45对17个叶锈菌系均表现出不同抗性, 可以通过苗期鉴定推导出来。编号为13、18、19、20、21、36、38、39和40的9个小麦品系对17个生理小种均表现抗病, 因此, 无法通过基因推导鉴定出其含有的抗性基因。根据基因推导和分子标记检测, 在40份材料共检测到Lr1、Lr10、Lr11、Lr14a、Lr15、Lr26、Lr34、Lr37和Lr46等9个小麦抗叶锈病基因。
| 表2 17个小麦叶锈菌生理小种与36个抗叶锈病基因载体品种苗期互作侵染型 Tab.2 Seedling infection types of 36 lines with known leaf rust resistance genes inoculated with 17 Puccinia triticina (Pt)races |
| 表3 17个小麦叶锈菌生理小种与40个小麦品系的苗期互作侵染型 Tab.3 Seedling infection types of the 40 wheat lines with 17 Puccinia triticina (Pt) races |
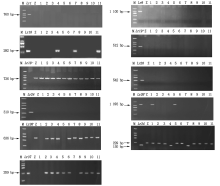
从表3可看出, Lr1对TGPS、THDB、PHTS表现感病, 对其余14个小种均表现低毒; 对Lr17、Lr44、Lr45无毒的小种对Lr1也无毒, 因此, Lr17、Lr44、Lr45无法在含有Lr1的小麦材料中通过基因推导鉴定出来; 通过基因推导出品系14含有Lr1, 小麦品系13、18、19、20、21、22对17个叶锈生理小种均表现抗病, 结合分子标记检测证实此6个品系中含有Lr1(图1)。
Lr11对TGPS、THDB、FHDS、FHDQ、FGDQ表现抗病, 对其余12个小种表现感病, 其中对Lr10低毒的小种THDB对Lr11也表现低侵染型, 因此Lr10无法在含有Lr11的小麦品系中鉴定出来, 推导结果显示, 品系1、2、9、14、15、22、23、24、33和35等10份材料可能含有Lr11。利用Lr10特异性标记对供试材料进行检测, 在对照材料TcLr10和9个品系(4、7、11、12、13、14、17、18和40)中检测到了Lr10的特异性条带(282 bp), 9个品系对Lr10低毒小种THDB均表现抗病。
Lr15对FHJR、TGPS、FHJQ②、THDB和PHTS表现感病, 对其余12个小种均表现抗病, 因此品系28、29、30、37可能携带Lr15; Lr26对FGJQ、TGPS、FGJQ、FGDQ表现抗病, 对其余13个小种表现感病, 推测品系1、5、35可能含有Lr26, 进一步利用Lr26正负相关STS引物ω -secalin和Glu-B3检测, 结果与基因推导结果一致。
Lr14a对FHJT、TGPS、PHTS、FHGS①、FHDS、FHGS②、FHJS表现感病, 对其他10个小种表现抗病, 其中对Lr10无毒的小种对Lr14a也无毒, 因此Lr10无法在含有Lr14a的小麦品系中通过基因推导鉴定出来, 经检测品系4、35可能含有Lr14a, 同时品系4经标记检测还携带Lr10。
Lr34、Lr37、Lr46为成株抗病基因, 苗期表现感病, 无法通过苗期基因推导, 其分子标记检测结果表明, 品系4、7、13、15、16、18、19、20、21、37共10个材料含有Lr34, 品系2、3、4、5、6等22个供试小麦材料中检测到Lr37, 携带Lr46的有39个供试品系(图2)。另外, 在40份国外小麦材料中均未检测到已知抗叶锈病基因Lr9、Lr19、Lr20、Lr24。
对2018— 2019年种植于河南周口和2019— 2020年种植于河北保定的试验材料进行田间抗性鉴定, 根据鉴定数据进行成株抗叶锈分析, 郑州5389作为感病对照品种, 在两点的最终严重度分别为80%和90%, SAAR作为成株抗性对照品种, 在两点的最终严重度分别为1%和5%(表4), 在田间表现明显的成株抗性。利用SAS进行显著差异性分析(表5), 表明在不同环境之间、不同品系之间、品系与环境之间均表现出显著的差异性(P< 0.05), 小麦品系在田间抗病性受到环境与基因共同作用。分析田间成株期最终严重度, 结果表明, 22个小麦品系具有成株抗性, 部分成株抗性品系经分子标记检测含有成株抗性基因Lr34、Lr37、Lr46, 另有些材料可能还含有其他成株抗性基因。
| 表4 22个成株抗性品系与小麦叶锈菌混合生理小种的苗期互作侵染型及成株期田间最终严重度(FDS) Tab.4 Seedling infection types and final disease severity(FDS)in field with mixed Puccinia triticina(Pt)races of 22 wheat lines with slow-rusting resistance |
| 表5 2018— 2019年, 2019— 2020年40个小麦品系以及慢锈对照SAAR和感病对照郑州5389的最终严重度数据方差分析 Tab.5 Analysis of variance for the final disease severity of the 40 wheat lines, slow rusting check SAAR and susceptible check Zhengzhou 5389 in 2018— 2019 and 2019— 2020 |
Lr1定位在5DL染色体上, 目前Lr1对我国多数流行小种已丧失抗性[31], 不过该基因可以用于基因聚合或基因布局防止小麦叶锈病。小麦品系20含有Lr1, 其亲本组合为:PBW343* 2/KUKUNA//PBW343* 2/KUKUNA* 2/6/WBLL1* 2/4/SNI/TRAP#1/3/KAUZ* 2/TRAP//KAUZ/5/KACHU, 其中TRAP[32]含有Lr1, 因此品系20中的Lr1可能来自TRAP。
本试验中40个小麦品系共有9个品系可能携带Lr10, 其中品系18系谱为WHEAR/KUKUNA/3/C80.1/3* ATAVIA//2* WBLL1* 2/6/WBLL1* 2/4/YACO/PBW65/3/KAUZ* 2/TRAP//KAUZ/5/KACHU #1, TRAP[32]含有Lr10, 因此品系18中Lr10可能来自TRAP。
Lr26来源于小麦与黑麦远缘杂交得到的1BL/1RS易位系, 该染色体臂含有多种抗病基因如Sr31、Yr9和Pm8。目前Lr26在我国小麦育种中应用广泛, 但已丧失抗性[28], 可将Lr26与其他抗病基因聚合提高抗病性[33]。本研究中3个供试小麦材料检测到含有Lr26, 基因推导与分子标记结果一致。小麦品系5由SAUAL/3/KAUZ/PASTOR//PBW343/4/TRCH/SRTU//KACHU组合选育而成, 其中PBW343[34]含有Lr26, 因此该品系的Lr26可能来自PBW343。
Lr34与Lr46均为慢锈抗病基因, 目前2个基因在田间仍具有良好抗性。分子标记检测结果显示, 10个供试小麦材料含有Lr34, 39个供试小麦材料含有Lr46, 仅小麦材料16未检测出含有Lr46。韩烨等[34]研究结果表明, 多数CIMMYT材料表现慢锈性, 本研究结果进一步证实了Lr34与Lr46广泛存在于CIMMYT小麦品系中, 这些品系可以作为抗源用于我国的小麦抗病育种。由于叶锈菌不断变异, 导致部分抗叶锈病基因丧失抗性, 因此, 获得抗性持久的小麦品系是小麦抗性育种的重要目标。了解国外小麦品系中丰富的抗叶锈病基因, 并将其利用到我国持久抗病育种中, 将丰富我国小麦品种抗病基因, 有效控制小麦叶锈病, 提高粮食产量进而保障我国粮食安全。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|